Introduction
In the complex landscape of medical regulations and professional development, the acronym PMA emerges with diverse implications across various fields. Most notably, in the realm of healthcare, PMA stands for Premarket Approval, a rigorous process mandated by the FDA to ensure that medical devices and pharmaceuticals meet stringent safety and efficacy standards before they reach consumers. This process not only safeguards public health but also shapes the trajectory of innovation within the industry.
Beyond its medical connotations, PMA also signifies elements such as Professional Meeting Allowance in academic settings, highlighting its role in fostering professional growth and collaboration. As this article explores the multifaceted meanings and applications of PMA, it underscores the critical importance of understanding the context in which these terms are utilized, particularly for professionals navigating the intricate regulatory and developmental frameworks that govern their respective fields.
Understanding the Diverse Meanings of PMA
The PMA full form, which stands for Premarket Approval, is mainly acknowledged within the medical equipment and pharmaceutical industries, where it represents a stringent regulatory procedure aimed at ensuring the safety and efficacy of new products before they reach the market. This process requires substantial evidence to affirm that a product is safe, derived from laboratory animal investigations, human subject trials, and nonclinical studies. Recent findings indicate that an apparatus is deemed safe if there is valid scientific evidence demonstrating that its health benefits outweigh any probable risks, supported by adequate directions and warnings.
Notably, a retrospective analysis of the FDA Medical Device Recalls database revealed that from 2002 to 2021:
- 81% of the items were approved via the 510(k) pathway, exhibiting a recall rate of 11.6%.
- The recall rate for the 19% of items approved through PMA was 2.3%.
This emphasizes that products approved through the 510(k) process were 5.32 times more likely to be recalled, highlighting the essential role of PMA full form in enhancing safety in healthcare. Furthermore, the percentage of products approved by the 510(k) pathway has decreased over this period, indicating a potential shift in regulatory practices and highlighting the increasing importance of the PMA full form.
Beyond the medical field, the PMA full form includes diverse meanings such as:
- Professional Meeting Allowance in academic contexts
- Private Manager Assessment in engineering and management sectors
This diversity in definitions emphasizes the importance of context when navigating professional environments. With bioaccess®'s extensive experience of over 20 years in managing clinical studies, including Early-Feasibility, First-In-Human, Pilot, Pivotal, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up studies, they provide comprehensive clinical trial management services that ensure compliance and effective project oversight.
Comprehending the function of regulatory organizations like INVIMA and utilizing the knowledge of experts such as Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Products and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, is vital for maneuvering through the intricacies of medical product approval and improving the safety and effectiveness of new healthcare technologies.
Applications of PMA in Healthcare and Engineering
In the healthcare industry, the PMA full form primarily signifies Premarket Approval, which is a strict procedure mandated by the FDA to ensure that medical products and pharmaceuticals are both safe and effective before their market launch. This process is vital; recent findings indicate that 75.4% of industry respondents believe that the totality of scientific evidence should often suffice for decision-making in this context. Additionally, specialists such as Dr. Murad Alam stress the necessity for improved research frameworks and more pertinent clinical information, promoting increased engagement of panelists in the research framework and product label development.
Notably, from 2002 to 2021, the percentage of devices approved by 510(k) decreased, while the recall rate remained consistent, highlighting the evolving landscape of device approvals and the importance of thorough assessments. In contrast, in the field of engineering, the pma full form is commonly understood to refer to Private Manager Assessment, which focuses on evaluating managerial competencies and the overall viability of projects. Both interpretations underscore the critical need for thorough assessments and strict compliance, shaping the landscape for innovation in their respective domains.
Furthermore, the FDA has observed ongoing challenges related to research designs and data evaluations in clinical investigations, emphasizing the need for researchers to refer to relevant FDA guidance documents to navigate the intricacies of the approval procedure efficiently. Companies like bioaccess® illustrate the significance of a dedicated focus on managing clinical trials, including:
- Early-Feasibility Trials (EFS)
- First-In-Human Trials (FIH)
- Pilot Trials
- Pivotal Trials
- Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Trials (PMCF)
Their adaptability and tailored method are crucial for tackling the difficulties encountered in clinical trials, like those emphasized by a recent case involving Artivion, which faced a ransomware attack that interrupted its shipping operations.
This case illustrates the real-world implications of the PMA full form processes on operational capabilities and emphasizes how bioaccess® helps mitigate such risks through their comprehensive services.
PMA in Professional Development and Funding Opportunities
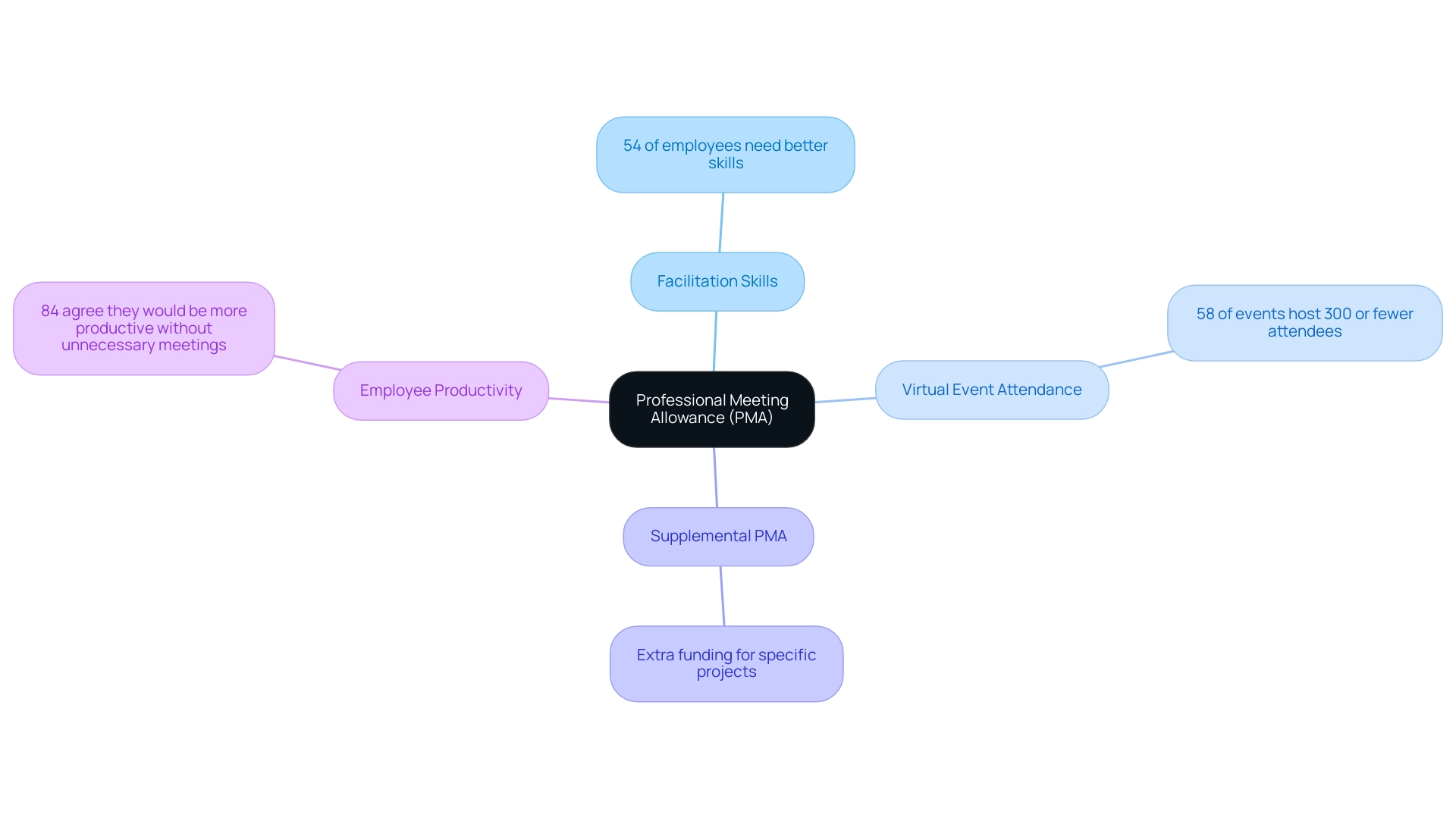
The PMA full form typically stands for the Professional Meeting Allowance, which is a crucial funding mechanism employed within academic and research environments to facilitate attendance at professional conferences. This allowance plays a pivotal role in fostering networking opportunities and enhancing professional development for both researchers and clinicians. Significantly, a recent analysis by Slido reveals that 54% of employees believe their managers need to improve their facilitation skills, emphasizing the necessity for effective meeting funding and management in achieving positive outcomes.
Furthermore, with 58% of virtual events hosting 300 or fewer live attendees, the understanding of the PMA full form becomes increasingly relevant in facilitating broader participation in meetings. Additionally, the concept of Supplemental PMA encompasses extra funding allocated for specific projects or initiatives, exemplifying the vital role that financial resources play in advancing research endeavors and career trajectories. A case analysis titled 'Employee Productivity and Meeting Attendance' demonstrates that allowing employees to skip unnecessary meetings can lead to improved productivity, with 84% of respondents agreeing they would be more productive if they could avoid such meetings.
By investing in such funding opportunities, institutions can significantly contribute to the professional growth of their researchers and clinicians, ultimately enriching the academic landscape.
PMA in Scientific Research: The Case of Phorbol Esters
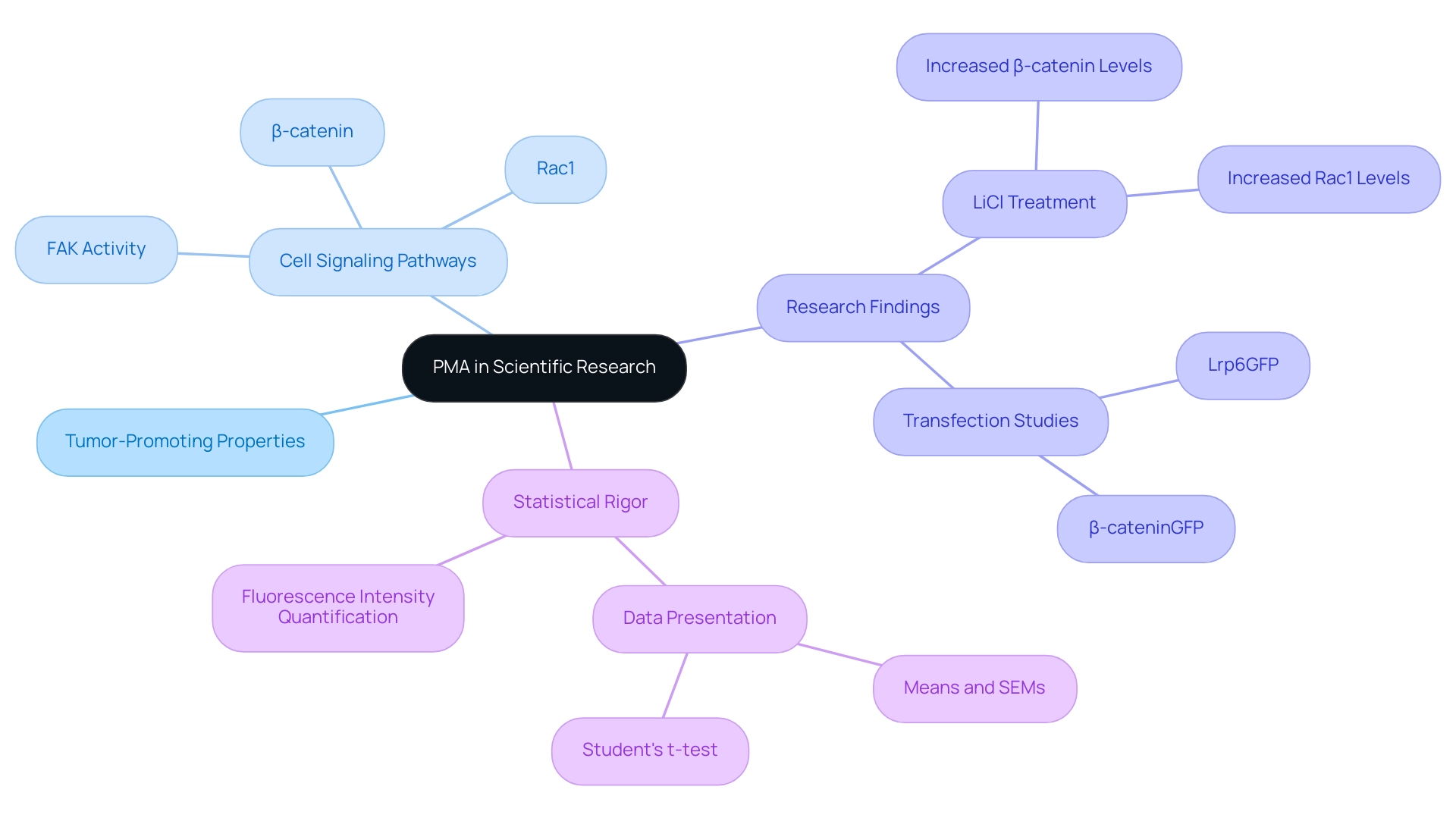
In the field of scientific research, the compound known as PMA, or pma full form Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, emerges as a critical compound, recognized for its potent tumor-promoting properties. The pma full form acts as an important instrument in various biological research, especially those centered on cell signaling pathways and cancer biology. Its application has been instrumental in elucidating the mechanisms underlying tumor development.
Recent research demonstrates that treatment with PMA influences signaling pathways relevant to cancer, including the activation of β-catenin and Rac1 in cellular models. Notably, treatment of 3T3 cells with Lithium Chloride (LiCl) has been shown to increase β-catenin and Rac1 levels, highlighting the interconnectedness of these pathways. Tejeda-Munoz notes,
The results imply that FAK activity influences Wnt signaling and dorsal development; the molecular mechanism of this interaction is unknown but deserving of future research.
This underscores the ongoing exploration of the pma full form's role in understanding complex biological interactions. Furthermore, the statistical rigor in related studies, where data were expressed as means and SEMs with analysis performed using the Student's t-test, enhances the credibility of findings in this area. As research advances, the PMA full form continues to be a vital component in developing therapeutic strategies, underscoring its significance in both medical knowledge and practical applications in cancer research.
Regulatory Framework: The Role of PMA in Premarket Approval
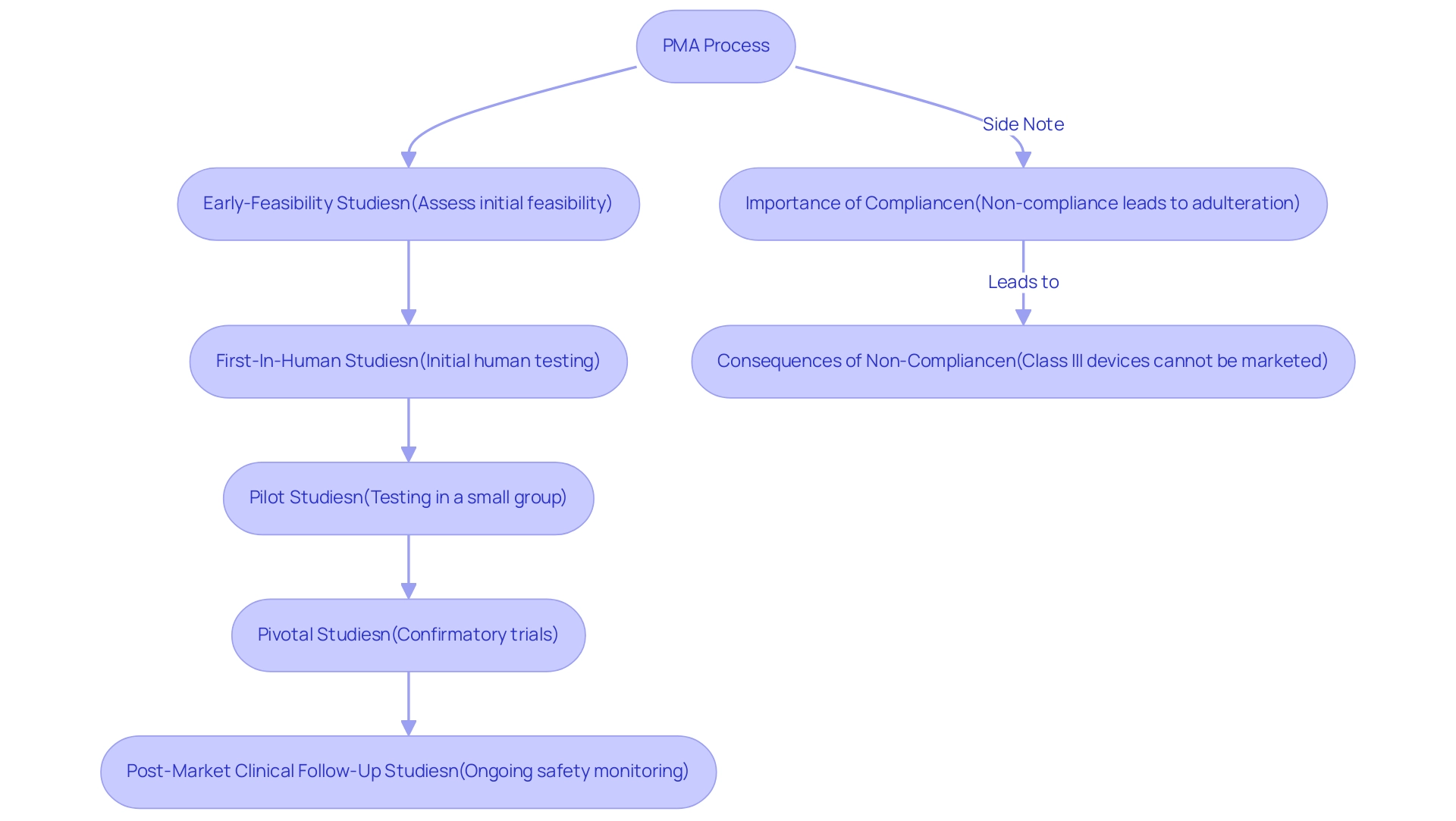
The PMA full form refers to the Premarket Approval system, which serves as a crucial regulatory framework established by the FDA to assess the safety and effectiveness of new medical devices and pharmaceuticals prior to market entry. This comprehensive procedure mandates rigorous clinical trials and meticulous data analysis, ensuring compliance with stringent guidelines that safeguard consumer health. As a result, only those products that meet these high standards are permitted to reach the market.
Significantly, 90 percent of industry leaders prioritize US regulatory approval over the EU, highlighting the importance of the PMA full form procedure in the broader regulatory landscape. For stakeholders within the medical field, particularly Directors of Clinical Research, a thorough understanding of the PMA full form procedure is imperative, as it not only influences patient safety but also fosters the advancement of innovative medical technologies. Furthermore, Class III products that do not meet the PMA full form requirements are regarded as adulterated and cannot be marketed, highlighting the severe consequences of non-compliance.
The procedure also emphasizes the need for ongoing education among physicians regarding potential flaws in the medical device approval pathway, as evidenced by a case study that revealed 67 percent of FDA 510(k) submissions resulted in requests for additional information, leading to avoidable delays and increased costs. In this context, leveraging the expertise and customized approach of bioaccess®, particularly in conducting:
- Early-Feasibility Studies
- First-In-Human Studies
- Pilot Studies
- Pivotal Studies
- Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies
can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of navigating the PMA process, which includes understanding the PMA full form, ultimately aligning with the specific needs of your clinical trials.
Conclusion
The exploration of PMA reveals its critical importance across various sectors, particularly within healthcare and academic settings. In the medical field, Premarket Approval serves as a stringent safeguard, ensuring that medical devices and pharmaceuticals meet essential safety and efficacy standards before being introduced to the market. The data illustrates a clear distinction between devices approved through the PMA process and those through the 510(k) pathway, underscoring the superior safety profile associated with PMA-approved products. This regulatory framework not only protects public health but also fosters innovation by encouraging thorough assessments that advance medical technology.
Beyond healthcare, the acronym PMA encompasses diverse meanings, such as Professional Meeting Allowance, which plays an essential role in facilitating professional development and collaboration within academic and research environments. The allocation of funding for professional meetings enhances networking opportunities and ultimately contributes to the growth of knowledge and expertise among professionals. This multifaceted nature of PMA emphasizes the necessity of context in understanding its implications across different domains.
As the landscape of PMA continues to evolve, it remains imperative for professionals to stay informed about the regulatory processes and funding opportunities available to them. By leveraging expertise in navigating these frameworks, stakeholders can enhance their operational capabilities and ensure compliance with industry standards. Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of PMA's diverse applications is not only beneficial for individual career advancement but also essential for fostering innovation and safety in the industries it touches.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does PMA stand for in the healthcare industry?
In the healthcare industry, PMA stands for Premarket Approval, which is a strict procedure mandated by the FDA to ensure that medical products and pharmaceuticals are safe and effective before they are launched in the market.
What is the significance of the PMA process?
The PMA process is vital as it requires substantial evidence demonstrating that a product's health benefits outweigh any potential risks, based on laboratory investigations, human trials, and nonclinical studies.
How does the recall rate differ between PMA and 510(k) approved products?
From 2002 to 2021, products approved through the 510(k) pathway had a recall rate of 11.6%, while those approved through PMA had a significantly lower recall rate of 2.3%. This indicates that PMA-approved products are less likely to be recalled.
What are some other meanings of PMA outside the healthcare context?
Beyond healthcare, PMA can also refer to Professional Meeting Allowance in academic contexts and Private Manager Assessment in engineering and management sectors.
Why is understanding regulatory organizations important in the PMA process?
Understanding regulatory organizations like INVIMA and utilizing expert knowledge is crucial for navigating the complexities of medical product approval and enhancing the safety and effectiveness of new healthcare technologies.
What types of clinical trials does bioaccess® manage?
Bioaccess® manages various types of clinical trials, including Early-Feasibility Trials (EFS), First-In-Human Trials (FIH), Pilot Trials, Pivotal Trials, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Trials (PMCF).
What challenges does the FDA face regarding clinical investigations?
The FDA has noted ongoing challenges related to research designs and data evaluations in clinical investigations, highlighting the need for researchers to consult relevant FDA guidance documents to navigate the approval process effectively.
How has the percentage of devices approved by the 510(k) pathway changed from 2002 to 2021?
The percentage of devices approved by the 510(k) pathway has decreased over this period, indicating a shift in regulatory practices and enhancing the importance of the PMA process.




