Introduction
Navigating the intricate landscape of medical device regulation in the United States requires a comprehensive understanding of the FDA 510(k) summary, a critical component in the premarket notification process. This summary not only serves as a formal assertion of a device's substantial equivalence to an already marketed counterpart but also encapsulates vital information regarding its intended use and technological characteristics.
As manufacturers strive to comply with stringent regulatory standards, the challenges they face—from identifying appropriate predicate devices to addressing potential risks—can significantly impact their market entry timelines. Recent statistics highlight alarming gaps in documentation, underscoring the need for meticulous preparation and thorough clinical research management.
This article delves into the essential elements of the 510(k) summary, outlines the preparation process, and discusses common challenges that manufacturers encounter, all while emphasizing the importance of regulatory expertise and collaboration in achieving successful device approvals.
Understanding the FDA 510(k) Summary: Definition and Significance
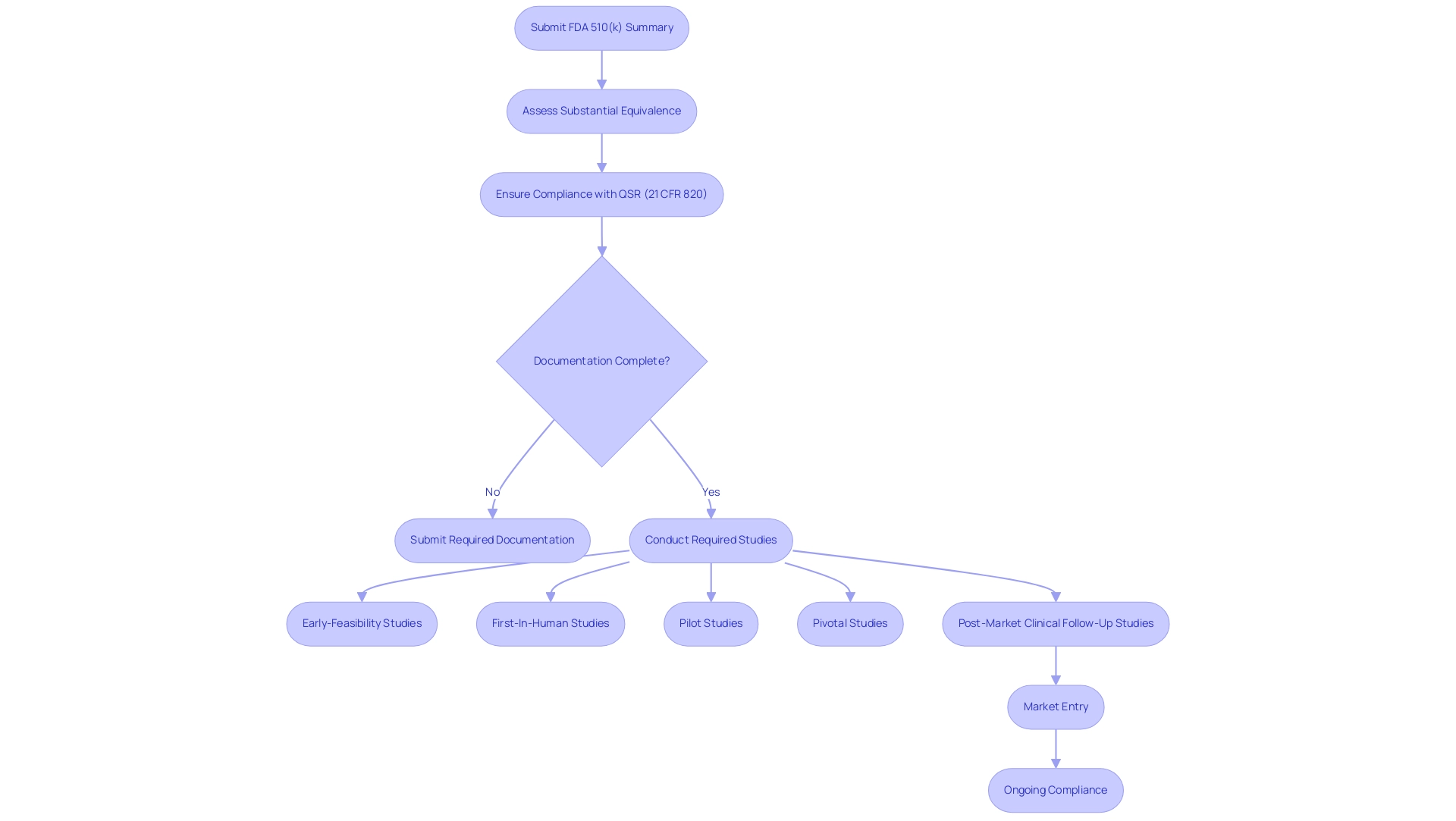
The fda 510 k summary plays a pivotal role in the premarket notification process for medical products in the United States, serving as a formal declaration by manufacturers that asserts a product's substantial equivalence to an already legally marketed item exempt from premarket approval. This FDA 510 K summary is essential, as it outlines the intended use and technological features of the apparatus while showcasing adherence to required standards. Recent statistics indicate a critical gap in documentation, with only 13 approval documents (1.9%) including a corresponding published scientific validation study.
Furthermore, all medical instruments, including those exempt from 510(k), must adhere to the Quality System Regulation (QSR) as outlined in 21 CFR 820, essential for ensuring safety and efficacy. This commitment to compliance is likewise echoed in the comprehensive clinical trial management services offered by bioaccess®, which navigates the complexities of various studies, including:
- Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS)
- First-In-Human Studies (FIH)
- Pilot Studies
- Pivotal Studies
- Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF) in Latin America.
With over 20 years of expertise, bioaccess® provides tailored support in feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, project management, and monitoring, thereby enhancing patient safety and fostering innovation within the healthcare sector.
For instance, a recent pharmacokinetic (PK) study involving 39 healthy adult subjects compared opiate levels in fingerprint sweat with those in blood, oral fluid, and urine samples after codeine administration, highlighting the practical implications of the 510(k) process on safety and efficacy. The knowledge acquired from such studies is crucial for stakeholders in clinical research and product development, emphasizing the importance of a comprehensive understanding of the FDA 510 k summary as a basis for compliance and successful market entry. As Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Compliance Affairs for Medical Instruments and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, highlights, grasping the oversight landscape, including the roles of INVIMA as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO, is essential for effective navigation of the medical instrument market.
Such insights solidify the importance of the FDA 510 K summary in aligning technological advancements with regulatory expectations.
Key Requirements for a Comprehensive 510(k) Summary
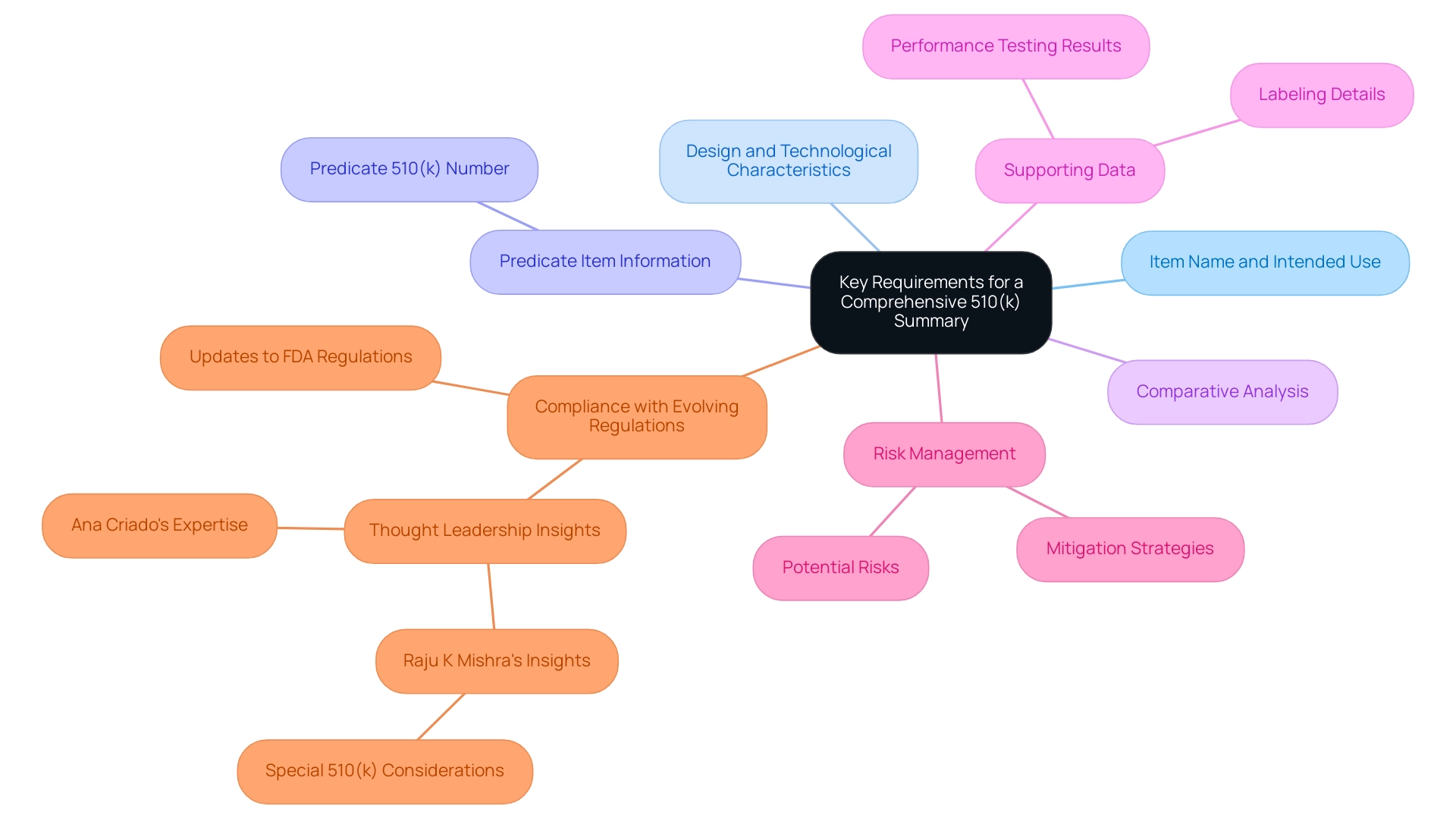
To meet FDA requirements, a comprehensive FDA 510(k) summary must encompass several essential components. Firstly, it should clearly identify the item's name and intended use, along with a thorough description of its design and technological characteristics. A critical aspect of the FDA 510(k) summary is the inclusion of information regarding the predicate item, specifically its 510(k) number, along with a comparative analysis of the new item's features against those of the predicate.
Furthermore, manufacturers are required to provide supporting data that demonstrates substantial equivalence, which may include performance testing results and labeling details. Along with these technical specifications, the summary must address potential risks related to the equipment and outline the strategies implemented to mitigate these risks. By carefully following these requirements outlined in the FDA 510(k) summary, manufacturers not only simplify the evaluation but also improve the chances of prompt market entry for their products.
This, in turn, contributes to improved patient outcomes and fosters advancements in medical technology. Staying informed about updates to FDA regulations and guidance is crucial for compliance, particularly as the landscape evolves towards the 2024 requirements. In light of this, it is noteworthy that a thought leadership session on FDA regulations will take place on July 31st at 7am PT, providing valuable insights into the evolving requirements.
Additionally, understanding when a 510(k) submission is necessary is illustrated in the case study titled When Are 510(k) Submissions Required?, which emphasizes the importance of compliance for new medical equipment. Furthermore, as Raju K Mishra, a Quality and Regulatory Affairs Specialist, aptly points out, What about Special 510(k)? highlighting the nuances and considerations that manufacturers must navigate in the submission process. Significantly, utilizing knowledge from specialists such as Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, can improve comprehension of health economics and compliance challenges, especially in the realm of innovative medical instruments. Ana's extensive qualifications, including her experience at INVIMA and her academic roles, enrich the discussion on these critical FDA requirements.
The Process of Preparing a 510(k) Summary
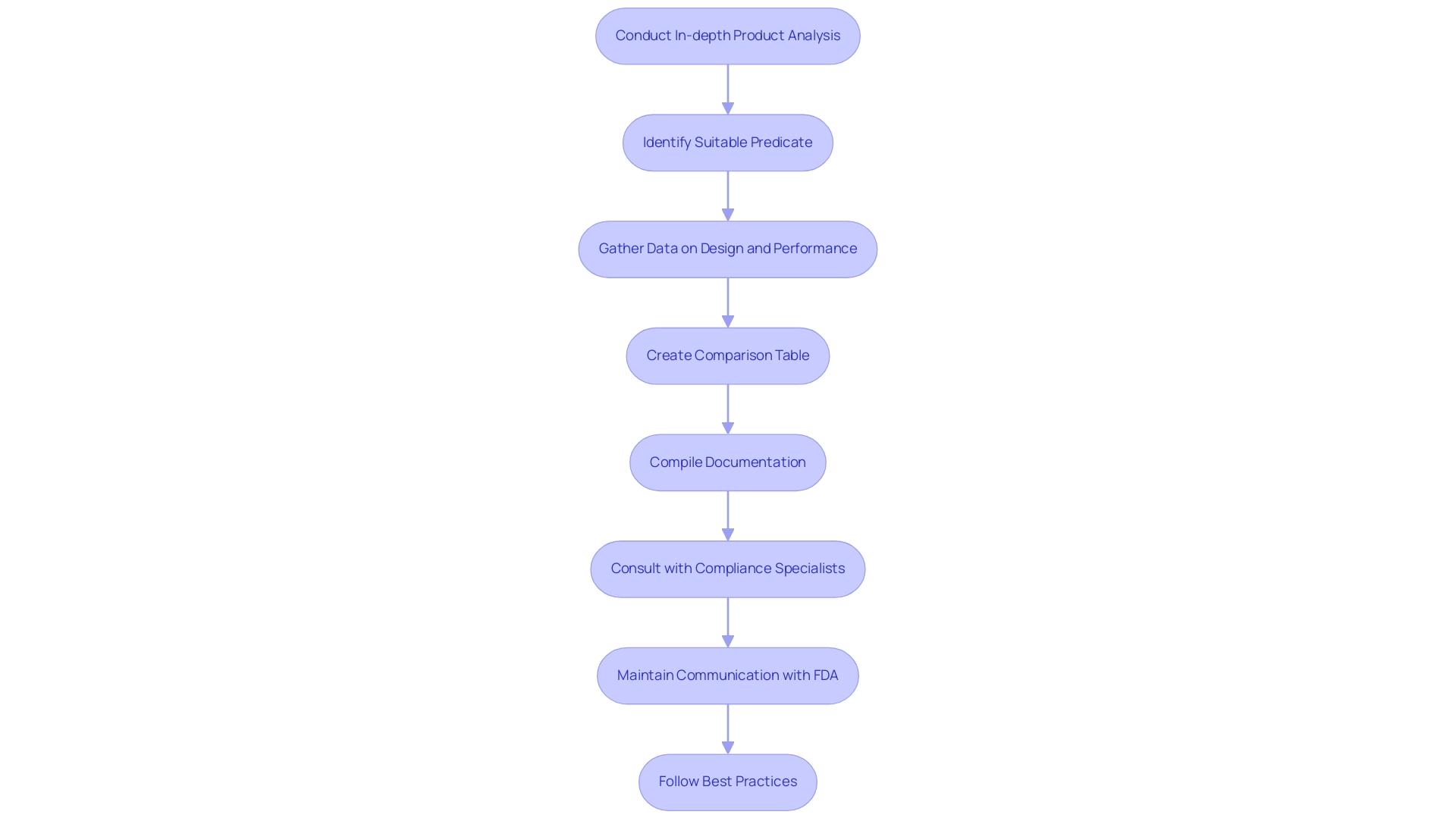
Preparing an FDA 510 k summary involves a series of essential steps that can significantly influence the success of the submission. Initially, manufacturers must conduct an in-depth analysis of their product, identifying a suitable predicate that aligns with the regulatory requirements. The FDA offers guidance on how to assess the appropriateness of a predicate instrument, which is essential for this process.
This includes meticulously gathering data related to the design, intended use, and performance characteristics, ensuring that the foundation for the summary is robust. Additionally, manufacturers should consider creating a comparison table that identifies similarities and differences in various characteristics of the predicate device to structure their analysis effectively. Once this information is collected, manufacturers should compile the necessary documentation, paying close attention to accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Consulting with compliance specialists, such as Ana Criado, who has extensive experience in oversight affairs and is a professor in biomedical engineering, is highly advisable. Her insights, derived from her experience with international firms such as General Electric and Omron Healthcare, can assist in recognizing potential challenges that may occur during the FDA evaluation. As Alex Pavlovic, a quality and compliance expert, emphasizes, 'a culture of quality is transformational, particularly in the context of compliance submissions,' underscoring the critical nature of meticulous preparation throughout the entire submission journey.
Additionally, Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in regulatory matters for medical equipment and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, recommends that keeping open channels of communication with the FDA during the preparation phase can simplify the submission procedure. Given that 30% of 510(k) submissions in 2022 were not accepted for initial review, following the FDA 510 k summary best practices is paramount. By following these steps, manufacturers can significantly improve their chances of obtaining a successful submission as outlined in the FDA 510 k summary, ultimately enabling quicker market access for their innovative medical products.
Common Challenges in the 510(k) Submission Process
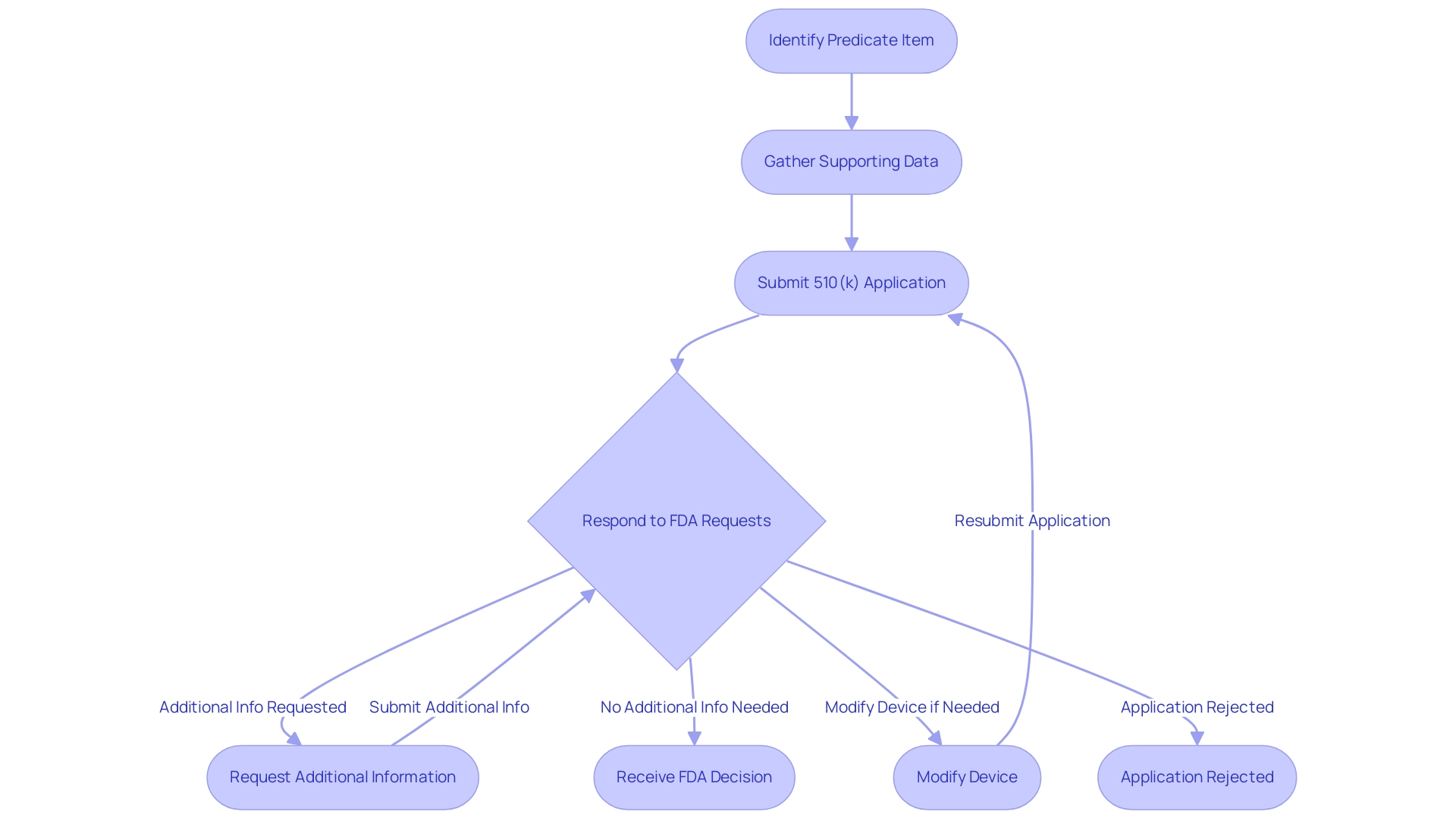
The FDA 510(k) summary indicates that the submission process presents considerable challenges for manufacturers, particularly in identifying an appropriate predicate item, which is essential for demonstrating substantial equivalence. Navigating the 510(k) database can greatly assist in finding the appropriate predicate product, crucial for a successful submission. Many manufacturers encounter difficulties in gathering sufficient data to support their claims, especially when their device includes innovative features that lack direct comparisons in existing products.
The regulatory environment introduces another level of complexity; for example, the FDA may issue requests for additional information that can extend the review duration. A notable case is that of a developer of a new cardiovascular catheter, who received an Additional Information (AI) letter from the FDA due to insufficient performance data. The reviewer highlighted the absence of critical metrics related to flexibility, raising concerns about the catheter's functionality in various clinical scenarios.
If the FDA does not receive a satisfactory response, the review can be significantly delayed or even lead to rejection, as statistics indicate that unsatisfactory responses can prolong the evaluation by several months. It is crucial to recognize that modifications can be made to a product that has already obtained 510(k) clearance, which allows manufacturers some flexibility in addressing issues identified during the review. To navigate these hurdles effectively, manufacturers should prioritize thorough pre-submission planning, engage experienced consultants like Ana Criado, a renowned expert in compliance affairs and biomedical engineering who has successfully guided numerous companies through the FDA 510(k) summary process, and foster open communication with FDA officials.
Ana's extensive experience includes consulting for innovative medical products and her expertise in cannabis legislation, which can provide unique insights into managing compliance challenges. By addressing these potential challenges proactively, manufacturers can enhance their likelihood of a successful submission and secure timely approvals.
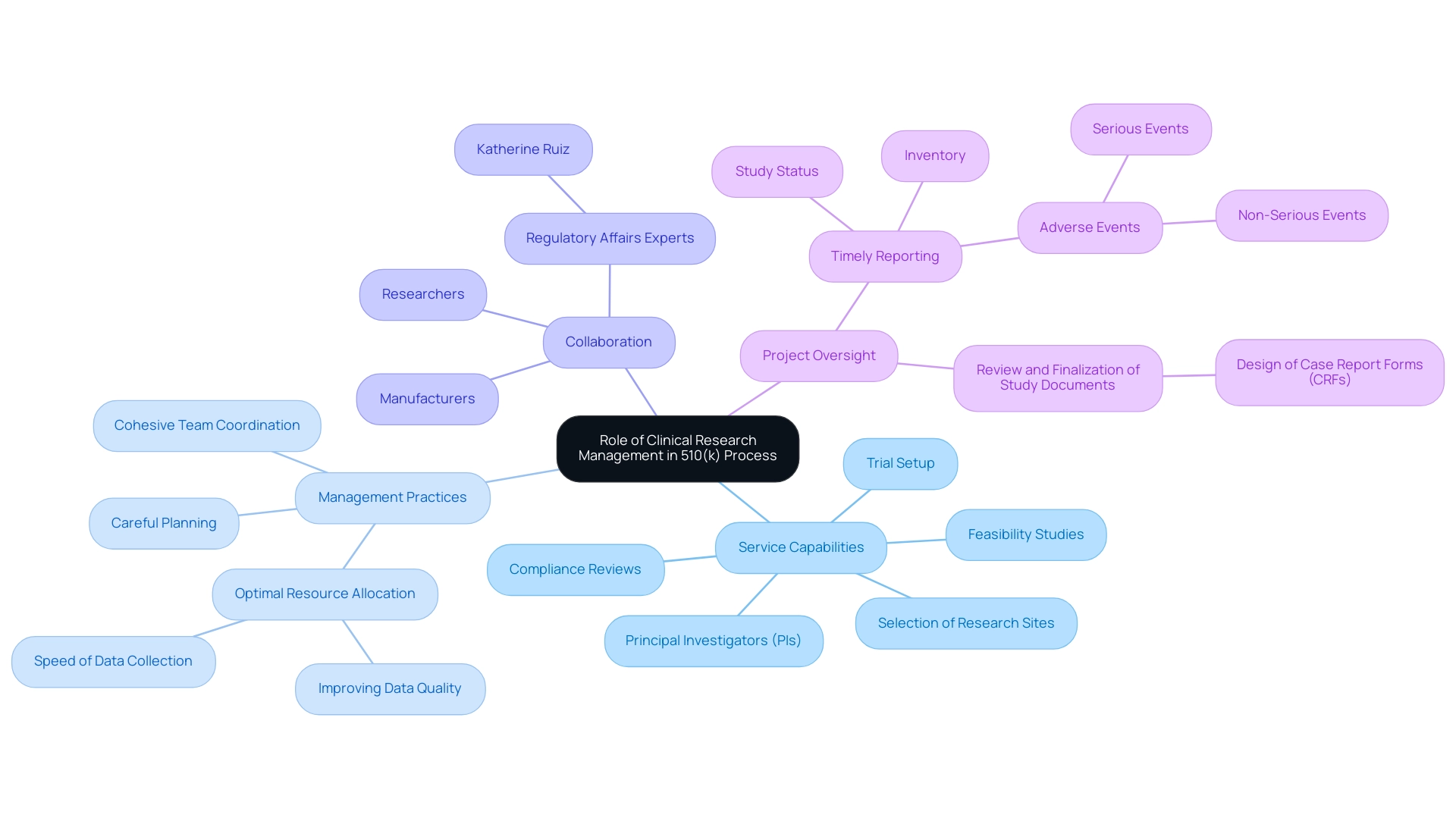
The Role of Clinical Research Management in the 510(k) Process
Clinical research management is essential in the 510(k) submission process, ensuring that every aspect of research complies with strict standards. Our comprehensive service capabilities encompass:
- Feasibility studies
- Selection of research sites
- Principal investigators (PIs)
- Thorough compliance reviews
- Trial setup
Furthermore, we manage import permits and the nationalization of investigational tools, which are crucial for compliance with regulations.
With the ongoing transition from paper-based to electronic systems, effective management practices now involve:
- Careful planning
- Cohesive team coordination
- Optimal resource allocation to improve data quality and speed
By promoting collaboration among researchers, Regulatory Affairs experts like Katherine Ruiz, and manufacturers, clinical research managers can significantly streamline the preparation of the FDA 510 K summary, thereby minimizing the potential for errors and omissions. This collaborative environment is essential for the efficient collection and analysis of data necessary to establish substantial equivalence, ultimately enhancing the quality of submissions.
The review and finalization of study documents, particularly the design of Case Report Forms (CRFs), exemplifies effective clinical research management practices that lead to error-free data acquisition, improving the quality of clinical trial data. Moreover, prioritizing efficient management throughout the FDA 510 K summary procedure not only boosts the overall efficiency and success rates of device approvals but also drives medical innovation and enhances patient care. As Binny Krishnankutty from Dr. Reddy's Laboratories mentions, 'This article emphasizes the procedures involved and offers the reader an overview of the tools and standards adopted along with the roles and responsibilities in clinical data management.'
With bioaccess® leading medtech clinical research in Latin America and supporting over 30 successful regulatory submissions, the effectiveness of clinical research management in navigating the complexities of the FDA 510 K summary is increasingly evident. Furthermore, our project management and monitoring processes ensure that all aspects of the clinical trials are meticulously overseen, facilitating timely reporting on study status, inventory, and adverse events, both serious and non-serious.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of the FDA 510(k) summary is crucial for medical device manufacturers seeking to achieve market approval in the United States. This process requires a thorough understanding of the essential elements of the summary, including:
- Identification of predicate devices
- Demonstration of substantial equivalence
- Meticulous preparation of comprehensive documentation
The challenges faced during this process, such as data collection and regulatory compliance, underscore the importance of collaboration with regulatory experts and clinical research managers to enhance the likelihood of successful submissions.
Moreover, the role of clinical research management cannot be overstated. Effective management practices ensure adherence to regulatory standards, improve data quality, and facilitate efficient submission processes. By prioritizing thorough preparation and maintaining open lines of communication with the FDA, manufacturers can navigate potential hurdles and expedite their market entry.
In conclusion, a solid grasp of the FDA 510(k) summary and its requirements, combined with strategic planning and expert guidance, is essential for manufacturers aiming to bring innovative medical devices to market. By embracing these principles, stakeholders can contribute to advancements in healthcare while ensuring patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the FDA 510(k) summary?
The FDA 510(k) summary serves as a formal declaration by manufacturers asserting a product's substantial equivalence to an already legally marketed item, which is exempt from premarket approval. It outlines the intended use and technological features of the product and demonstrates adherence to required standards.
What are the recent statistics regarding FDA 510(k) approvals?
Recent statistics indicate that only 13 approval documents (1.9%) included a corresponding published scientific validation study, highlighting a critical gap in documentation.
Do all medical instruments have to comply with the Quality System Regulation (QSR)?
Yes, all medical instruments, including those exempt from 510(k), must adhere to the Quality System Regulation (QSR) as outlined in 21 CFR 820 to ensure safety and efficacy.
What types of studies are managed by bioaccess® in relation to clinical trials?
Bioaccess® manages various types of studies, including Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF).
How does the FDA 510(k) process impact safety and efficacy?
The FDA 510(k) process is crucial for demonstrating safety and efficacy through supporting data, including performance testing results and labeling details, which ultimately contributes to improved patient outcomes.
What essential components must be included in an FDA 510(k) summary?
An FDA 510(k) summary must include the item's name and intended use, a description of its design and technological characteristics, information regarding the predicate item (including its 510(k) number), a comparative analysis of features, supporting data demonstrating substantial equivalence, potential risks, and risk mitigation strategies.
Why is it important for manufacturers to stay informed about FDA regulations?
Staying informed about updates to FDA regulations and guidance is crucial for compliance, especially as the regulatory landscape evolves towards the 2024 requirements.
What is the significance of the case study titled 'When Are 510(k) Submissions Required?'
This case study emphasizes the importance of compliance for new medical equipment and illustrates when a 510(k) submission is necessary.
Who can provide insights into the nuances of the 510(k) submission process?
Specialists such as Raju K Mishra, a Quality and Regulatory Affairs Specialist, and Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, can provide valuable insights into the nuances and compliance challenges of the 510(k) submission process.

