Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of medical technology, the Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) emerges as a critical regulatory mechanism that enables the testing of innovative devices in clinical trials. This framework not only facilitates the collection of vital safety and efficacy data for devices that have yet to receive FDA approval but also underscores the importance of ethical standards in research.
As Medtech companies, particularly in Latin America, grapple with regulatory challenges and communication barriers, the role of the IDE becomes increasingly significant in fostering collaboration and advancing medical knowledge.
The FDA's rigorous oversight of IDE applications ensures that participant safety remains a priority, while a growing emphasis on artificial intelligence and machine learning in device development highlights the need for accountability in clinical research.
This article delves into the intricacies of the IDE process, the categories of investigational devices, and the essential considerations for navigating the regulatory landscape, ultimately illuminating the path toward innovation in the medical device sector.
Understanding Investigational Device Exemption (IDE)
An Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) serves as a pivotal regulatory framework that permits the utilization of investigational devices in clinical trials, highlighting the importance of understanding what is an IDE device. This exemption is vital for items lacking FDA approval, allowing researchers to gather essential data on their safety and effectiveness. IDEs not only facilitate the exploration of innovative medical technologies but also prioritize patient safety by ensuring that these instruments are tested in a controlled and ethical manner.
However, Medtech companies in Latin America face significant challenges, including:
- Regulatory hurdles
- Language barriers
- A fragmented resource landscape
These obstacles hinder smooth communication and cooperation between Latin American hospitals and American trial clients, especially in the medical equipment first-in-human trial sector. The importance of the IDE is further highlighted by the FDA’s focus on adopting a risk-based strategy designed for the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning in product development, ensuring accountability and transparency essential for maintaining trust in research.
For example, in the PHOENIX trial, there was no significant difference in the ALSFRS-R total score change from baseline at Week 48 compared to placebo, illustrating the importance of rigorous evaluation in investigational device research. Furthermore, the partnership among entities like Greenlight Guru and bioaccess™ seeks to speed up medtech innovations and trials in Latin America, illustrated by Dr. Jorge Hernando Ulloa’s presentation of one-year first-in-human VenoValve® data at the Charing Cross International Symposium. Additionally, ReGelTec's early feasibility study on HYDRAFIL™ for treating chronic low back pain in Colombia reflects the ongoing advancements in vascular medicine and the potential for IDEs to drive innovation.
Ultimately, understanding what is an IDE device is instrumental in advancing medical knowledge and expanding treatment options, playing a crucial role in fostering innovation within the medical landscape while underscoring the urgent need for a solution-driven approach to bridge the gaps in clinical research and innovation.
The Role of the FDA in IDE Regulation
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in the oversight of Investigational Device Exemptions (IDE), which pertains to what is an IDE device, ensuring a comprehensive process for advancing medical device trials. By meticulously reviewing IDE applications, the FDA ensures that proposed research is scientifically sound and prioritizes participant rights and safety. This governance framework includes essential components such as:
- Site feasibility
- Investigator selection
- Compliance with regulations
- Project management
- Reporting
For example, the case analysis of Defencath—a catheter lock solution incorporating taurolidine and heparin—underscores how the FDA's regulations facilitate effective catheter management through its antimicrobial and anticoagulant properties, illustrating the significance of project management in supervising such equipment. The rising number of IDE applications reviewed by the FDA reflects its commitment to fostering innovation while addressing the challenges that arise from understanding what is an IDE device for medical device startups, including regulatory hurdles and financial constraints. Iseult McMahon, an analyst at BTIG, remarked, 'We think that this is a directional positive for the broader medical technology space as it provides both improving certainty to companies (and investors) as well as reduces cash burn during the interim period when a company is awaiting a decision.'
Furthermore, a recent study titled 'Tirzepatide versus semaglutide for weight loss in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A value for money analysis,' published in Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023 highlights the significance of FDA supervision in the changing environment of research involving human participants.
By implementing strict oversight measures, the FDA guarantees that investigational instruments undergo a thorough evaluation process prior to market entry. As we approach 2024, the FDA's ongoing commitment to enhancing trial safety statistics and its continual review of applications, including what is an IDE device, remain integral to fostering innovation within the medical technology space, supported by effective project management and comprehensive reporting.
Categories of Investigational Devices
Investigational instruments are categorized into separate groups that indicate their risk levels and compliance requirements. Understanding these classifications is crucial for clinical researchers as they navigate the complex regulatory landscape, particularly in the context of INVIMA, the Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, which oversees health product regulation in Colombia. INVIMA, designated as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO, plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of medical products.
The categories include:
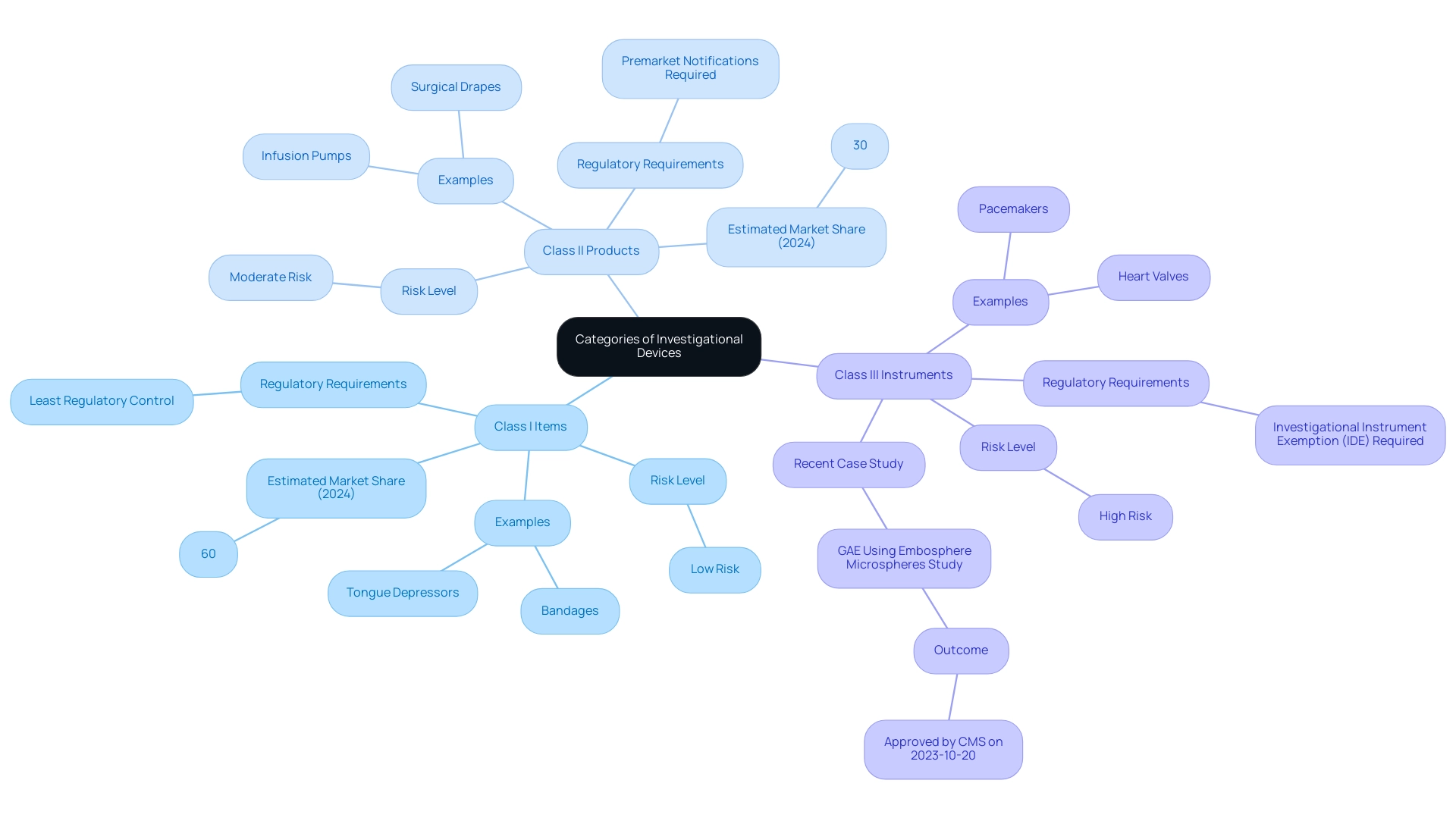
- Class I Items: Generally regarded as low-risk, these products encompass items such as bandages and tongue depressors. They are subject to the least regulatory control, allowing for easier market entry. In 2024, it is estimated that Class I products will constitute approximately 60% of investigational items in clinical trials.
- Class II Products: Moderate-risk items, including infusion pumps and surgical drapes, fall under this category. These require more stringent regulatory oversight, often necessitating premarket notifications to ensure safety and efficacy. Class II products are expected to account for approximately 30% of investigational items in the coming year.
- Class III Instruments: High-risk tools, such as pacemakers and heart valves, are classified here and usually necessitate an Investigational Instrument Exemption (IDE) for testing in a medical setting. The recent endorsement of Merit Medical Systems, Inc.'s research on knee osteoarthritis treatment, specifically the GAE trial comparing Embosphere microspheres to corticosteroid injections, emphasizes what is an IDE device in advancing clinical research. Approved by CMS on October 20, 2023, this study exemplifies the rigorous process that Class III products undergo. INVIMA's Directorate for Medical Equipment and other Technologies is responsible for overseeing these processes, ensuring that all medical products meet established safety and efficacy standards before market entry. Frank Samuelson from the FDA emphasizes that "AI/ML Applications and Challenges in the Development of In-Vivo Diagnostic Instruments" are crucial to understanding the hurdles faced in creating investigational tools, further illustrating the evolving landscape. Familiarity with these categories and their respective regulations, particularly those governed by INVIMA, not only ensures compliance but also enhances the integrity of research.
The Process of Obtaining an IDE
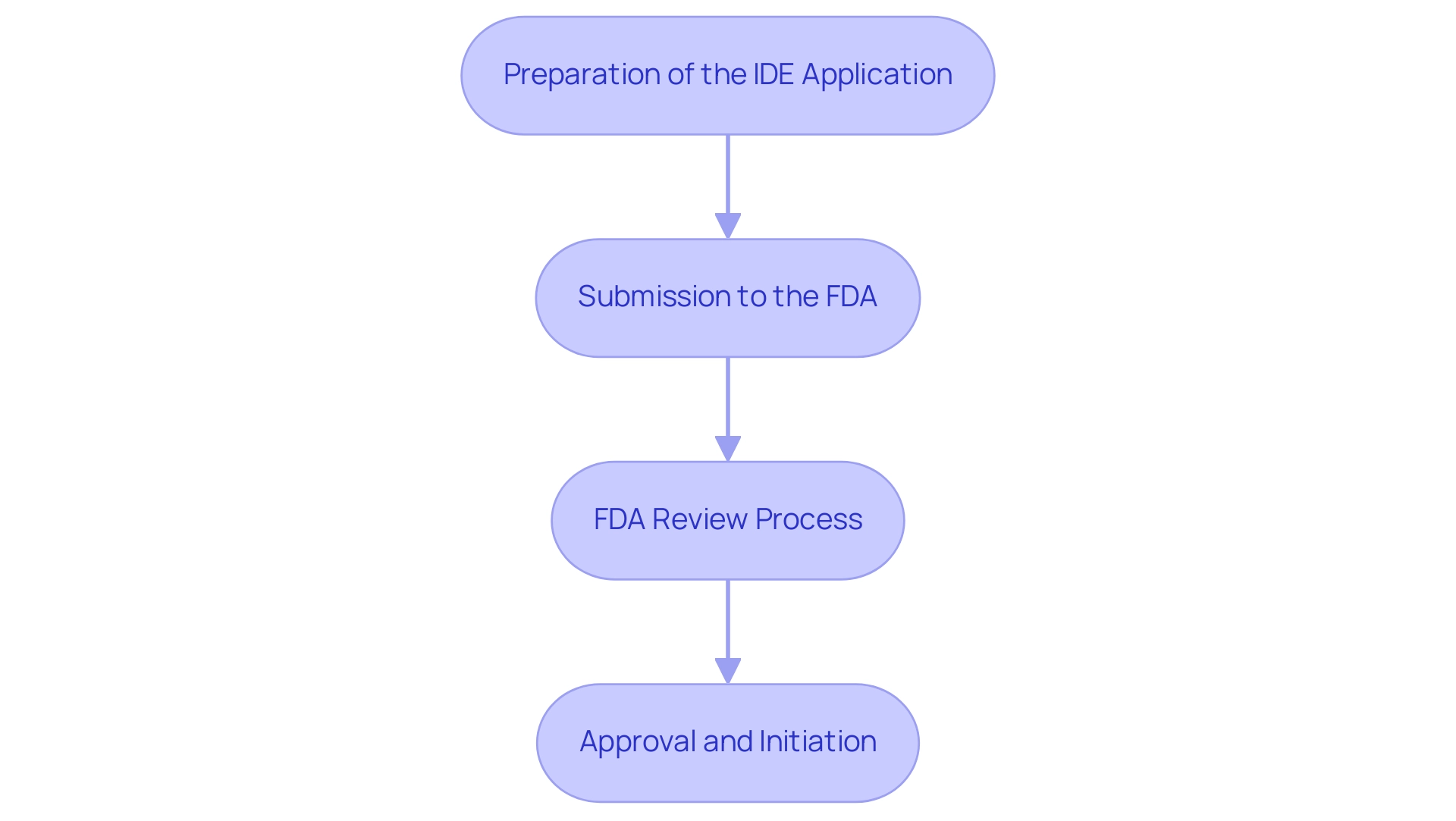
The process of obtaining an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) is critical for conducting clinical trials involving investigational instruments and comprises several essential steps:
- Preparation of the IDE Application: This preliminary phase requires meticulous compilation of necessary documentation, including detailed device descriptions, comprehensive study protocols, and informed consent forms to ensure participants are fully aware of their involvement.
- Submission to the FDA: After the application is thoroughly prepared, it is submitted to the FDA for an extensive review process. This submission signifies an important shift from planning to oversight.
- FDA Review Process: The FDA undertakes a rigorous evaluation of the application to ensure that it aligns with regulatory standards and prioritizes participant safety. Notably, sponsors are notified via email if the FDA disapproves an IDE application or proposes to withdraw approval, indicating the importance of maintaining open communication throughout this process.
- Approval and Initiation: Upon receiving FDA approval, the sponsor is authorized to commence the research study with the investigational apparatus, thereby advancing the research agenda.
A practical example of efficiency in the IDE process is the self-registration process for Class 1 instruments, which can potentially be completed in just one week, streamlining the pathway for sponsors. Grasping these steps is crucial for researchers seeking to understand what is an IDE device in order to navigate the complexities of trials effectively.
Moreover, bioaccess® provides expedited medical instrument research services in Latin America, with proficiency in overseeing various investigations, including Early-Feasibility, First-In-Human, Pilot, Pivotal, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Investigations. The team's extensive experience—over 20 years in Medtech—combined with the specialized knowledge of professionals like Juan Cuya, MD, and Katherine Ruiz in compliance matters, enhances the support available for navigating the IDE process. Their flexibility and customized approach have resulted in successful outcomes in numerous trials, ensuring that sponsors can adapt to the evolving landscape of medical device research.
Additionally, the recent Artivion case study, where the company faced disruptions in its shipping processes due to a ransomware attack, highlights the real-world challenges that can impact trial operations. bioaccess®'s expertise in Regulatory Affairs and crisis management positions them to effectively mitigate such challenges, providing sponsors with the confidence needed to navigate potential disruptions. As the landscape evolves, staying informed about the average approval timeline for 2024 and success rates of IDE applications in clinical trials will be instrumental in planning and executing successful research endeavors.
Significantly, sponsors must also stay alert about the necessary updates, including informing the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) in the event of a trial discontinuation and reflecting such changes on clinicaltrials.gov.
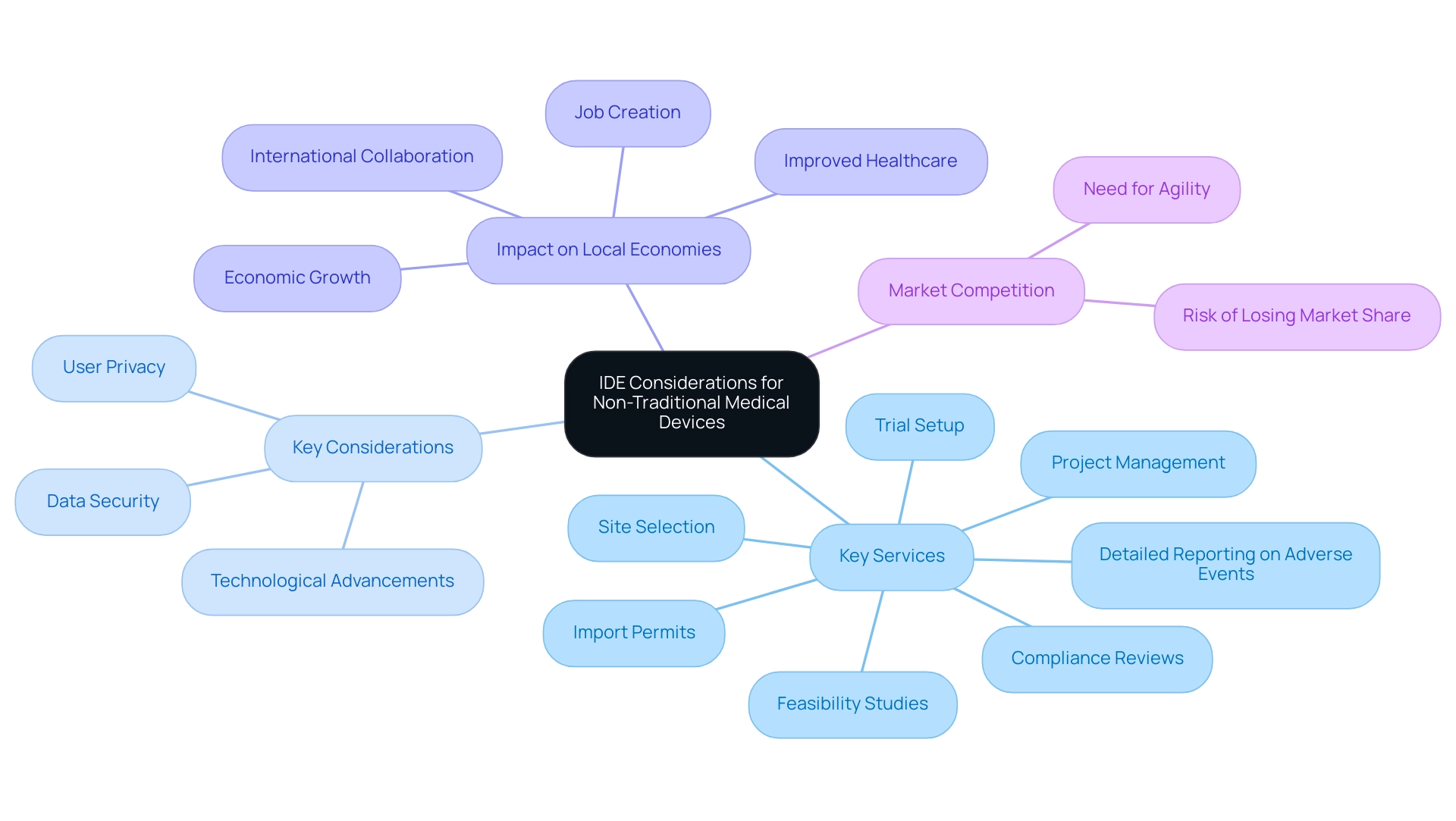
IDE Considerations for Non-Traditional Medical Devices
The rapid evolution of medical technology, including non-traditional tools such as software-based solutions and wearable technologies, raises distinct challenges related to what is an IDE device. As emphasized by specialists such as Katherine Ruiz, a leader in oversight matters for medical instruments and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, navigating these complexities demands a thorough approach that encompasses:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Detailed reporting on adverse events
These services are essential for ensuring compliance with requirements while promoting innovation.
Key considerations include:
- Data security
- User privacy
- The pace of technological advancements
Each significantly impacts compliance. According to a recent survey of medtech leaders, 63% believe that digital therapeutics will profoundly influence the industry over the next decade, underscoring the importance of staying agile and informed. As highlighted by a representative from Benchmark Electronics Inc., in the competitive medical equipment marketplace, companies cannot afford to lose time.
If you have a leading-edge product that successfully addresses a problem, your competitors are likely already on your heels, and you might not get a second chance to capture the market. To effectively navigate these regulatory challenges, researchers and manufacturers must adapt their strategies in alignment with evolving regulatory expectations concerning what is an IDE device, all while fostering innovation within the medical device sector. Additionally, comprehensive clinical trial management services have been shown to impact local economies positively by creating jobs, promoting economic growth, improving healthcare, and fostering international collaboration.
By leveraging best practices and insights from case studies like 'Quality Statistical Review for Therapeutic Devices and Best Practices,' stakeholders can better navigate the intricacies of ideas for software-based and wearable medical technologies, while ensuring compliance with country requirements in study documents.
Conclusion
The Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) is an essential regulatory mechanism that facilitates the clinical testing of innovative medical devices, enabling researchers to gather crucial safety and efficacy data for devices awaiting FDA approval. This framework is particularly vital for Medtech companies in Latin America, where regulatory challenges and communication barriers can impede progress.
The FDA's rigorous oversight ensures participant safety and thorough evaluation of investigational devices before market entry. Understanding the classifications of devices—from low-risk Class I to high-risk Class III—is critical for researchers navigating the regulatory landscape. The IDE application process requires careful preparation, submission, and review, ultimately allowing for the initiation of clinical trials.
As medical technology evolves, particularly with non-traditional devices like software and wearables, the IDE framework must adapt to address these new challenges. By embracing a solution-driven approach and implementing best practices, stakeholders can enhance compliance and foster innovation.
In conclusion, the IDE is pivotal for advancing medical knowledge and expanding treatment options within the medical device sector. By prioritizing collaboration, regulatory adherence, and ethical research practices, stakeholders can fully realize the potential of innovative medical technologies, contributing to a safer and more effective healthcare environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE)?
An Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) is a regulatory framework that allows the use of investigational devices in clinical trials, enabling researchers to collect essential data on their safety and effectiveness for items that lack FDA approval.
Why is an IDE important in medical research?
An IDE is crucial as it facilitates the exploration of innovative medical technologies while prioritizing patient safety through controlled and ethical testing of these devices.
What challenges do Medtech companies in Latin America face regarding IDEs?
Medtech companies in Latin America encounter significant challenges such as regulatory hurdles, language barriers, and a fragmented resource landscape, which complicate communication and cooperation with American trial clients.
How does the FDA influence the IDE process?
The FDA plays a vital role in overseeing IDEs by reviewing applications to ensure that the proposed research is scientifically sound and prioritizes participant rights and safety, which includes site feasibility, investigator selection, compliance, project management, and reporting.
Can you provide an example of an IDE application?
An example is the case analysis of Defencath, a catheter lock solution that incorporates taurolidine and heparin, which illustrates how FDA regulations facilitate effective catheter management through its antimicrobial and anticoagulant properties.
What is the significance of the FDA's risk-based strategy?
The FDA's risk-based strategy is designed for the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning in product development, ensuring accountability and transparency, which are essential for maintaining trust in research.
What are some examples of recent advancements related to IDEs?
Recent advancements include the presentation of one-year first-in-human VenoValve® data at the Charing Cross International Symposium and ReGelTec's early feasibility study on HYDRAFIL™ for treating chronic low back pain in Colombia.
How does the FDA ensure the safety of investigational devices?
The FDA implements strict oversight measures to guarantee that investigational instruments undergo a thorough evaluation process before entering the market, which is essential for fostering innovation in the medical technology space.
What role does project management play in the IDE process?
Effective project management is crucial in supervising the development and testing of investigational devices, ensuring compliance with FDA regulations and facilitating the overall management of clinical trials.




