Introduction
The Premarket Approval (PMA) process stands as a pivotal component in the landscape of medical device regulation, ensuring that high-risk products meet rigorous safety and efficacy standards before they reach the market. Unlike the more streamlined 510(k) pathway, the PMA framework demands comprehensive clinical data and thorough evaluations, thereby safeguarding patient health and fostering trust in medical innovations.
As manufacturers navigate the complexities of this process, they encounter various challenges, from regulatory hurdles to the nuances of clinical trial management. This article delves into the intricacies of PMA, exploring its significance, the steps involved in the submission process, and the comparative analysis with the 510(k) pathway.
Furthermore, it highlights the essential resources and support available to manufacturers, emphasizing the critical role of PMA in enhancing market access and ensuring patient safety.
Understanding Premarket Approval (PMA) in Healthcare
What is a PMA in healthcare? It serves as an essential regulatory framework established by the FDA to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of high-risk medical products before they are introduced to the market. What is a PMA in healthcare is that unlike the 510(k) submissions, which merely demonstrate substantial equivalence to existing products, it demands extensive clinical data to substantiate claims regarding safety and efficacy. This thorough assessment procedure not only ensures that only those products complying with strict standards obtain approval but also plays an essential role in protecting patient safety.
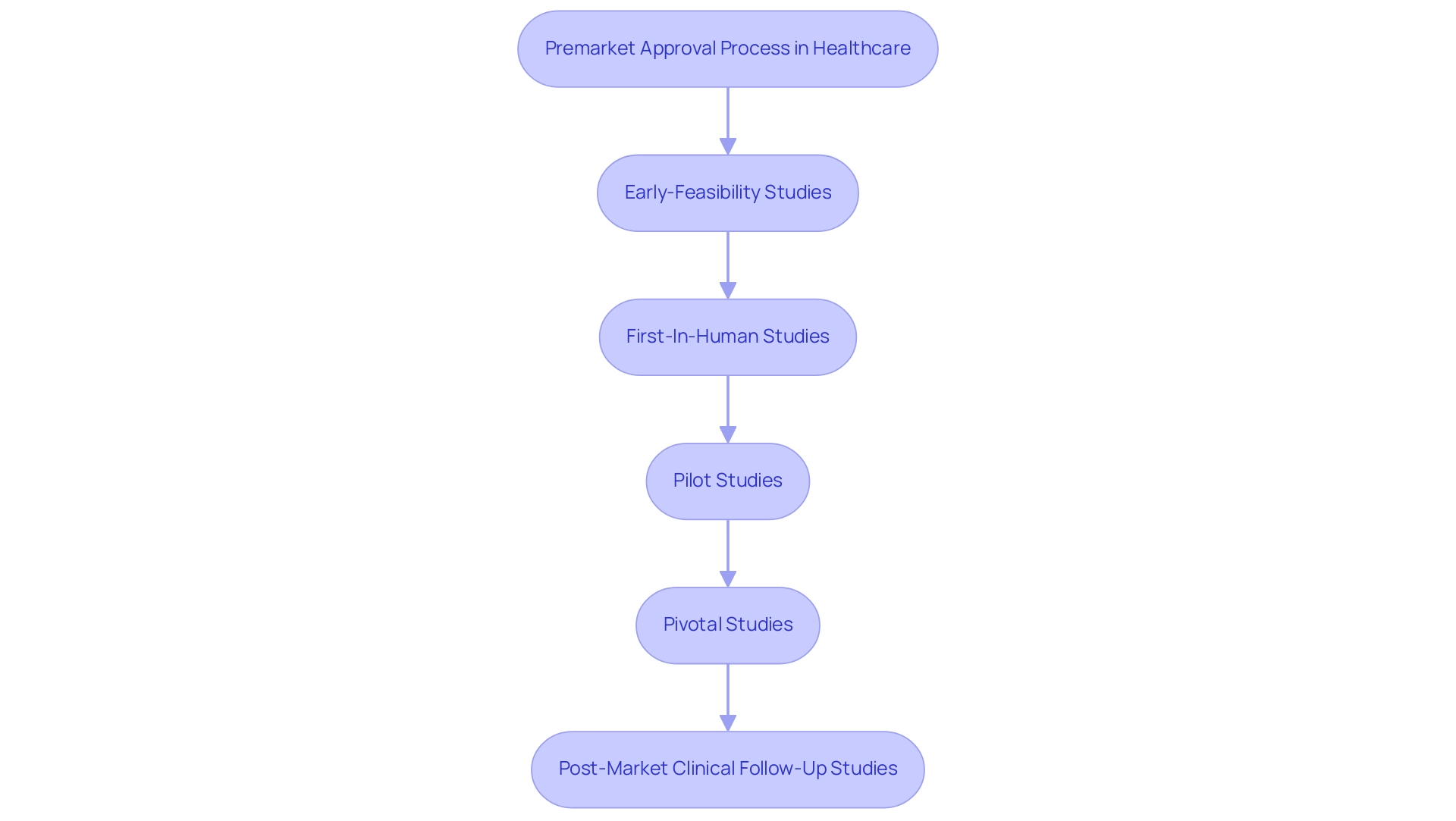
The significance of this procedure is emphasized by the fact that for the year ending September 2022, 67 percent of 510(k) submissions prompted requests for additional information, highlighting the complexities of product approvals and the challenges faced by manufacturers, especially in Latin America. With a landscape defined by compliance challenges, including language barriers and resource fragmentation, companies like bioaccess® provide comprehensive clinical trial management services, including:
- Early-Feasibility Studies
- First-In-Human Studies
- Pilot Studies
- Pivotal Studies
- Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies
These services are essential for navigating these challenges effectively.
Additionally, performance reports from the FDA demonstrate continuous efforts to simplify these procedures, ensuring that high-risk products fulfill essential compliance standards. A notable example of what is a PMA in healthcare is the impact of the investment in the left atrial appendage closure market by Medtronic and Johnson & Johnson, reflecting strategic moves within the industry to enhance patient outcomes. The procedure known as PMA in healthcare fosters trust in medical innovations by ensuring that high-risk instruments undergo thorough scrutiny, reinforcing their reliability and effectiveness in clinical settings.
Additionally, the regulatory landscape overseen by INVIMA plays a significant role in shaping the approval framework for medical devices in Latin America, further emphasizing the need for robust clinical trial management to address these unique challenges.
Navigating the PMA Submission Process: Key Steps and Requirements
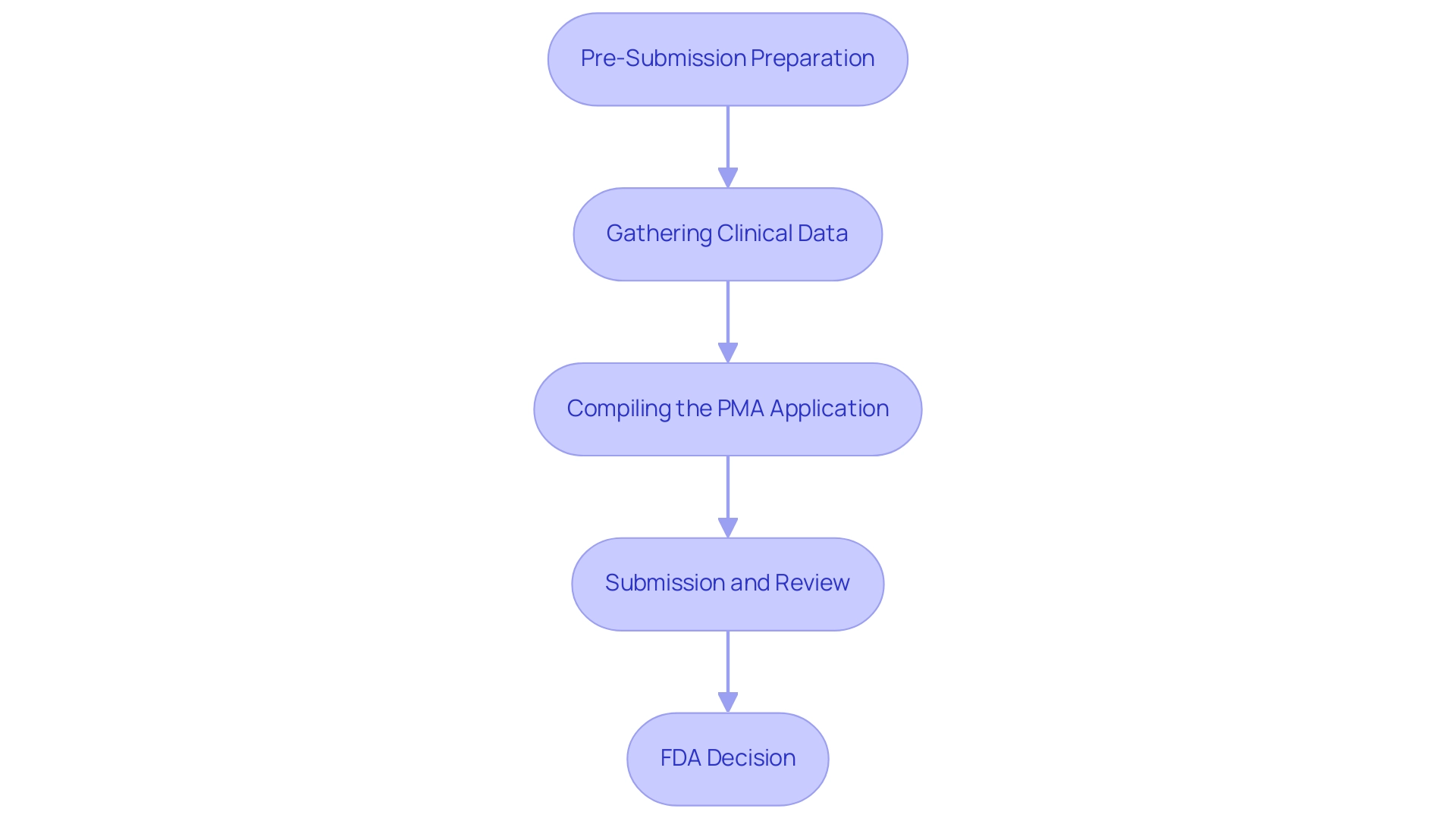
- Pre-Submission Preparation: Before understanding what is a PMA in healthcare, manufacturers must undertake comprehensive research, including feasibility studies and the collection of preliminary data prior to submitting a Premarket Approval (PMA) application. Interacting with the FDA via organized pre-submission meetings can provide essential insights, aiding in clarifying expectations and optimizing the application. Notably, the recent recalls of Accolade pacemakers by Boston Scientific, tied to two deaths, highlight the critical importance of ensuring safety and efficacy in what is a PMA in healthcare. At bioaccess®, our extensive experience of over 20 years in Medtech and our specialized knowledge in managing Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS) ensure that you have the foundational data needed for a successful application.
- Gathering Clinical Data: To understand what is a PMA in healthcare, it's essential to recognize that its foundation lies in robust clinical data that substantiates the safety and efficacy of the medical instrument. This may encompass a variety of research methodologies, including randomized controlled trials and observational studies, to provide compelling evidence supporting the performance of the instrument. Bioaccess® specializes in First-In-Human (FIH) and Pilot Studies, enabling comprehensive data collection and analysis customized to your particular requirements, demonstrating our adaptability in tackling distinct challenges.
- Compiling the PMA Application: To understand what is a PMA in healthcare, a successful PMA application must include exhaustive details, such as a thorough device description, proposed labeling, clinical study protocols, and results. Moreover, it necessitates thorough information on production methods and quality assurance measures, which are essential for proving adherence to legal standards. As emphasized by Nick Paul Taylor, compliance with quality system regulations is paramount, as evidenced by BD's recent FDA warning letter over quality system violations. With bioaccess®, you benefit from our expertise in Pivotal Studies, ensuring that all aspects of your application meet strict compliance standards, backed by our 20+ years of experience.
- Submission and Review: Upon submission, the FDA initiates an initial review to confirm the application’s completeness. This is followed by a more in-depth evaluation, which may necessitate further data requests or the involvement of advisory committees to assess the application comprehensively. Our team at bioaccess® is prepared to support in this phase, providing project management and reporting that keep you informed throughout the review, showcasing our specialized knowledge in navigating regulatory landscapes.
- FDA Decision: After a meticulous review process, the FDA will render a decision regarding what is a PMA in healthcare application. The outcomes may include approval, a request for additional information, or outright rejection. ZuriMED Technologies Ag's successful FDA clearance for its FiberLocker® System exemplifies the positive outcomes that can result from a well-prepared PMA application. If granted approval, the manufacturer is permitted to market the product, typically accompanied by specific post-market surveillance obligations to ensure ongoing safety and efficacy. Bioaccess® also provides Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF) to support compliance with these obligations, particularly in the Latin American market.
PMA vs. 510(k): Understanding the Regulatory Pathways
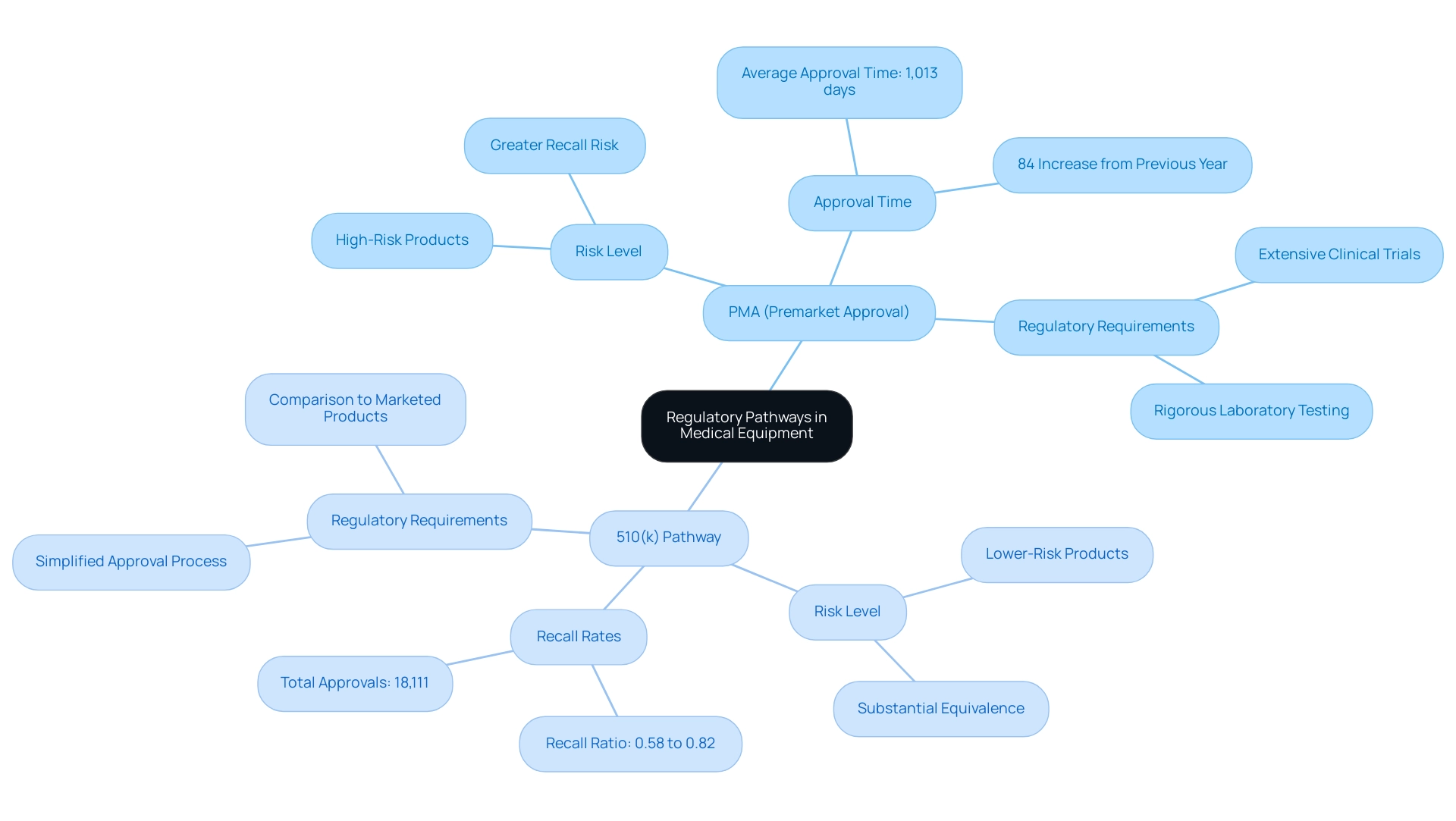
The Premarket Approval (PMA) and 510(k) pathways are integral components of the medical equipment approval landscape, each tailored to specific classifications. In healthcare, what is a PMA refers to the requirement for high-risk items that present considerable potential risks to patients, which entails a comprehensive evaluation supported by extensive clinical data and rigorous laboratory testing. Recent reports indicate that the average time for original PMA approval has surged to 1,013 days, an 84% increase from the previous year and the longest wait on record.
This scrutiny reflects the necessity for ensuring the safety and efficacy of these items, especially given that high-risk PMA products have been found to have a greater risk of recall than previously recognized. As noted, while the US approval system for products has its strengths and weaknesses, it must be thoroughly evaluated before any attempt is made to demolish something that served well for so many years, the 510(k) process.
In contrast, the 510(k) pathway is intended for lower-risk products, allowing manufacturers to establish that their product is substantially equivalent to an already marketed item. Statistics indicate that the ratio of 510(k) recalls to approvals varies from 0.58% to 0.82% of the 18,111 total approvals, emphasizing the relative safety concerns linked to these products. As manufacturers evaluate the risk level related to their products, they should consider what is a PMA in healthcare when choosing between PMA and 510(k), based on the intended use and risk profile of the item.
This careful consideration is vital, as shown by findings from the case study titled 'Conclusions on Equipment Safety and Recall Risks,' which concluded that high-risk products approved through PMA have a greater risk of recall than previously reported. Specialists, including Katherine Ruiz, support improved postmarketing monitoring and strict compliance procedures to more effectively identify safety concerns associated with devices authorized through both routes.
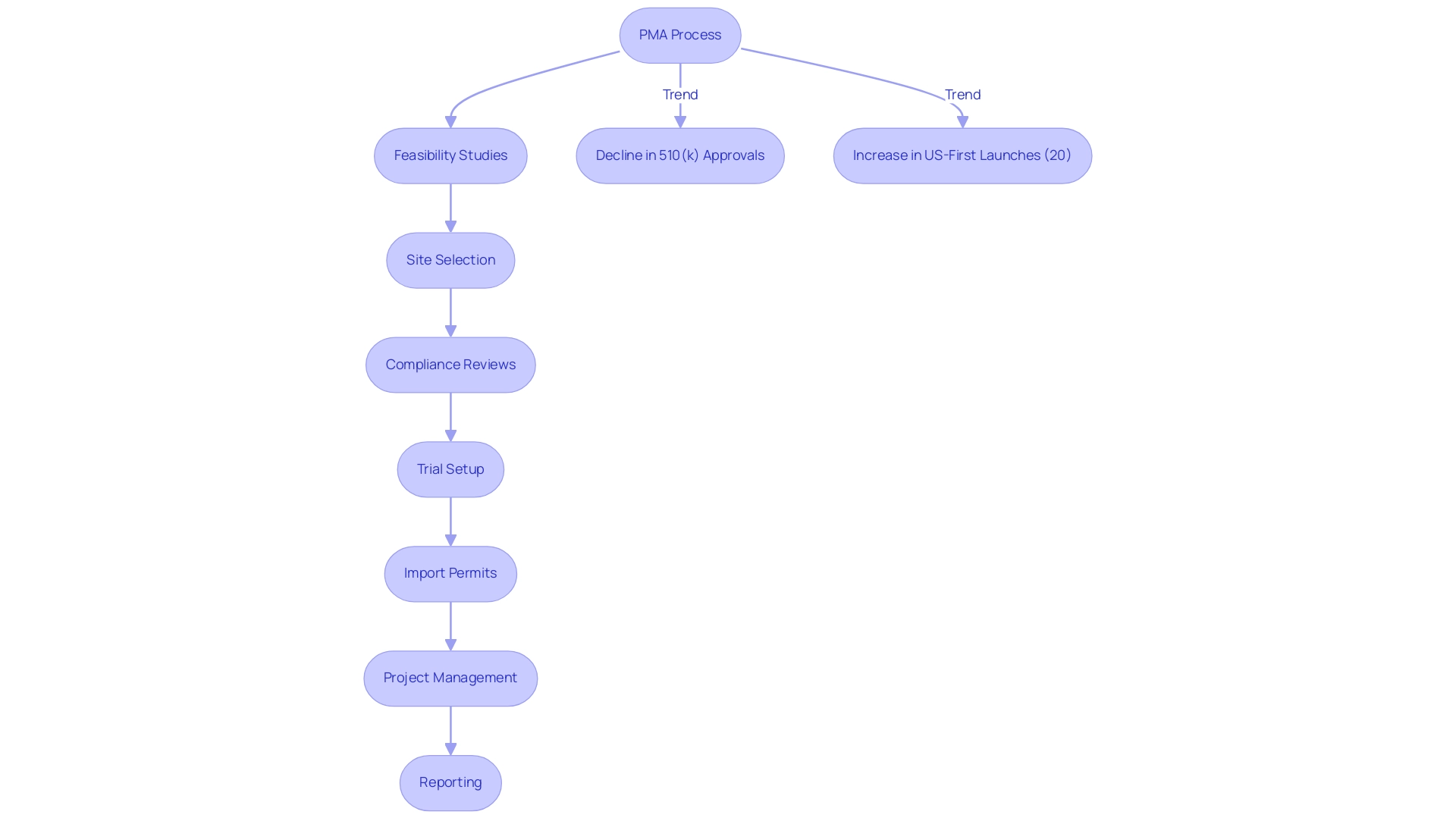
Our comprehensive clinical trial management services, which include feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, project management, and reporting, play a crucial role in navigating these regulatory challenges.
By ensuring meticulous project management and thorough reporting, we assist manufacturers in navigating the complexities of what is a PMA in healthcare and 510(k) procedures, ultimately enhancing adherence to INVIMA's rigorous standards and mitigating risks linked to lengthy approval durations and potential recalls.
The Impact of PMA on Market Access and Patient Safety
To understand what is a PMA in healthcare, one must recognize its crucial role in shaping market access for medical devices. By adhering to this stringent regulatory pathway, manufacturers can effectively validate the safety and efficacy of their products, thereby instilling confidence among healthcare providers and patients alike. The PMA procedure not only paves the way for successful market entry but also plays a critical role in enhancing patient safety.
It ensures that only meticulously evaluated products reach the market, significantly mitigating risks associated with untested technologies. Comprehensive clinical trial management services—including:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
are essential in supporting the PMA workflow and ensuring that clinical studies are conducted efficiently and transparently. This involvement not only contributes to healthcare improvement but also stimulates economic growth and job creation within local economies.
In recent years, there has been a notable decline in the percentage of items authorized by the 510(k) pathway from 2002 to 2021, highlighting the growing dependence on the PMA method for high-risk products. Recent studies indicate a marked increase in the proportion of US-first launches of high-risk therapeutic medical products, rising from 2013 to 2023, with 20% of products entering the market first in the US. This trend reflects the positive influence of regulatory reforms and the PMA system on market access.
As noted in the study with PMC ID PMC9923248 and PMID 36793371, Mr. Kushal T. Kadakia, MSc, had full access to all of the data and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. This dedication to data integrity emphasizes the significance of what is a PMA in healthcare, as it systematically tackles potential safety incidents associated with PMA-approved instruments to ensure patient safety. In 2024, understanding what is a PMA in healthcare will likely continue to influence market trends and patient safety improvements, solidifying its essential role in the medical device industry.
Resources and Support for Successful PMA Applications
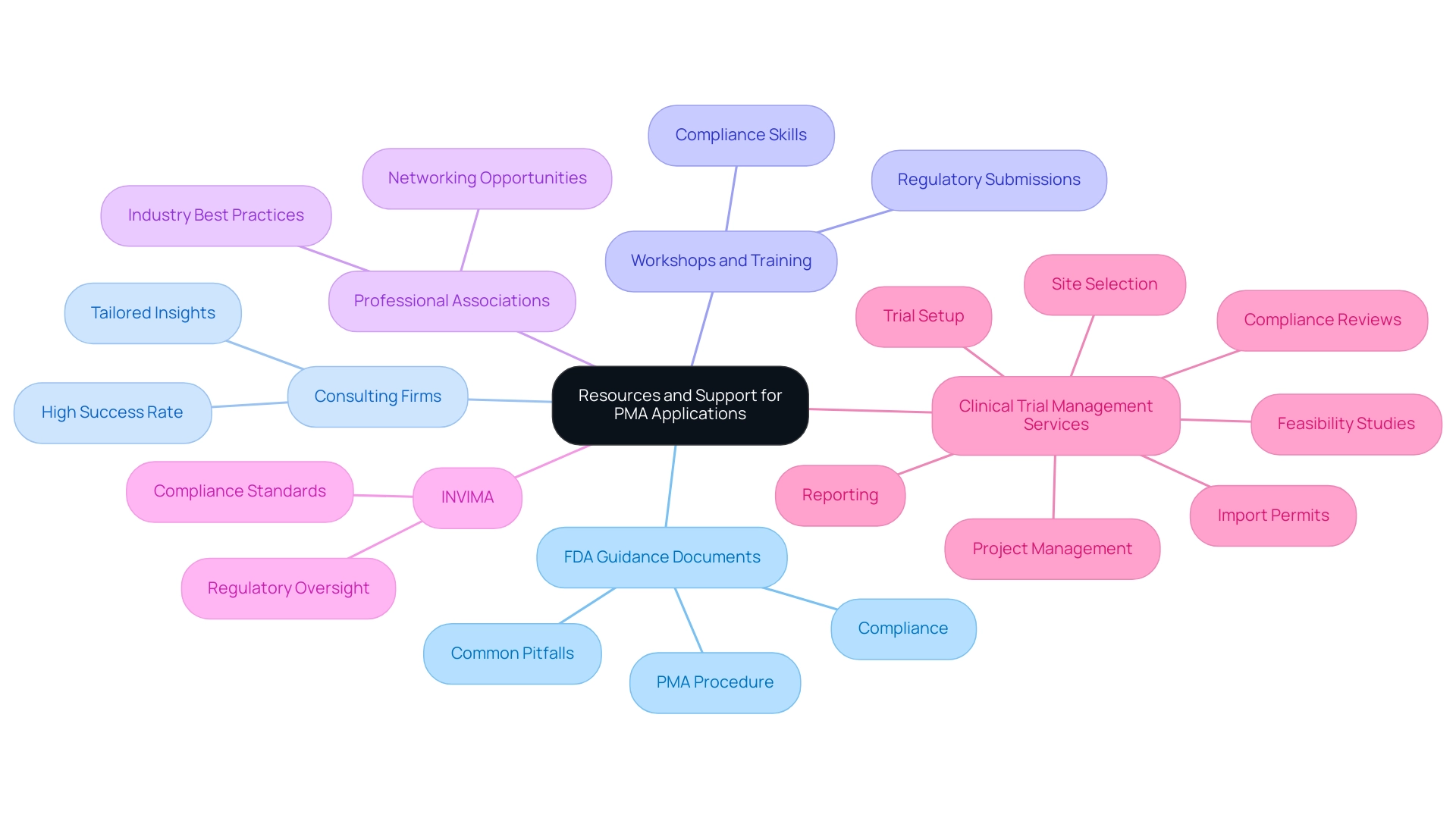
Manufacturers seeking to understand what is a PMA in healthcare can greatly gain from a range of resources intended to assist them throughout the application. Key resources include:
- FDA Guidance Documents: The FDA provides thorough guidance documents that outline the PMA procedure, set clear expectations, and highlight common pitfalls encountered during submissions. Staying updated with the latest FDA guidance documents is crucial for compliance and successful outcomes.
- Consulting Firms: Collaborating with consulting firms that focus on compliance matters can provide manufacturers with tailored insights and expertise specific to their devices. These firms often have a high success rate in navigating the complexities of PMA applications, thus streamlining the process.
- Workshops and Training: Numerous organizations conduct workshops and training sessions focused on regulatory submissions and compliance. These educational opportunities equip manufacturers with essential knowledge and skills necessary for understanding what is a PMA in healthcare applications.
- Professional Associations: Becoming a member of professional associations related to medical devices fosters networking opportunities and grants access to industry best practices. Interacting with colleagues in the field can improve manufacturers' understanding of what is a PMA in healthcare and offer assistance throughout their journey.
In Colombia, understanding the role of INVIMA (the National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute) is essential. Established under the Ministry of Health and Social Protection, INVIMA oversees health product regulation, ensuring compliance with safety, efficacy, and quality standards. As a Level 4 health authority recognized by PAHO/WHO, INVIMA's regulatory framework is critical for manufacturers aiming for successful market entry.
Additionally, extensive clinical trial management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, import permits, project management, and reporting, are essential for navigating the complexities of the PMA application. As the aptamers market in Latin America is projected to grow from 2023 to 2028, manufacturers must understand what is a PMA in healthcare to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this expanding market.
Additionally, PMA generates frequent, high-quality surveys monitoring key health indicators in nine countries in Africa and Asia, underscoring its importance in the broader health landscape. A relevant case study is the review procedure carried out by the Center for Biologics, Evaluation, and Research (CBER), which supervises marketing and investigational device submissions for medical devices associated with blood collection and processing. This illustrates the regulatory scrutiny and the need for compliance that manufacturers must navigate when understanding what is a PMA in healthcare.
The journey can be challenging, as aptly summarized by a quote from a Uganda Resident Enumerator:
'... be patient, believe in yourself, work hard and stay resilient.'
This mindset is essential as manufacturers tackle the complexities of the PMA application process.
Conclusion
The Premarket Approval (PMA) process is a cornerstone of medical device regulation, ensuring that high-risk products undergo thorough evaluation before reaching the market. By demanding extensive clinical data and rigorous testing, the PMA framework plays a crucial role in safeguarding patient safety and enhancing trust in medical innovations. As highlighted throughout the article, the challenges faced by manufacturers, particularly in navigating regulatory landscapes and conducting clinical trials, underscore the importance of comprehensive support and resources.
The comparative analysis of PMA and 510(k) pathways emphasizes that while both serve essential functions, the PMA process is vital for high-risk devices, reflecting a commitment to patient safety through stringent evaluation. With the increasing reliance on PMA approvals, especially in the context of high-risk therapeutic devices, the implications for market access and patient outcomes are profound. The ongoing trends indicate that manufacturers who embrace the PMA process are better positioned to deliver safe and effective medical devices to the market.
In conclusion, as manufacturers embark on the path to PMA approval, leveraging available resources, expert guidance, and comprehensive clinical trial management services will be essential for success. This commitment to regulatory compliance not only facilitates smoother market entry but also reinforces the overarching goal of ensuring patient safety and fostering confidence in medical technologies. The future of medical device innovation hinges on the effectiveness of the PMA process, making it indispensable in advancing healthcare and improving patient lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a PMA in healthcare?
A PMA, or Premarket Approval, is a regulatory framework established by the FDA to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of high-risk medical products before they are introduced to the market. It requires extensive clinical data to substantiate claims regarding safety and efficacy.
How does a PMA differ from a 510(k) submission?
Unlike 510(k) submissions, which demonstrate substantial equivalence to existing products, a PMA requires comprehensive clinical data to prove safety and efficacy. This thorough assessment ensures that only products meeting strict standards receive approval.
Why is the PMA process significant?
The PMA process is significant because it plays a crucial role in protecting patient safety by ensuring that high-risk medical products undergo rigorous evaluation before market introduction.
What challenges do manufacturers face with PMA submissions?
Manufacturers often face complexities in product approvals, as evidenced by the fact that 67 percent of 510(k) submissions required additional information. Challenges include compliance issues, language barriers, and resource fragmentation, especially in Latin America.
What services does bioaccess® provide to assist with PMA submissions?
Bioaccess® offers comprehensive clinical trial management services, including Early-Feasibility Studies, First-In-Human Studies, Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies to help manufacturers navigate the PMA process.
What role does the FDA play in the PMA process?
The FDA initiates an initial review of the PMA application for completeness, followed by a thorough evaluation that may involve requests for additional data or advisory committee involvement to assess the application comprehensively.
What happens after the FDA reviews a PMA application?
After review, the FDA will make a decision regarding the PMA application, which can result in approval, a request for more information, or rejection. If approved, the manufacturer can market the product, often with post-market surveillance obligations.
How does the regulatory landscape in Latin America differ regarding PMA?
The regulatory landscape in Latin America, overseen by INVIMA, presents unique challenges that necessitate robust clinical trial management to address compliance and approval frameworks specific to the region.




