Overview
Usability in medical devices refers to the ease with which healthcare professionals and patients can use these devices effectively and safely, significantly impacting patient safety and healthcare efficiency. The article emphasizes that high usability is essential for minimizing errors, improving clinical workflows, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, underlining the critical role of user-centered design in enhancing both device effectiveness and patient care.
Introduction
The usability of medical devices stands at the intersection of technology and patient care, playing a crucial role in ensuring that healthcare professionals and patients can effectively and safely utilize these tools. As the healthcare landscape evolves with the integration of advanced technologies, the significance of usability becomes increasingly evident. High usability not only enhances the efficiency of medical procedures and the accuracy of diagnoses but also directly impacts patient safety—an aspect underscored by alarming statistics regarding cybersecurity threats in the sector.
With regulatory bodies emphasizing compliance with established standards, manufacturers are tasked with navigating a complex landscape that prioritizes user-friendly designs. This article delves into the multifaceted dimensions of medical device usability, exploring its:
- Definition
- Regulatory frameworks
- Testing methodologies
- Vital role of human factors in enhancing user experiences
All while highlighting the profound impact on patient safety and device effectiveness.
Defining Usability in Medical Devices
The usability of medical devices in healthcare is defined as the ease with which healthcare professionals and patients can effectively and safely utilize a device to achieve its intended outcomes. This concept encompasses multiple factors, including design, functionality, and interface. The importance of high usability medical devices cannot be overstated; their user-friendliness directly affects the efficiency of healthcare procedures, the accuracy of diagnoses, and, ultimately, patient safety.
According to recent findings, nearly 50% of the 40 million healthcare records compromised in the first eight months of 2023 stemmed from attacks on third-party business associates, highlighting the need for strong design principles that enhance security and minimize user errors. A well-designed healthcare tool improves the usability of medical devices, reducing the risk of mistakes and enabling providers to offer optimal care without unnecessary complications. As the sector adjusts to the growing incorporation of intelligent, interconnected tools, the emphasis on usability medical devices becomes crucial in guaranteeing patient safety and building confidence in healthcare technology.
The recent case study on cybersecurity in healthcare equipment emphasizes this point; with the FDA requiring the incorporation of cybersecurity in the evaluation of internet-connected tools, producers must prioritize user-friendliness to safeguard patient information and improve safety. Moreover, a recent Ponemon report indicated that 64% of healthcare IT experts are worried about their susceptibility to ransomware attacks, emphasizing the importance of the usability of medical devices in equipment design. Furthermore, updates from AlphaSense emphasize the changing environment of healthcare tools, urging participants to remain knowledgeable and adjust to the newest developments in functionality and safety.
Regulatory Standards and Guidelines for Medical Device Usability
Regulatory standards are essential for ensuring the usability of medical devices, with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 62366 providing a comprehensive framework for user-centered design. This standard emphasizes a systematic approach to identifying and mitigating risks related to usability medical devices throughout the product lifecycle. Recent FDA guidelines further reinforce the importance of demonstrating compliance with the usability medical devices requirements during the premarket submission process, making it crucial for manufacturers to align with these standards.
Notably, the recent addition of ISO 17665:2024 to the FDA consensus list for sterilization processes underscores the evolving nature of regulatory standards that manufacturers must navigate. Furthermore, the transitional provisions for products without a therapeutic purpose have been amended to align with the Devices Regulation, impacting market entry conditions for certain products. Compliance not only enhances equipment safety but also fosters user confidence, which is vital for successful adoption in clinical environments.
As pointed out by a leading regulatory specialist, Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs at Mahu Pharma, 'The shift toward purely software-based healthcare solutions amplifies the importance of understanding ISO and IEC regulations.' The emphasis on usability medical devices is becoming progressively essential as the environment of healthcare tools changes, thus requiring compliance with existing regulatory standards to guarantee both safety and effectiveness. Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Regulatory Affairs for Healthcare Products and In Vitro Diagnostics, highlights that grasping regulatory compliance can aid in overcoming the challenges encountered by healthcare product startups, including competition and recruitment concerns.
In particular, our services include:
- Feasibility and selection of research sites
- Obtaining import permits
- Comprehensive reporting on study status, inventory, and adverse events
A recent case study highlights how these amendments affect compliance strategies and market access, illustrating the practical implications of regulatory changes on usability medical devices. For more information or to discuss how we can assist your organization in navigating these complexities, please BOOK A MEETING.
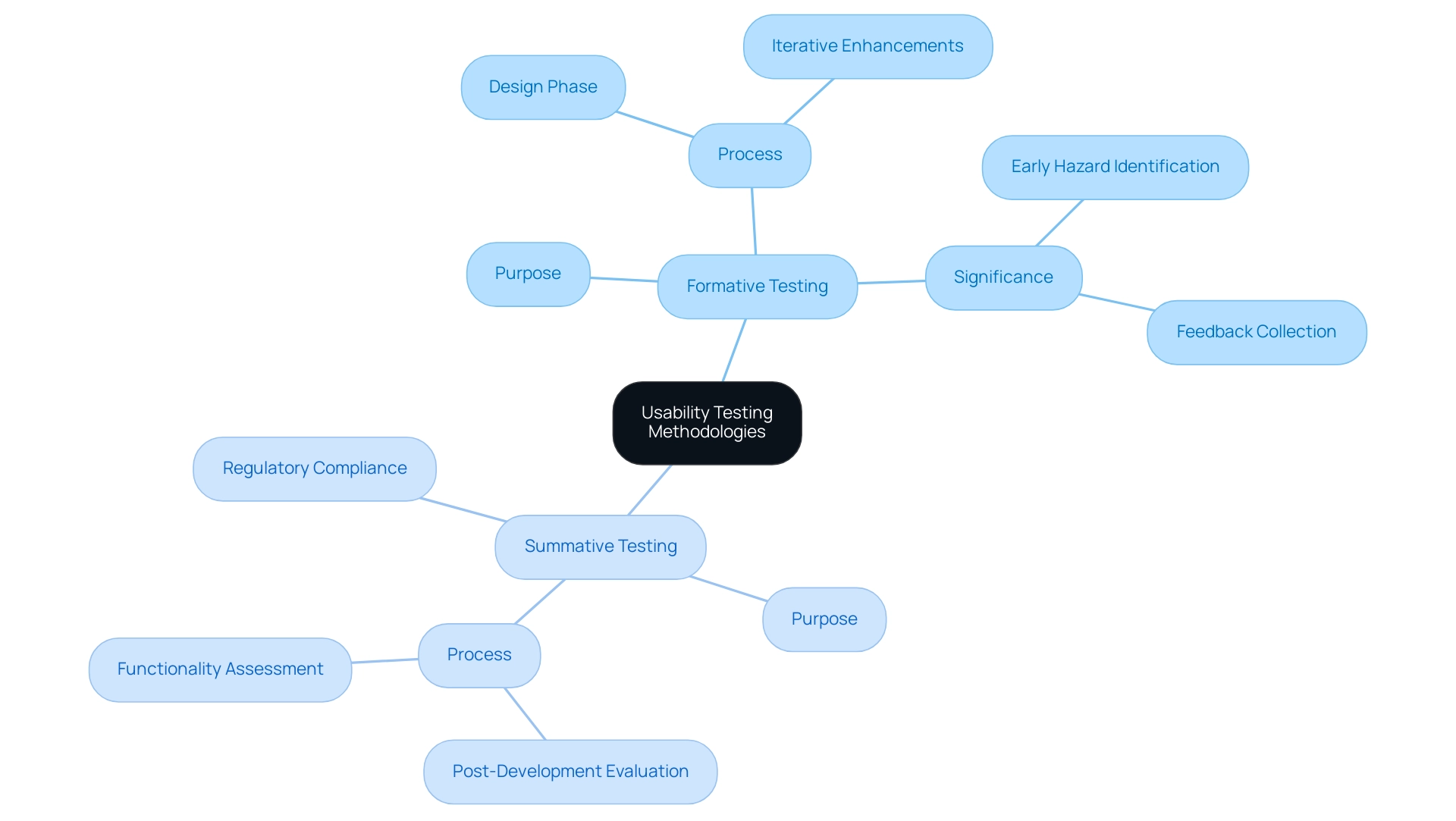
Usability Testing Methodologies: Formative vs. Summative
Usability testing for medical devices is fundamentally divided into two primary methodologies: formative testing and summative testing, both of which are essential for evaluating the usability of medical devices.
-
Formative testing is carried out during the design phase, allowing developers to collect valuable feedback and make iterative enhancements based on interactions. This methodology is especially crucial as it reveals functional issues early, allowing for modifications that improve the experience and reduce potential risks.
In fact, the FDA emphasizes that
formative evaluation can reveal previously unrecognized use-related hazards and use errors, and help identify new critical tasks.
-
Summative testing occurs after the product has been fully developed. Its main goal is to evaluate the overall functionality and efficiency of the equipment, ensuring that it complies with regulatory standards and meets expectations of those who utilize it.
A key goal of summative evaluation is to demonstrate that the apparatus is safe to use regarding the user interface. Recent studies suggest that user evaluation is essential for the market entry of health products, which underscores the importance of usability in medical devices alongside both approaches. Furthermore, a case study titled 'Value-of-Information Analysis in Usability Testing of Healthcare Products' emphasizes that design problems are the primary reason for recalls.
This study advocates for the application of value-of-information analysis, which quantifies risks and informs sample size adjustments in usability tests. By implementing this analysis, manufacturers can enhance patient safety and facilitate timely access to new technologies. By utilizing both formative and summative assessments, manufacturers can ensure that the usability of medical devices meets regulatory requirements while also providing safer and more effective healthcare solutions.
The Role of Human Factors in Enhancing Usability
Human factors engineering is an essential field that emphasizes the usability of medical devices by examining how individuals interact with medical instruments, taking into account their needs, preferences, and constraints. By adhering to the principles of human factors, designers are able to create usability medical devices that are intuitive and user-friendly, significantly reducing the likelihood of errors. For example, ergonomic design strategies can alleviate physical strain on individuals, while clear and concise labeling enhances understanding and accessibility.
According to recent advancements, the average coverage probabilities for various design methods—naive, generalized theory (GT), and double-deflation—were reported at 17.9%, 31.5%, and 33.7%, respectively, underscoring the importance of careful design choices. A pertinent case study titled 'Establishing a Human Factors Design Process' illustrates the necessity of developing a human factors plan early in the engineering process to ensure the usability of medical devices. This proactive strategy encompasses:
- Participant research
- Assessment
- Confirmation
Ultimately resulting in an enhanced experience and increased marketability of healthcare products.
As regulations like the Medical Equipment Regulation (MDR) 2017/745 emphasize the incorporation of Risk Management into product development, prioritizing human factors becomes crucial for ensuring the usability of medical devices, which helps in making healthcare products not only functional but also enhancing safety and efficiency in clinical practice. As noted by industry experts, including James Lewis, 'the focus on usability medical devices is paramount,' paving the way for innovative designs that meet the evolving needs of healthcare professionals and patients alike. Moreover, data modeling and analysis employ top-down and bottom-up strategies, along with company shares evaluation models, to ensure precision in market insights, further emphasizing the importance of human factors in healthcare product design.
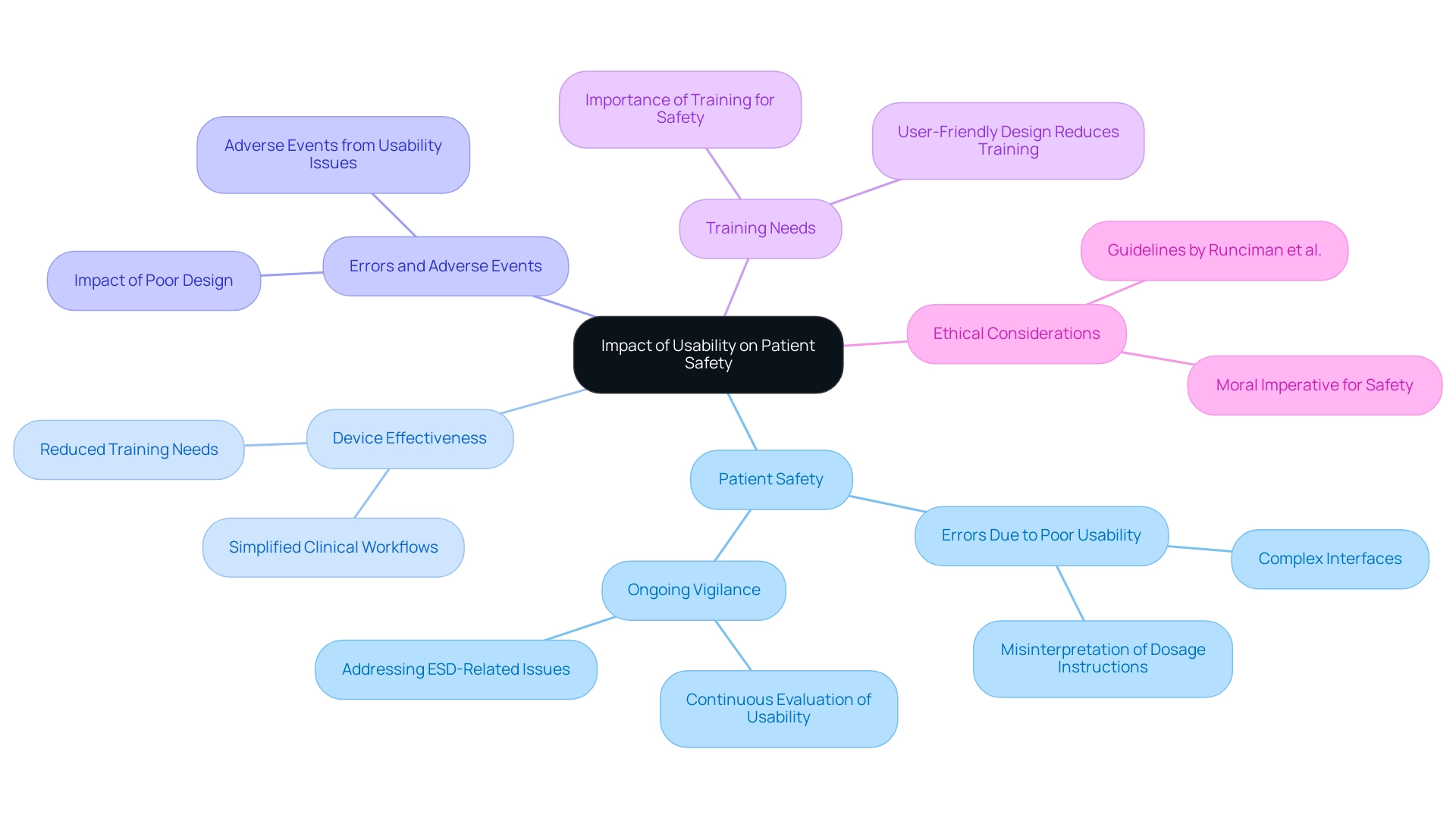
Impact of Usability on Patient Safety and Device Effectiveness
The functionality of usability medical devices greatly impacts both patient safety and the overall efficiency of these tools. Poorly designed usability medical devices can lead to errors, which may result in adverse events that jeopardize patient care. For instance, a complex interface may cause misinterpretation of dosage instructions, posing a serious risk to patient safety.
Recent studies indicate that only 0.2% of all reported incidents were attributed to computer-related issues, suggesting that while technology plays a role, the usability of medical devices remains a paramount concern in clinical settings. As emphasized by Farah Magrabi,
Evidence-based user interface design must focus on the safe entry and retrieval of clinical information and support users in detecting and correcting errors and malfunctions.
The significance of user-friendliness is further emphasized by the guide from Runciman WB, Merry A, and Walton M, which highlights the ethical imperative of ensuring safety in healthcare practices.
On the other hand, tools that emphasize the usability of medical devices can simplify clinical workflows, reduce training needs, and ultimately improve patient outcomes. The implications of user-friendliness extend beyond regulatory compliance; they represent a moral imperative to safeguard patients and ensure the delivery of effective healthcare services. Continuous focus on the usability of medical devices is essential, especially considering recent reports emphasizing that problems associated with electronic systems design (ESD) can still jeopardize patient safety, highlighting the need for ongoing vigilance and enhancement in the effectiveness of these devices.
Furthermore, the necessity for effective evaluation and management of digital resources, as illustrated by the case study on website evaluation protocols, reflects the broader challenges of usability in healthcare settings.
Conclusion
Usability in medical devices is crucial for enhancing patient safety and ensuring effective healthcare delivery. It encompasses design, functionality, and user interface, all of which significantly influence the efficiency of medical procedures and diagnostic accuracy. With increasing cybersecurity threats, robust usability designs are essential to minimize user errors and protect sensitive patient information.
Manufacturers must adhere to regulatory frameworks like IEC 62366 and FDA guidelines to ensure compliance and build user confidence. Employing usability testing methodologies, including formative and summative testing, is vital for identifying issues throughout the device lifecycle, leading to safer healthcare solutions.
The integration of human factors engineering is also essential for creating intuitive and user-friendly devices, reducing the likelihood of errors. The consequences of poor usability can jeopardize patient safety, making it imperative to prioritize usability as both a regulatory necessity and a moral obligation.
In conclusion, a steadfast commitment to usability in medical device design is essential for navigating the complexities of modern healthcare technology. By focusing on regulatory compliance, effective testing methodologies, and human factors, stakeholders can ensure that medical devices are functional, safe, and effective. This dedication to usability will foster trust and enhance the quality of patient care in an evolving healthcare landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the definition of usability in medical devices?
The usability of medical devices in healthcare is defined as the ease with which healthcare professionals and patients can effectively and safely utilize a device to achieve its intended outcomes, encompassing factors such as design, functionality, and interface.
Why is high usability important for medical devices?
High usability is crucial because it directly affects the efficiency of healthcare procedures, the accuracy of diagnoses, and ultimately, patient safety. User-friendly devices reduce the risk of mistakes and complications, enabling providers to offer optimal care.
What recent findings highlight the importance of usability and security in medical devices?
Nearly 50% of the 40 million healthcare records compromised in the first eight months of 2023 resulted from attacks on third-party business associates, underscoring the need for strong design principles that enhance security and minimize user errors.
What role do regulatory standards play in ensuring the usability of medical devices?
Regulatory standards, such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 62366, provide a framework for user-centered design, emphasizing a systematic approach to identifying and mitigating usability risks throughout the product lifecycle.
How do recent FDA guidelines affect manufacturers of medical devices?
Recent FDA guidelines require manufacturers to demonstrate compliance with usability requirements during the premarket submission process, making it essential for them to align with these standards to enhance safety and foster user confidence.
What is the significance of the addition of ISO 17665:2024 to the FDA consensus list?
The addition of ISO 17665:2024 underscores the evolving nature of regulatory standards related to sterilization processes, which manufacturers must navigate to ensure compliance and market entry.
How can understanding regulatory compliance benefit healthcare product startups?
Grasping regulatory compliance can help healthcare product startups overcome challenges such as competition and recruitment concerns, facilitating successful adoption in clinical environments.
What services are offered to assist organizations in navigating regulatory complexities?
Services include feasibility and selection of research sites, obtaining import permits, and comprehensive reporting on study status, inventory, and adverse events.




