Overview
Clinical research companies, particularly Contract Research Organizations (CROs), play a vital role in medical research by providing essential services such as trial management, patient recruitment, regulatory compliance, and data management. The article emphasizes that these companies not only enhance the efficiency of clinical studies but also help navigate complex regulatory environments, which is crucial for advancing medical knowledge and improving patient outcomes.
Introduction
In the realm of clinical research, the role of Contract Research Organizations (CROs) is pivotal, serving as the backbone for the planning, execution, and management of clinical trials. These specialized entities are particularly crucial for medical device startups navigating a complex landscape filled with regulatory challenges, competition, and resource constraints. In countries like Colombia, CROs offer tailored services that facilitate the operationalization of first-in-human trials, ensuring that studies are designed, monitored, and executed with precision.
As the industry evolves, the collaboration between CROs and Academic Research Organizations (AROs) highlights the dynamic interplay of innovative trial designs and operational expertise, ultimately driving advancements in medical knowledge and patient care. This article explores the multifaceted roles of clinical research companies, the challenges they face, and the future trends poised to reshape the landscape of clinical trials.
Defining Clinical Research Companies: Their Role and Importance
Clinical research companies, specifically Contract Research Organizations (CROs), are essential to the field of clinical research, acting as specialized entities that provide a comprehensive array of services to aid in the planning, execution, and management of clinical studies. This is particularly critical for medical device startups facing challenges such as regulatory hurdles, competition, recruitment issues, and financial constraints. In Colombia, companies can operationalize their first-in-human medical device experiments with tailored services, including:
- Design
- Protocol writing
- Investigator's brochure
- Informed consent
- Feasibility assessments
- Investigator/site selection
- Regulatory submissions
- To ethics committees
- To INVIMA
- Project management
- Monitoring
Significant achievements, like ReGelTec's initial feasibility assessment on HYDRAFIL™ for chronic low back discomfort, highlight the potential for CROss to improve research efficiency. In this research, all eleven patients were successfully treated, demonstrating effective recruitment and retention strategies facilitated by the CRO's expertise in navigating regulatory requirements and managing site operations. The GUSTO clinical experiment, which randomized 41,021 myocardial infarction patients across 1,081 hospitals worldwide, exemplifies CROs' involvement in large-scale research.
By managing critical components such as patient recruitment, data management, and regulatory submissions, CROs enable sponsors to focus on their core competencies while ensuring that studies adhere to regulatory standards with efficiency and precision. Recent trends suggest that Aros (Academic Research Organizations) are leading practical design approaches that utilize real-world data, aiming to decrease expenses and improve patient involvement in studies. The partnership between Aros and clinical research companies like CROss emphasizes their unique roles, with Aros concentrating on thought leadership and innovative study designs, while clinical research companies like CROss excel in operational execution.
Such innovations underscore the dynamic nature of the field, where emerging challenges and opportunities will likely drive further evolution in CRO practices. As reported by Fortune Business Insights, the growth in clinical research companies is primarily driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, highlighting their essential role in advancing medical knowledge and improving patient outcomes through rigorous research methodologies.
Key Functions and Services of Clinical Research Organizations
Clinical research companies play a crucial role in the success of studies by providing a thorough range of services vital for efficient study management. These key functions include:
-
Trial Management: CROss carefully supervise the entire research process, from feasibility assessments and site selection to protocol formulation and project completion, ensuring compliance with established timelines and budgets.
This systematic method is crucial for maintaining the integrity and efficiency of assessments, significantly impacting local economies through job creation and economic growth. Effective communication between research sites and sponsors is emphasized as a key factor for successful collaboration and compliance, as highlighted in a case analysis on effective communication strategies for research.
-
Patient Recruitment and Retention: The success of any clinical trial hinges on effective patient recruitment strategies. Clinical research companies utilize a range of innovative techniques to identify and involve potential participants, significantly improving retention rates throughout the research. For instance, employing targeted outreach campaigns and community engagement initiatives can lead to higher enrollment success.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the intricate regulatory landscape is a core responsibility of clinical research companies such as CROss. They guarantee that all research adheres to local and international regulations, including oversight by authorities such as INVIMA, which plays a crucial role in medical device regulation as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO.
This safeguards the research's integrity and ensures ethical standards are upheld.
-
Review and Feedback on Research Documents: CROss offer crucial review and feedback on research documents to ensure adherence to country requirements, which is vital for regulatory approval and successful execution of the investigation.
-
Setup and Reporting: CROss oversee the setup process, including acquiring necessary import permits and nationalizing investigational devices. They also manage reporting on research status, including inventory and serious and non-serious adverse events, ensuring all stakeholders are informed and compliant with regulations.
-
Data Management and Analysis: With the ability to manage large volumes of data generated during trials, CROss utilize advanced statistical methods for data analysis. This is critical, especially in light of findings that only 6.1% of studies reporting findings that failed to reach statistical significance had a statistical power analysis, as noted by Sexton in his examination of British orthopedic journals.
Robust data management practices enable researchers to draw reliable conclusions, ultimately contributing to evidence-based clinical care.
-
Monitoring and Quality Assurance: Ongoing observation of progress and strict adherence to protocols is essential for maintaining high standards throughout the study process.
CROss implement rigorous quality assurance measures to ensure that every aspect of the study meets the required benchmarks. By providing these vital services, clinical research companies such as CROss not only improve the effectiveness of medical evaluations but also greatly assist in the successful creation of new healthcare solutions, thus meeting the urgent demand for methodologically sound examinations and suitable statistical assessments in health investigations. Furthermore, through international collaboration and innovation in Medtech, CROss drive global health improvement.
The Importance of Regulatory Compliance in Clinical Research
Regulatory compliance serves as a fundamental pillar of medical research, ensuring that trials are conducted with the highest ethical standards and responsibility. Regulatory authorities, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), establish comprehensive guidelines that govern the conduct of clinical trials. These regulations encompass crucial elements such as study design, patient safety, informed consent, and data integrity.
Adhering to these standards not only safeguards participants but also bolsters the credibility and reliability of research outcomes. For instance, in cases involving pediatric participants, it is essential to obtain permission from a legal representative or guardian, with specific provisions allowing for a single representative’s consent under certain circumstances. This highlights the delicate balance between regulatory compliance and ethical considerations in clinical trials, guided by fidelity in medical ethics which underpins healthcare professionals' commitment to patients.
A noteworthy example is the case of a waiver of consent, where an ethics committee may forgo the requirement for a signed informed consent form under conditions deemed to involve minimal risk or cultural considerations, thereby facilitating participation while protecting participants' rights and welfare. It is crucial to note that sponsors must discontinue a project presenting unreasonable risk to participants no later than 5 working days after making such a determination. Neglecting these regulatory standards can lead to dire repercussions, including the termination of research, legal actions, and irreparable harm to the reputation of sponsoring organizations.
As a result, clinical research companies are essential in ensuring that every aspect of research studies complies with the relevant regulations, thus protecting the interests of all parties involved. Our service capabilities encompass:
- Feasibility analyses for selecting suitable investigation locations and principal investigators (PIs)
- Thorough reviews and feedback on documentation to ensure adherence to country requirements
- Careful setup and approval processes involving ethics committees and health ministries
- Assistance with import permits and the nationalization of investigational devices
- Efficient project management to supervise the lifecycle
- Detailed reporting on project status, inventory, and both serious and non-serious adverse events
As Anthony Keyes from Johns Hopkins University expresses, 'By sharing his work and resources through presentations, publications, and the Taskforce, the program honors study participants while promoting transparency in experiments and responsible stewardship through effective management and maintenance of Clinicaltrials.gov study records.' This sentiment highlights the significance of adherence in promoting trust and integrity within medical studies.
Challenges Faced by Clinical Research Companies
Research organizations face numerous obstacles that can greatly affect the success of medical studies. Among the most pressing issues are:
-
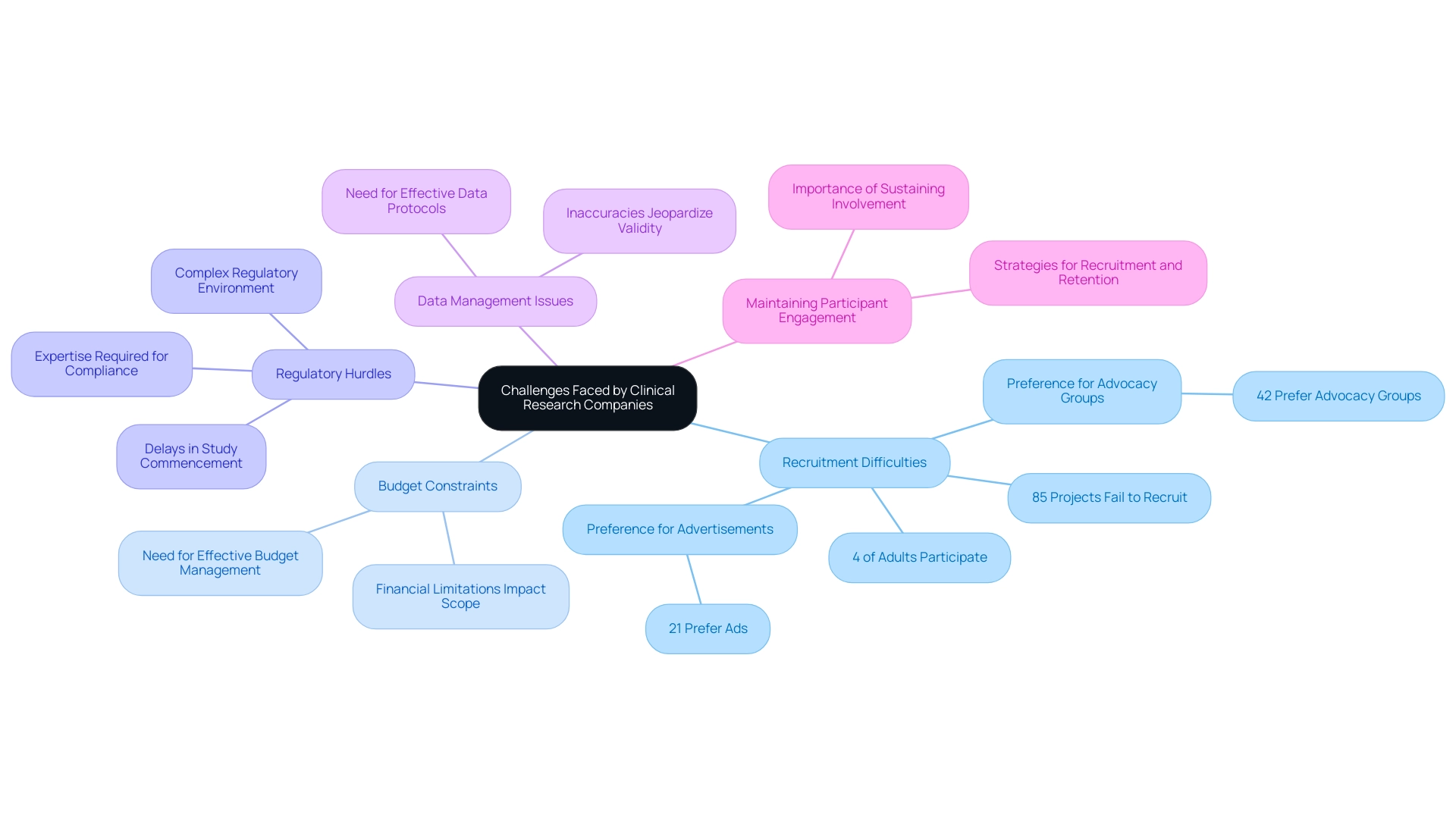
Recruitment Difficulties: Securing appropriate participants for medical research remains a formidable task, particularly for investigations focused on rare diseases or specific demographic groups.
Research shows that despite significant investments in recruitment initiatives, fewer than 4% of adults in the US engage in clinical studies, with up to 85% of projects failing to achieve recruitment goals. Additionally, 21% of patients express a preference for finding out about studies through advertisements, while 42% would like to hear about studies from advocacy groups and nonprofit organizations. This not only escalates costs but also compromises the integrity of outcomes.
The difficulty in deriving accurate statistics on eligible participants further complicates recruitment efforts, highlighting the need for optimized strategies.
-
Budget Constraints: Financial limitations can severely restrict the scope and scale of medical studies, leading to potential compromises in study design and execution.
Effective budget management is essential; organizations must develop strategies that maximize resource allocation without compromising the quality of their studies.
-
Regulatory Hurdles: The intricate regulatory environment presents considerable obstacles for clinical research companies, frequently causing delays that hinder the prompt commencement of studies.
Navigating these regulatory requirements requires considerable expertise and resources. For example, acquiring import permits and ensuring adherence to local health authorities, like INVIMA in Colombia, are essential steps in the setup process.
-
Data Management Issues: The vast amounts of data generated during experiments necessitate effective data management protocols. Inadequate handling of data can result in inaccuracies, jeopardizing the validity of research outcomes.
-
Maintaining Participant Engagement: Sustaining participant involvement throughout the study is essential for ensuring data integrity. As emphasized by Nicola Armitstead, Vice President of Site Clinical Operations, "At MAC, we are dedicated to tackling these challenges, and our thorough strategy assists in guaranteeing effective recruitment and retention, allowing us to fulfill and surpass the requirements of clinical investigations while speeding up timelines and delivering therapies to participants more quickly."
To tackle these challenges, our service capabilities encompass feasibility and selection of investigation locations and principal investigators, review and feedback on project documents to comply with country requirements, detailed trial setup and approval processes with ethics committees and health ministries, and robust project management and monitoring.
We also focus on timely reporting of study status and adverse events, which are crucial for maintaining compliance and ensuring participant safety. By proactively identifying and tackling these challenges, healthcare organizations can improve their operational efficiency, thus aiding the successful progress of medical studies and fostering economic growth through job creation and healthcare enhancement.
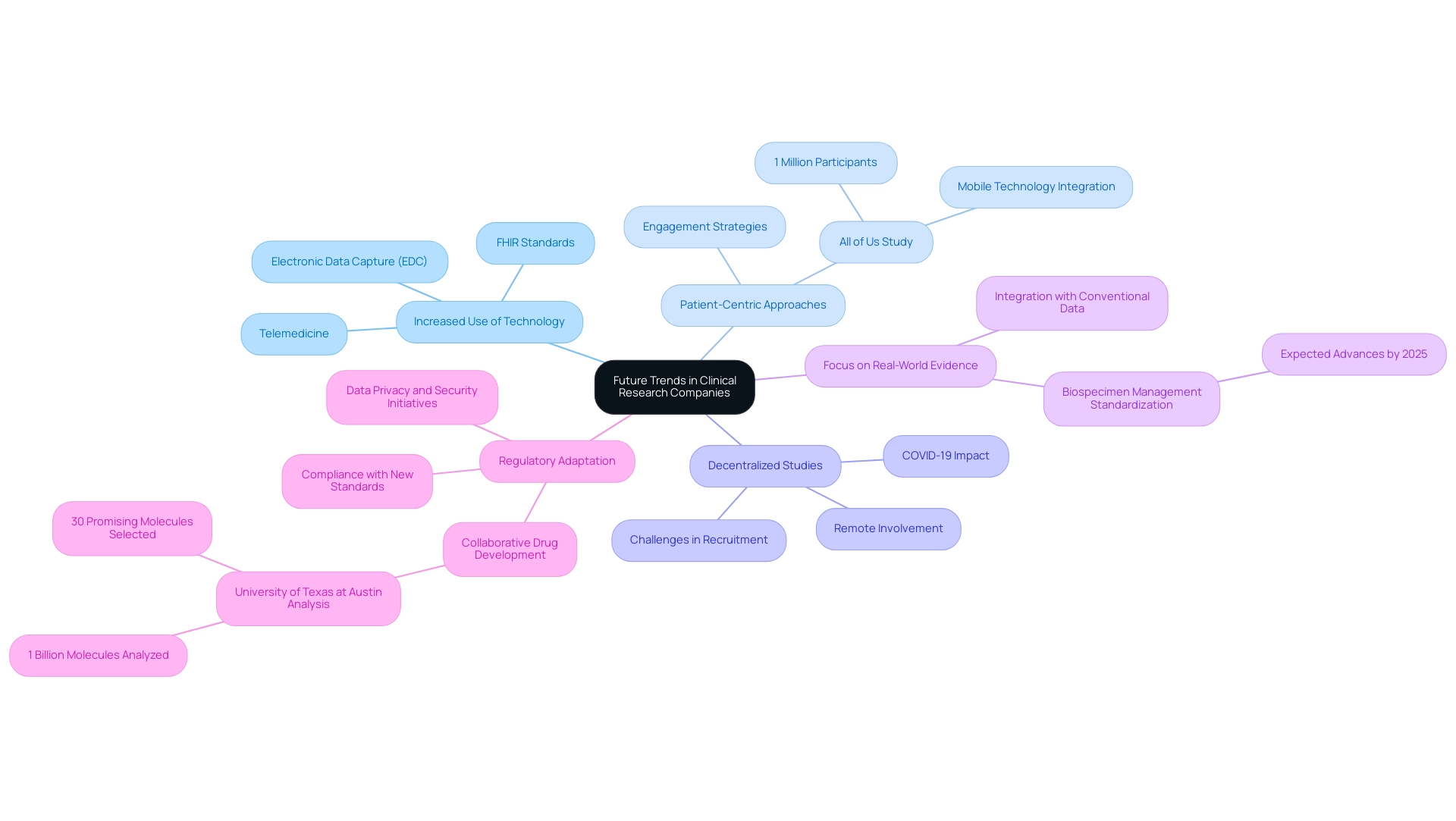
Future Trends in Clinical Research Companies
The terrain of medical inquiry is experiencing substantial change, driven by technological progress and developing regulatory structures. Key trends shaping this evolution include:
-
Increased Use of Technology: The adoption of digital tools, including electronic data capture (EDC) and telemedicine, is transforming research methodologies.
These technologies enhance efficiency and ensure greater accuracy in data collection. Recent efforts to implement Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standards for electronic health information exchange are ongoing, facilitating improved interoperability and supporting these advancements.
-
Patient-Centric Approaches: A significant movement toward emphasizing patient engagement and experience is clear, with research organizations (CROs) adopting strategies to actively involve patients in the research process.
This approach not only fosters better outcomes but also enhances participant satisfaction within clinical research companies. The All of Us Study exemplifies this trend, as it engages 1 million participants through mobile technology for comprehensive data collection, aiming to advance precision medicine.
-
Decentralized Studies: The growth of decentralized research studies, which allow remote involvement, has gained considerable momentum, especially due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
This model has demonstrated effectiveness in enhancing recruitment and retention rates, making studies more accessible to diverse populations, including in Latin America, where addressing language barriers and resource fragmentation is crucial.
However, prolonged subject recruitment timelines remain a challenge that needs to be addressed through innovative strategies.
-
Focus on Real-World Evidence: CROs are increasingly utilizing real-world evidence in conjunction with conventional study data to offer a comprehensive perspective on treatment effectiveness and safety.
This focus is particularly relevant as the industry moves toward greater standardization in biospecimen management, with significant strides expected by 2025.
-
Regulatory Adaptation: As regulatory landscapes evolve, CROs must remain nimble, adapting their practices to comply with new standards while fostering innovation.
Initiatives focused on improving data privacy and security in medical studies are actively being developed by various organizations, indicating a proactive approach to these challenges.
Notably, a collaborative team from the University of Texas at Austin recently analyzed 1 billion possible molecules using supercomputers, selecting the 30 most promising for further drug development consideration.
By addressing the challenges faced by Medtech companies in Latin America, such as the lack of CRO corporate structures and prolonged subject recruitment timelines, and emphasizing collaboration, particularly in comprehensive clinical trial management services, clinical research companies can effectively position themselves for success in a rapidly changing medical research environment.
Conclusion
The critical role of Contract Research Organizations (CROs) in clinical research cannot be overstated, especially for medical device startups navigating complex regulatory landscapes. Through their comprehensive suite of services—ranging from trial management and patient recruitment to regulatory compliance—CROs enhance the efficiency and integrity of clinical trials. The success of various studies, including those involving innovative medical devices, illustrates the value CROs bring in streamlining processes and ensuring adherence to ethical standards.
As highlighted, the collaboration between CROs and Academic Research Organizations (AROs) marks a significant evolution in the industry, fostering innovative trial designs that prioritize patient engagement and real-world evidence. This partnership not only addresses the pressing challenges of recruitment and budget constraints but also enhances the overall quality and reliability of research outcomes.
Looking ahead, the future of clinical research is poised for transformation, driven by technological advancements and a patient-centric focus. The rise of decentralized trials and the integration of real-world evidence are reshaping how studies are conducted, making them more accessible and relevant to diverse populations. As CROs adapt to evolving regulatory frameworks and embrace new methodologies, they will continue to play a pivotal role in advancing medical knowledge and improving patient care.
In conclusion, the landscape of clinical trials is increasingly dynamic, and the collaboration between CROs and AROs will be essential in overcoming challenges while driving innovation. By prioritizing regulatory compliance, patient engagement, and the effective use of technology, the industry is well-positioned to enhance the success of clinical trials, ultimately benefiting patients and the broader healthcare ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Contract Research Organizations (CROs) and their role in clinical research?
CROs are specialized entities that provide a comprehensive range of services to assist in the planning, execution, and management of clinical studies, particularly aiding medical device startups in overcoming regulatory challenges, competition, recruitment issues, and financial constraints.
What specific services do CROs offer for medical device experiments in Colombia?
CROs in Colombia provide tailored services including protocol writing, investigator's brochures, informed consent, feasibility assessments, regulatory submissions to ethics committees and INVIMA, project management, and monitoring.
Can you give an example of a successful clinical study managed by a CRO?
An example is ReGelTec's initial feasibility assessment on HYDRAFIL™ for chronic low back discomfort, where all eleven patients were successfully treated, showcasing effective recruitment and retention strategies facilitated by the CRO's expertise.
How do CROs contribute to large-scale clinical research?
CROs manage critical components such as patient recruitment, data management, and regulatory submissions, enabling sponsors to focus on their core competencies while ensuring studies adhere to regulatory standards efficiently.
What trends are emerging in the collaboration between academic research organizations and CROs?
Recent trends show that academic research organizations (Aros) are leading practical design approaches that utilize real-world data to decrease expenses and improve patient involvement in studies, while CROs excel in operational execution.
What are the key functions of CROs in clinical research?
Key functions of CROs include trial management, patient recruitment and retention, regulatory compliance, review and feedback on research documents, setup and reporting, data management and analysis, and monitoring and quality assurance.
How do CROs ensure regulatory compliance in clinical trials?
CROs navigate the complex regulatory landscape to ensure that all research adheres to local and international regulations, including oversight by authorities like INVIMA, thus safeguarding the integrity of the research and upholding ethical standards.
Why is effective patient recruitment and retention important in clinical trials?
Effective patient recruitment and retention are crucial as the success of any clinical trial depends on the ability to identify and involve potential participants, which significantly improves retention rates throughout the research process.
How do CROs manage data during clinical trials?
CROs utilize advanced statistical methods for data analysis and manage large volumes of data generated during trials, ensuring reliable conclusions that contribute to evidence-based clinical care.
What impact do CROs have on the healthcare industry?
By providing essential services and improving the effectiveness of medical evaluations, CROs assist in the successful creation of new healthcare solutions, addressing the urgent demand for methodologically sound examinations and suitable statistical assessments in health investigations.

