Introduction
The Premarket Approval (PMA) process stands as a cornerstone of medical device regulation, ensuring that high-risk products meet stringent safety and efficacy standards before they enter the market. This rigorous framework, established by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), necessitates a comprehensive evaluation of clinical data, manufacturing practices, and labeling requirements.
As the landscape of medical technology evolves, understanding the intricacies of the PMA process becomes paramount for manufacturers navigating the complexities of regulatory compliance. Recent insights highlight the importance of enhancing stakeholder engagement and optimizing trial designs to streamline approvals, while also addressing the challenges posed by increasing wait times.
This article delves into the essential components of the PMA process, contrasting it with the 510(k) pathway, and examines the implications for manufacturers aiming to bring innovative medical devices to market.
Defining Premarket Approval (PMA): An Overview
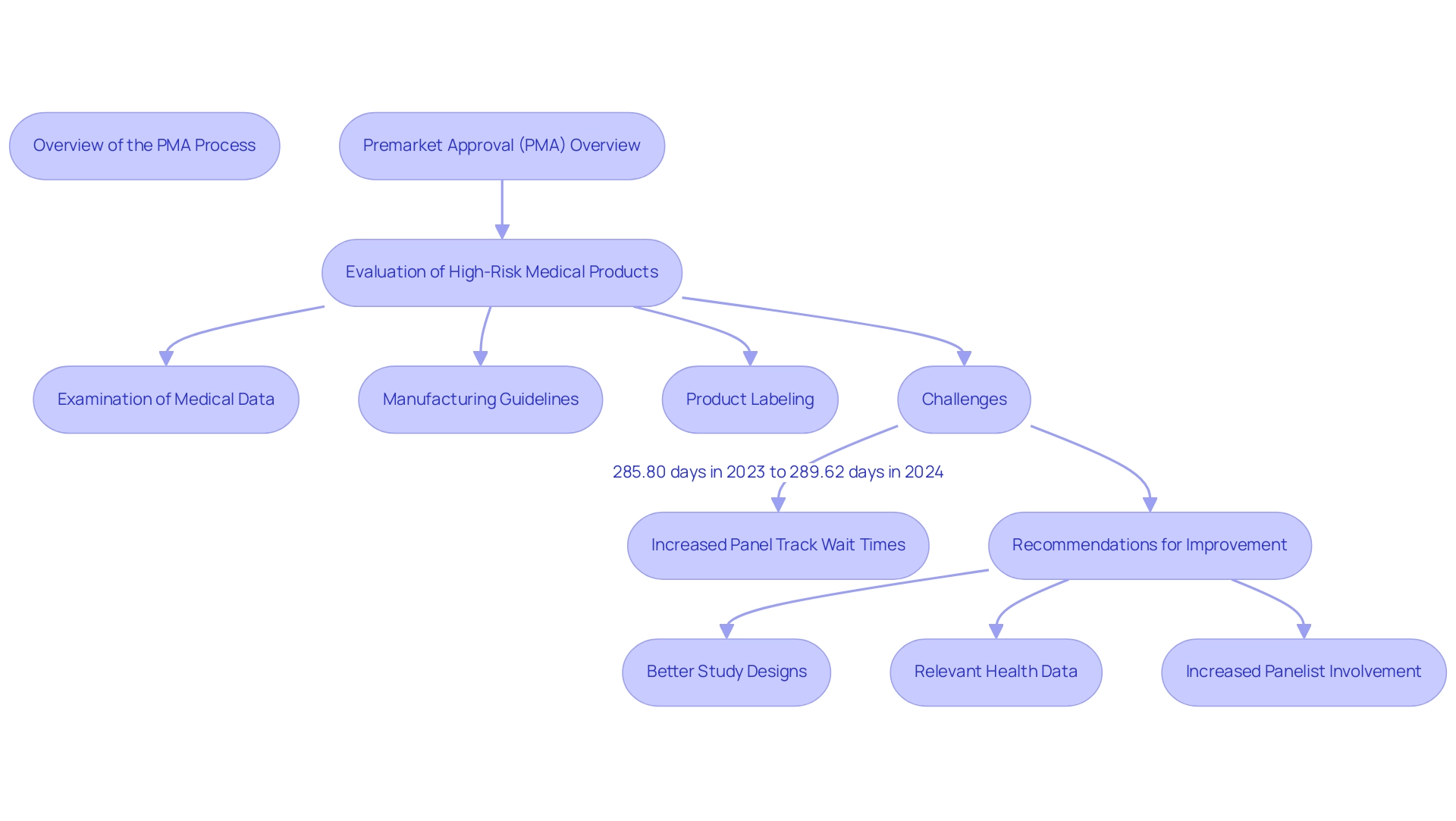
To understand what is PMA approval, it is important to note that Premarket Approval (PMA) represents a critical regulatory framework established by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) specifically for the evaluation of high-risk medical products. This thorough procedure is crucial to confirm that such instruments are not only safe but also effective for their intended uses before their launch into the marketplace. The PMA procedure involves a thorough examination of medical data, manufacturing guidelines, and product labeling, all focused on assessing the item's overall performance and safety profile.
Unlike alternative regulatory pathways, what is PMA approval demands a higher level of scrutiny, reflecting the intricate nature and inherent risks associated with high-risk products. Recent studies suggest that increasing panelist participation in crucial trial design and label development could significantly simplify the PMA process, ensuring that the regulatory framework evolves in accordance with technological advancements and medical needs. However, current challenges persist, as evidenced by the increase in panel track wait times, which rose from 285.80 days in 2023 to 289.62 days in 2024.
Iseult McMahon, an analyst at BTIG, notes, 'We think that this is a directional positive for the broader medical technology space as it provides both improving certainty to companies (and investors) as well as reduces cash burn during the interim period when a company is awaiting a decision.' Furthermore, insights from the case study titled 'Panel Members' Recommendations for Improvement' emphasize the need for better study designs, more pertinent health data, and increased panelist involvement in label development, which could encourage more open discussions prior to voting. In this context, utilizing the expertise of bioaccess®—with over 20 years of experience in Medtech—in managing comprehensive trial services, including Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies (PMCF), is crucial for understanding what is PMA approval and successfully navigating the complexities involved.
Significantly, Katherine Ruiz’s expertise in Regulatory Affairs for medical equipment and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia enhances our capability to address these challenges effectively, showcasing the specialized knowledge and flexibility required in clinical trials.
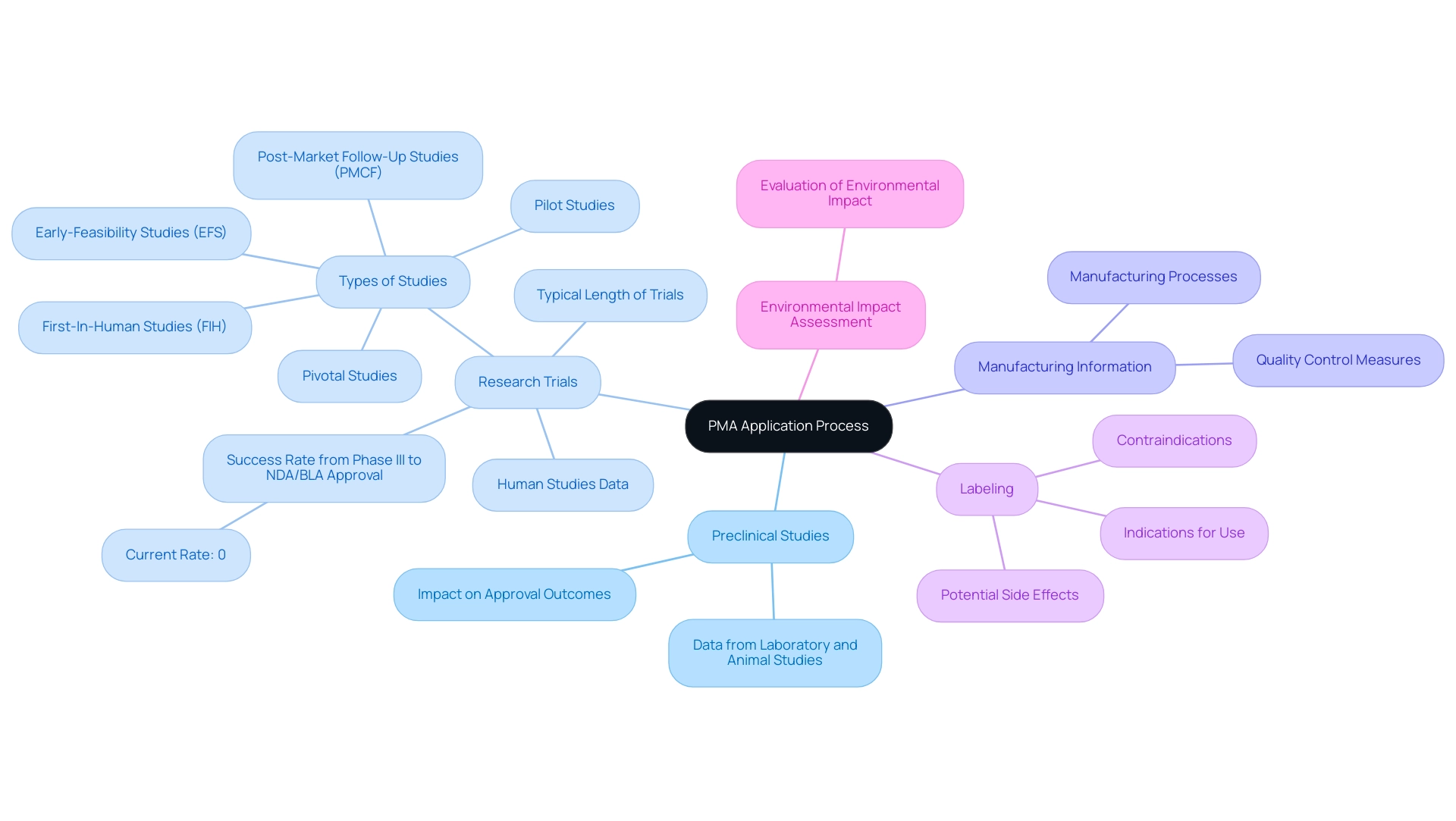
Key Components of the PMA Application Process
The PMA (Premarket Approval) application process is essential for answering what is PMA approval, as it serves as a crucial pathway for demonstrating the safety and effectiveness of medical instruments, comprising several key components that must be meticulously documented for FDA review. These components include:
-
Preclinical Studies: This section presents data from laboratory and animal studies that validate the apparatus's safety and effectiveness, forming the foundation for further testing.
Recent statistics indicate that the success rates of preclinical studies can significantly impact overall approval outcomes.
-
Research Trials: Comprehensive data collected from human studies are essential to substantiate the device's intended use.
The typical length of trials for PMA applications is generally lengthy, indicating the thorough assessment needed to guarantee patient safety and effectiveness. Significantly, statistics indicate that the success rate from Phase III to NDA/BLA approval is currently 0%, highlighting the difficulties encountered in the approval. Bioaccess® focuses on overseeing a range of studies, such as Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies (PMCF), which are essential to understanding what is PMA approval in the context of the application procedure in Latin America.
With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, Bioaccess® offers a customized approach that ensures flexibility and responsiveness to client needs.
-
Manufacturing Information: Detailed descriptions of manufacturing processes and quality control measures are critical to ensure product consistency and safety, addressing any potential concerns that may arise during the review.
-
Labeling: Proposed labeling must provide necessary information for users, including indications for use, contraindications, and potential side effects. Clear and informative labeling is vital for guiding clinical practice and ensuring patient safety.
-
Environmental Impact Assessment: If applicable, an evaluation of the device’s potential environmental impact must be included, reflecting a growing awareness of the ecological considerations in medical device development. Each of these components plays a vital role in facilitating a thorough review by the FDA, helping to clarify what is PMA approval.
Tohru Takebe from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation emphasizes this significance, stating,
Collaboration between academic institutions and the pharmaceutical industry appeared more crucial at later stages than earlier ones,
highlighting the necessity for strong partnerships throughout the PMA framework. Additionally, a recent case study titled 'Combined Parameter Success Rates' explored how specific combinations of target and action parameters can influence approval success rates, revealing that the combination of enzyme and stimulant had the highest success rate at 23.4%. Additionally, the National Institute of Health offers awards data by institute/center through RePORT, which emphasizes the significance of funding and research support in the context of what is PMA approval.
Recent studies also show that the count of drugs in the R&D pipeline globally is anticipated to hit 22,825 in 2024, indicating a growing focus on thorough assessment and approval procedures throughout the medical sector. The influence of Medtech clinical studies reaches beyond individual products, contributing to local economies through job creation, economic growth, and enhancements in healthcare, fostering international collaboration.
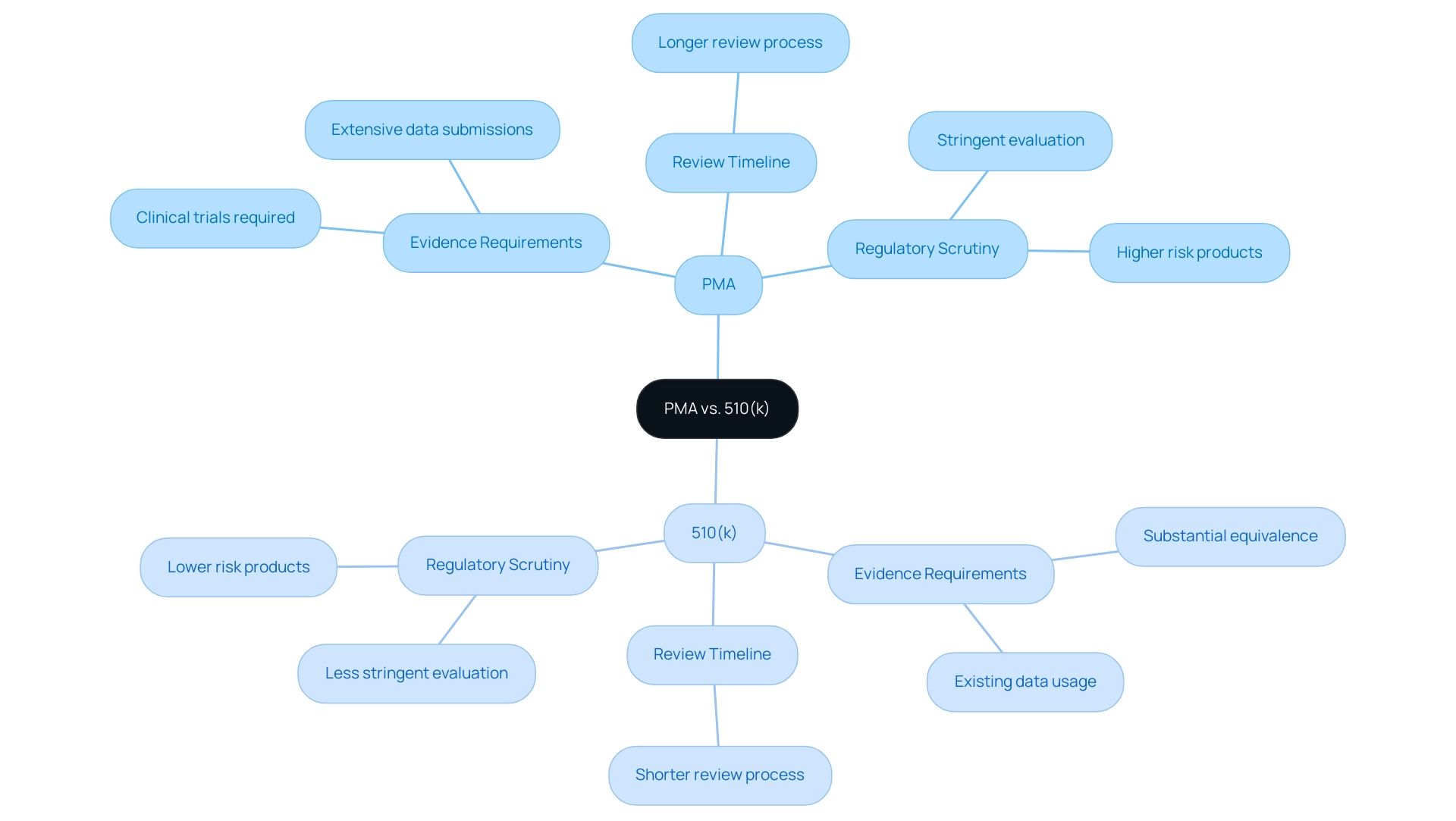
PMA vs. 510(k): Understanding the Differences
In understanding the regulation of medical equipment, one might ask what is PMA approval, as the Premarket Approval (PMA) and 510(k) procedures fulfill different functions designed to cater to diverse levels of risk. The 510(k) pathway is intended for products that are substantially equivalent to those already available, requiring less stringent evidence of safety and effectiveness. On the other hand, what is PMA approval is a method utilized for high-risk products, requiring extensive medical data to confirm their safety and effectiveness.
Key differences between the two include:
- Evidence Requirements: The PMA process mandates clinical trials and extensive data submissions, while the 510(k) pathway relies on existing data to establish equivalence. This fundamental difference emphasizes the varied evidentiary standards required for approval of the apparatus.
- Review Timeline: Owing to the complexity and depth of information required by PMA submissions, understanding what is PMA approval means that the review timeline is generally longer compared to the 510(k) procedure, reflecting the thoroughness of the evaluation.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: PMA submissions undergo a more stringent evaluation to understand what is PMA approval, considering the increased risks linked to the instruments involved. Notably, recent findings indicate that six specialties had significantly lower recall rates compared to orthopedics, raising significant safety concerns and highlighting the imperative for robust postmarketing surveillance. Insights from regulatory experts, including Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Regulatory Affairs for medical products and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, suggest that understanding these distinctions is crucial for manufacturers as they navigate the regulatory landscape, ensuring that they choose the appropriate pathway for their products.
Moreover, our service capabilities include compliance assessments to ensure conformity with national regulations, import permits for investigational tools, and efficient project management and oversight throughout the study. The lack of extra documentation like an 'Indications for Use' page or 'Premarket Review Submission Cover Sheet' with Estar submissions streamlines the procedure for specific equipment. Jonathan R. Dubin, MD, emphasized the delicate balance between ensuring safety and expediting access to innovative treatments, remarking that,
Although not specifically addressed in this study, we recognize the importance of balancing the need to ensure safety and effectiveness with bringing innovative treatments to patients as quickly as possible.
Furthermore, a case study entitled 'Implications for Equipment Safety and Regulation' indicates that most recalls are linked to products authorized through the 510(k) pathway, raising substantial safety issues and advocating for enhanced postmarketing monitoring strategies and better quality of evidence in critical trials for items approved under what is PMA approval. This perspective reinforces the ongoing dialogue about the evolving regulatory scrutiny surrounding both pathways.
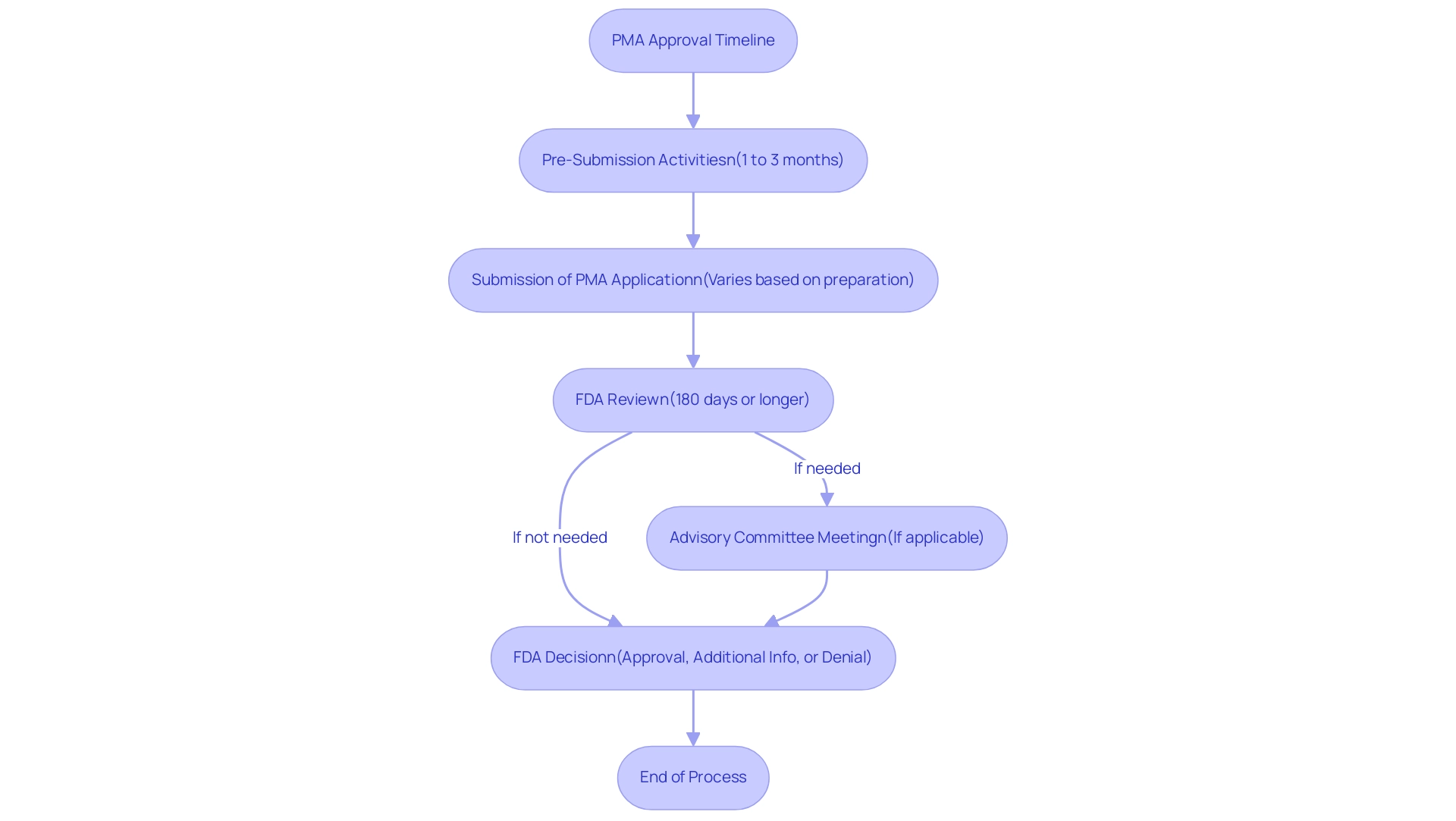
Navigating the PMA Timeline: Steps to Approval
The PMA approval procedure is characterized by a structured timeline that encompasses several critical steps:
- Pre-Submission Activities: This initial phase involves engaging with the FDA to discuss the proposed product, allowing manufacturers to gather valuable feedback. This step typically spans 1 to 3 months.
- Submission of PMA Application: Following pre-submission discussions, the formal submission of the PMA application occurs, which includes comprehensive data and documentation. The timeline for this step varies based on the preparation required.
- FDA Review: The FDA conducts a thorough examination of the application, which may take 180 days or longer, depending on the complexity of the device. Notably, the average approval time for panel-track supplements was recorded at 304 days in the first half of 2023, marking a significant 27% decline from the previous year. This statistic highlights the significance of efficient planning and execution in the PMA method.
- Advisory Committee Meeting: In certain instances, the FDA may convene an advisory committee to provide expert recommendations, necessitating additional time in the timeline.
- FDA Decision: The conclusion of the procedure is the FDA's decision regarding the PMA application, which can result in approval, a request for additional information, or outright denial. Understanding what is PMA approval is crucial for manufacturers, as it aids in effectively planning their development and marketing strategies. As Tom Rish aptly noted,
Assembling the necessary data, insights, and design requirements will likely take several rounds of internal revisions,
underscoring the importance of meticulous preparation in navigating the PMA landscape. Furthermore, using tools such as Greenlight Guru's quality management system (QMS) software can assist in streamlining the PMA procedure and aligning with FDA and ISO best practices. A practical illustration of this method in action is ZuriMED Technologies AG, which successfully obtained FDA clearance for its FiberLocker® System, allowing them to enhance their product offerings in the medical equipment sector. This real-world application exemplifies the importance of understanding and navigating what is PMA approval in the timeline. Furthermore, leveraging a partner like bioaccess®, which specializes in accelerated medical device research study services in Latin America, provides manufacturers with the necessary expertise in managing Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies (PMCF). This guarantees adherence and regulatory excellence throughout the trial, showcasing bioaccess®'s specialized expertise and adaptability in managing the intricacies of trials.
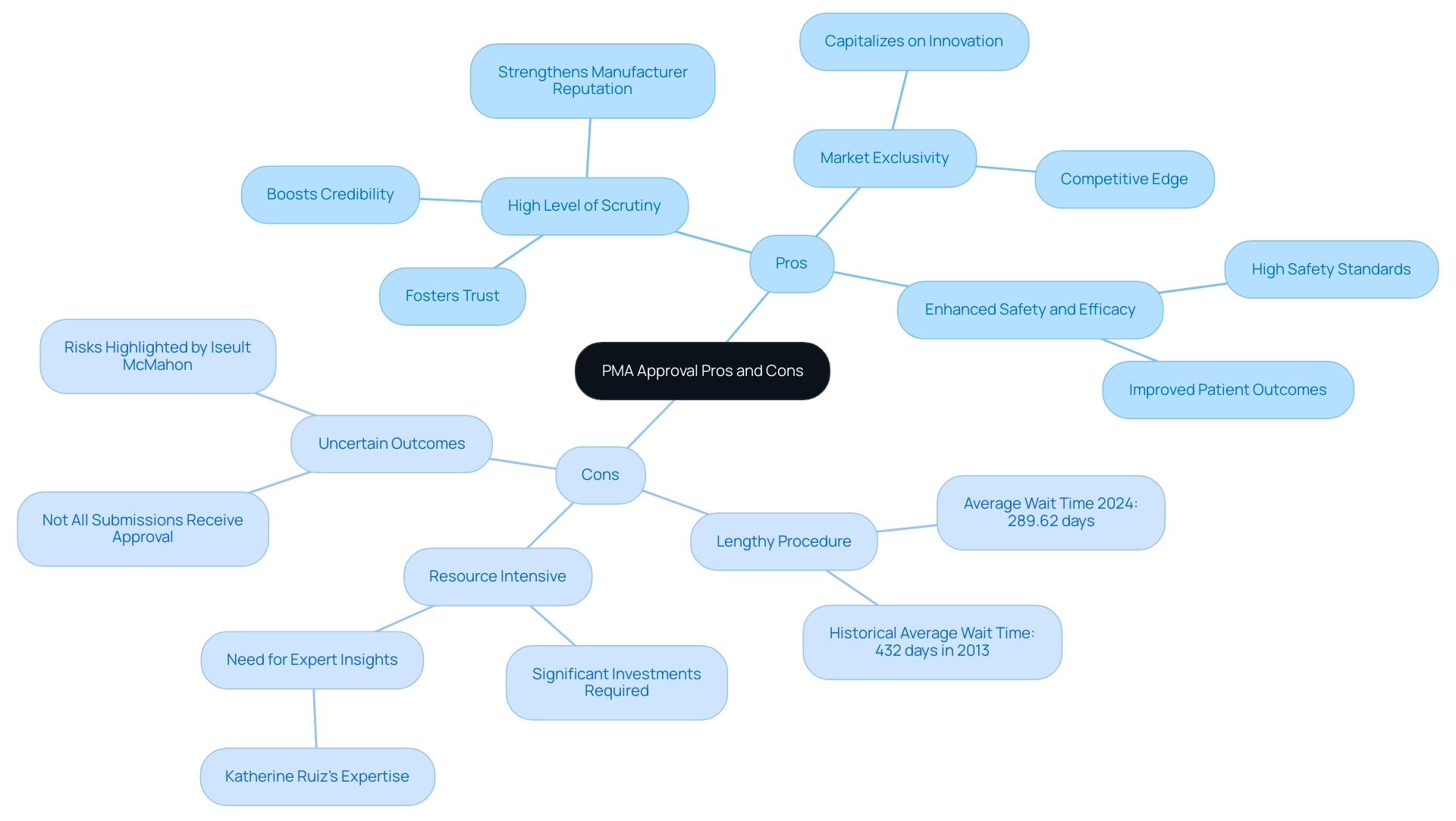
Evaluating the Pros and Cons of PMA Approval
Understanding what is PMA approval involves navigating a complex interplay of advantages and disadvantages that stakeholders must manage carefully, a challenge that can be effectively addressed through comprehensive clinical trial management services.
Pros:
- High Level of Scrutiny: The PMA pathway guarantees a thorough assessment, which greatly boosts the credibility of medical instruments. This scrutiny not only fosters trust among healthcare providers and patients but also strengthens the reputation of manufacturers.
- Market Exclusivity: Understanding what is PMA approval is essential, as successfully obtaining it can provide a substantial competitive edge in the medical equipment marketplace, allowing companies to capitalize on their innovation without facing immediate competition.
- Enhanced Safety and Efficacy: The extensive data collection needed in the PMA procedure often results in improved patient outcomes, illustrating what is PMA approval, as it ensures that devices meet high safety and efficacy standards.
Cons:
- Lengthy Procedure: One of the foremost challenges of the PMA method is its duration. While the FDA aims for a review period of six months, actual approval times can be significantly longer, with average wait times for Panel Track increasing from 285.80 days in 2023 to 289.62 days in 2024. Historically, the FDA review for PMA was supposed to take six months but often exceeded this, averaging 432 days in 2013.
- Resource Intensive: Manufacturers often face substantial resource demands, necessitating significant investments in clinical trials and comprehensive data collection to support their submissions. Utilizing the knowledge of experts such as Katherine Ruiz, who focuses on Regulatory Affairs for medical devices and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, can simplify this task by offering insights into compliance reviews and effective reporting on study status and adverse events.
- Uncertain Outcomes: Given the rigorous nature of the PMA procedure, manufacturers must understand what is PMA approval, as not all submissions receive it, presenting inherent risks. As noted by industry analyst Iseult McMahon,
We think that this is a directional positive for the broader medical technology space as it provides both improving certainty to companies (and investors) as well as reduces cash burn during the interim period when a company is awaiting a decision.
Additionally, the slight increases in wait times for De Novo and Panel Track approvals highlight ongoing challenges in the regulatory process. Evaluating these factors meticulously, alongside the comprehensive services offered, including feasibility studies, compliance reviews, trial setup, and project management, is crucial for stakeholders aiming to develop informed regulatory strategies that align with their business objectives.
Conclusion
The Premarket Approval (PMA) process is essential for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of high-risk medical devices, playing a pivotal role in the regulatory landscape. By demanding rigorous clinical data, comprehensive manufacturing information, and detailed labeling, the PMA pathway establishes a high standard that manufacturers must meet to secure market entry. Understanding the key components, including preclinical studies and clinical trials, is crucial for navigating the complexities of this approval process.
While the PMA process offers advantages such as enhanced credibility and market exclusivity, it also poses significant challenges, including:
- Lengthy review timelines
- Resource-intensive requirements
The differences between the PMA and 510(k) pathways further underscore the necessity for manufacturers to carefully consider their regulatory strategies based on the unique characteristics of their devices.
As the medical technology landscape evolves, optimizing stakeholder engagement and trial designs will be paramount in addressing the challenges of increasing approval times. Collaboration with experts in regulatory affairs and clinical trial management can pave the way for more efficient submissions and improved outcomes. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of the PMA process, coupled with strategic planning and expert guidance, is essential for manufacturers aiming to bring innovative medical devices to market successfully.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PMA approval?
PMA (Premarket Approval) is a regulatory framework established by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for evaluating high-risk medical products to ensure they are safe and effective for their intended uses before entering the market.
What does the PMA process involve?
The PMA process includes a thorough examination of medical data, manufacturing guidelines, and product labeling, all aimed at assessing the product's overall performance and safety profile.
How does PMA approval differ from other regulatory pathways?
PMA approval requires a higher level of scrutiny compared to alternative regulatory pathways due to the complex nature and inherent risks associated with high-risk medical products.
What are the key components of the PMA application process?
The key components include: 1. Preclinical Studies: Laboratory and animal data validating safety and effectiveness. 2. Research Trials: Comprehensive human study data to support the device's intended use. 3. Manufacturing Information: Detailed descriptions of manufacturing processes and quality control measures. 4. Labeling: Proposed labeling that includes necessary information for users. 5. Environmental Impact Assessment: Evaluation of the device’s potential environmental impact, if applicable.
What challenges are currently faced in the PMA process?
Current challenges include increased panel track wait times for approval, which rose from 285.80 days in 2023 to 289.62 days in 2024.
How can increasing panelist participation impact the PMA process?
Increasing panelist participation in trial design and label development could simplify the PMA process and ensure the regulatory framework adapts to technological advancements and medical needs.
What role does Bioaccess® play in the PMA process?
Bioaccess® manages comprehensive trial services, including Early-Feasibility Studies, First-In-Human Studies, Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies, which are crucial for navigating the complexities of PMA approval.
What is the significance of collaboration in the PMA framework?
Collaboration between academic institutions and the pharmaceutical industry is crucial, especially at later stages of the PMA process, to enhance the likelihood of successful approvals.
How does the PMA process contribute to the medical sector?
The PMA process impacts not only individual products but also contributes to local economies through job creation, economic growth, and improvements in healthcare, fostering international collaboration.

