Overview
This article examines best practices for designing clinical trials that effectively integrate wearable devices in Colombia, underscoring the critical need for technological integration to enhance patient engagement and data collection. It highlights key advantages, including:
- Improved data accuracy
- Cost savings
- Regulatory compliance
Furthermore, it emphasizes the necessity of user-friendly equipment and comprehensive training for participants, which are essential for maximizing trial success. By addressing these factors, the article positions itself as a vital resource for clinical researchers navigating the Medtech landscape.
Introduction
As wearable devices revolutionize the healthcare landscape, their integration into clinical trials is fundamentally reshaping how researchers collect and analyze data. These innovative tools, from smartwatches to specialized medical sensors, facilitate continuous monitoring of participants' health metrics, providing a wealth of real-time information that traditional methods cannot match.
Studies show that wearables enhance patient engagement and adherence due to the immediate feedback they offer, significantly increasing the potential for improved trial outcomes. However, researchers must navigate the regulatory landscape, ensure data privacy, and overcome technical challenges, which remain critical considerations.
This article explores the transformative role of wearable technology in clinical trials, examining its advantages, best practices for integration, and future trends that promise to elevate its impact on patient care and research efficacy.
The Transformative Role of Wearable Devices in Clinical Trials
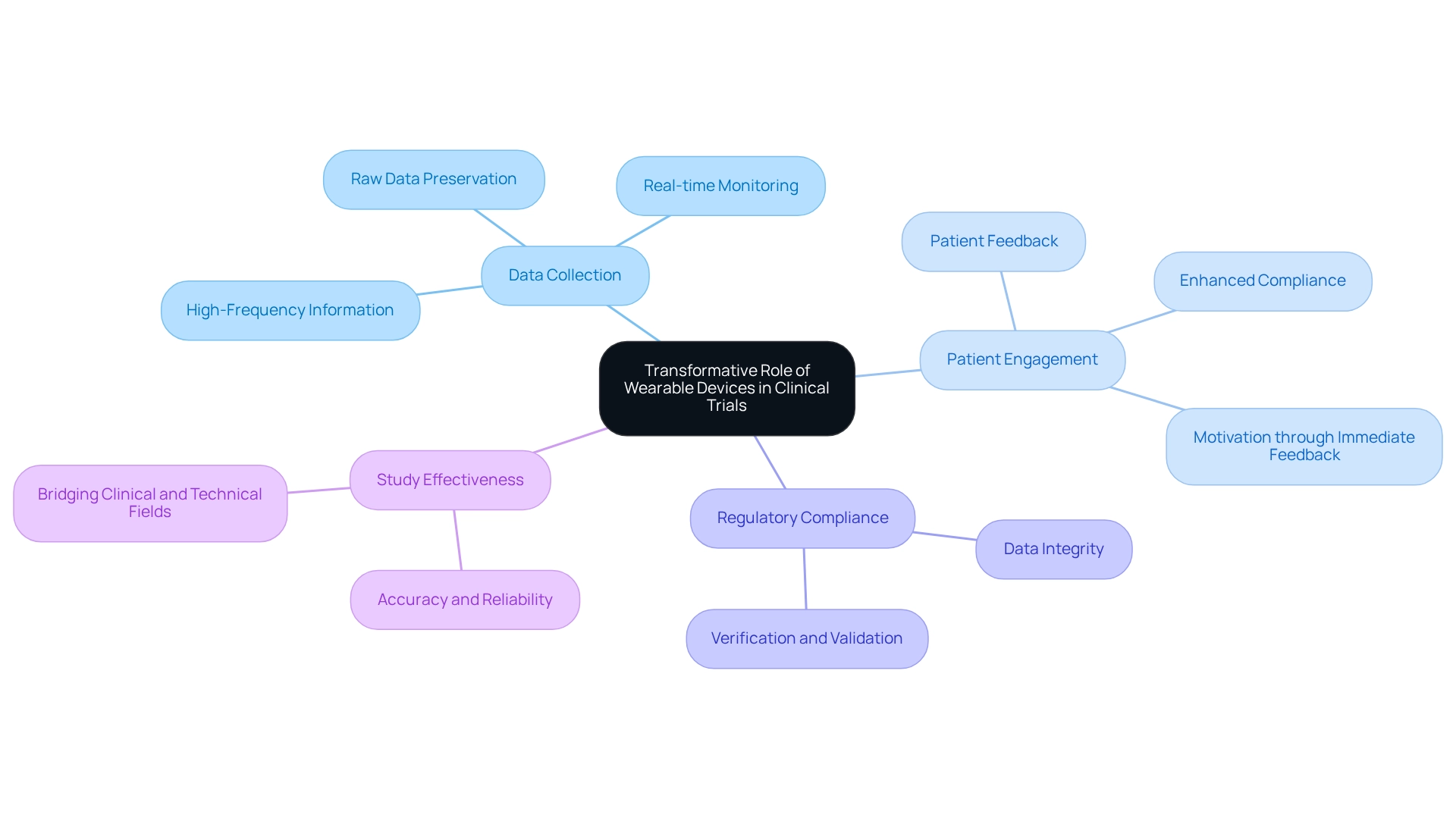
The landscape of clinical trials has fundamentally transformed with the integration of wearable devices in Colombia, facilitating continuous, real-time monitoring of participants' health metrics. This innovative approach involves employing devices such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and specialized medical sensors, allowing researchers to collect extensive information that surpasses the limitations of conventional clinical environments. Such an evolution not only enhances the quality of data collected but also fosters a more patient-centric approach to research in the design of trials for wearable devices in Colombia.
Significant studies, including the Datenspende study and the Apple Heart Study, have underscored the utility of these devices in health research. Particularly in the context of designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia, these studies highlight the capacity of wearable technology to enhance patient involvement and compliance with study protocols. By providing participants with immediate feedback on their health, researchers can foster greater compliance and motivation, ultimately leading to more reliable outcomes.
Moreover, the preservation of raw data collected from these devices is crucial for maximizing the insights gained during clinical development. This high-frequency information serves as a foundation for deriving digital clinical measures, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements concerning information integrity, verification, and validation. Consequently, researchers can adopt improved health metrics that accurately reflect real-world conditions.
The significance of retaining unprocessed information is further emphasized by its role in aiding regulatory compliance and enhancing the overall quality of clinical studies.
Recent advancements in portable technology have further augmented their application in clinical studies, particularly in the context of designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia, enabling more sophisticated information gathering and analysis. A literature search utilizing databases such as PubMed, Ovid, Web of Science, and CINAHL, alongside manual reviews of reference lists, reveals that a notable majority of studies (58.1%) identify precision and dependability as key strengths of portable devices, highlighting their impact on clinical study information gathering and overall study effectiveness. Christine Guo, Chief Scientific Officer, states, 'By connecting clinical and technical fields, we can utilize information and technology to enhance individuals' health,' thereby emphasizing the potential of these devices to significantly improve health outcomes and bridge the gap between clinical research and patient care.
Advantages of Integrating Wearable Technology in Clinical Research
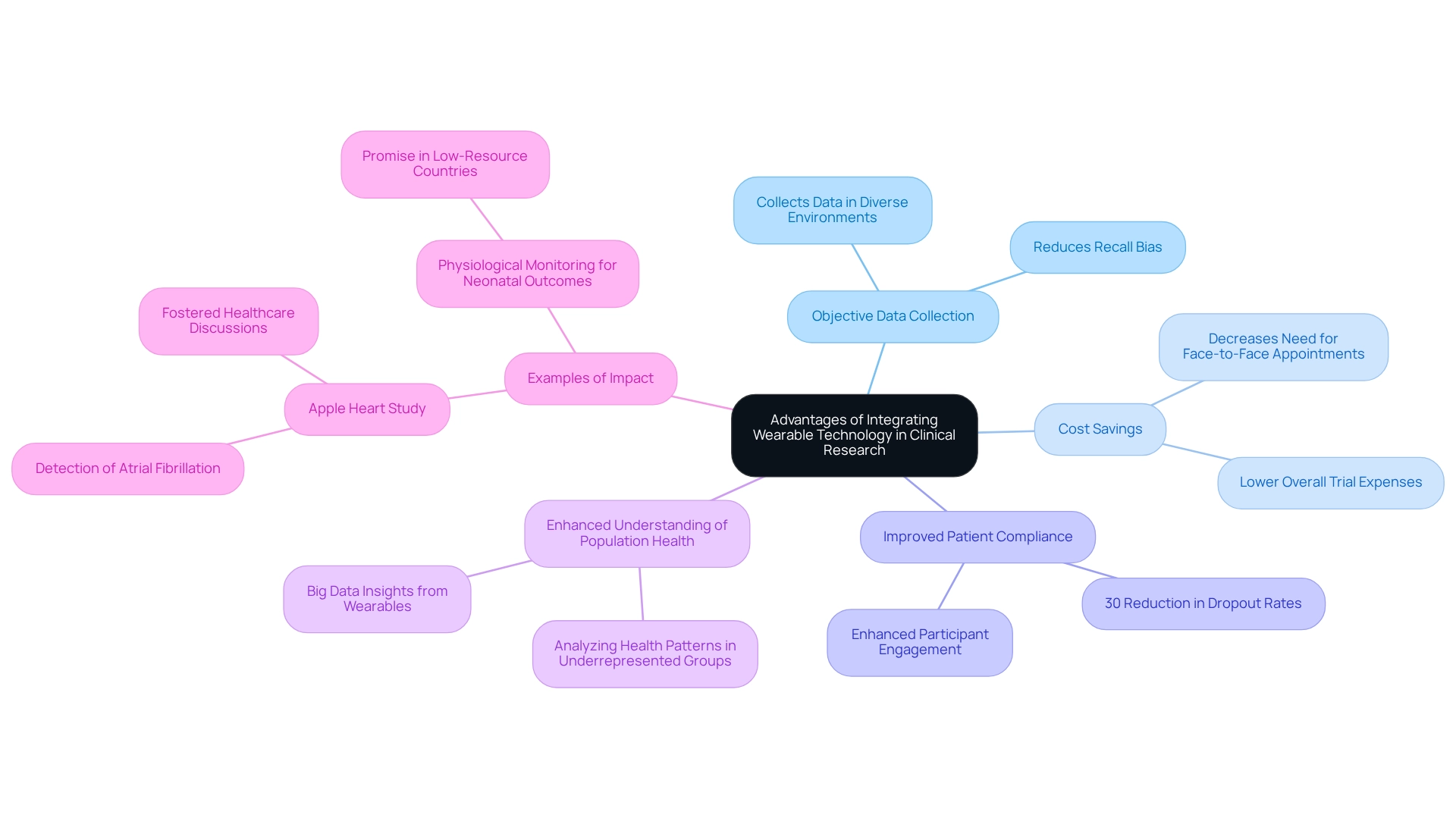
Designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia integrates advanced technology into clinical research, presenting numerous benefits that can significantly enhance the trial process. A primary advantage lies in the ability to collect objective information, effectively reducing recall bias often associated with self-reported measures. This objective data collection is crucial across various settings, facilitating more accurate evaluations of health outcomes and potentially decreasing skewed data, thereby improving the reliability of conclusions.
Moreover, these devices can lead to considerable cost savings by diminishing the necessity for frequent face-to-face appointments. This optimization of the testing process not only lowers expenses but also boosts patient compliance. For example, a recent study indicated that the implementation of devices in a cardiovascular trial achieved an impressive 30% reduction in patient dropout rates, highlighting their effectiveness in sustaining participant engagement.
The potential of such technology transcends individual trials; it also enhances our understanding of population health dynamics. Recent discussions have underscored that designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia can revolutionize how researchers analyze health patterns, especially in underrepresented groups and low-resource environments. This potential underscores the urgent need for future research aimed at exploring the usability of these devices in such contexts, ensuring that the benefits of this technology are accessible to all.
A prominent illustration is the Apple Heart Study, which showcased the capacity of these devices in detecting atrial fibrillation (AF). This study not only demonstrated how devices can assist in health monitoring but also sparked further dialogue among healthcare providers, researchers, and the media regarding their implications in healthcare.
Furthermore, as Xu et al. noted, physiological monitoring through devices holds significant promise for improving neonatal outcomes in low- and middle-resource countries. This observation highlights the potential benefits of smart technology across diverse settings and emphasizes the importance of inclusivity in research related to such innovations.
In summary, the integration of these tools into clinical studies enhances data accuracy and patient engagement while providing substantial cost savings. This establishes them as a vital resource in the evolving landscape of clinical evaluations.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape for Wearable Devices
Designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia necessitates a thorough understanding of the regulatory environment governing wearable technology, which is critical for clinical researchers. Adherence to INVIMA regulations is non-negotiable, as these guidelines govern the use of medical equipment in clinical studies. Researchers must validate devices for their intended use and rigorously comply with privacy regulations.
At bioaccess®, we prioritize information security and client trust, ensuring that robust data protection measures are implemented throughout the clinical research process. Early collaboration with regulatory agencies during the study design phase is essential for clarifying requirements and expediting approvals. For example, a recent study that adopted a proactive approach in its regulatory interactions experienced a markedly smoother approval process, allowing the study to begin ahead of schedule.
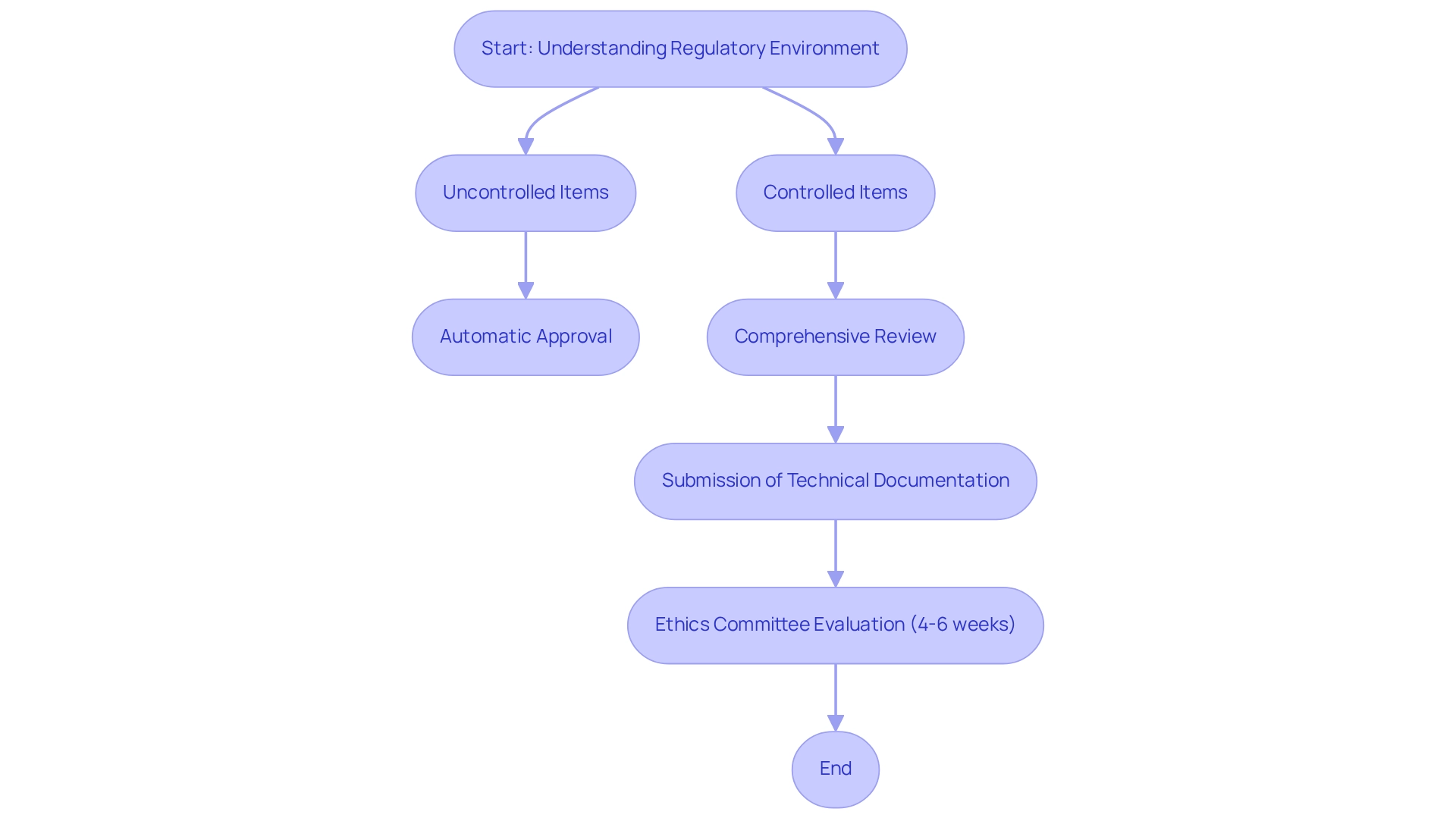
The timeline for ethics committee evaluation of clinical study documentation typically spans 4 to 6 weeks, underscoring the importance of meticulous preparation. Furthermore, INVIMA has set specific requirements for approving first-in-human medical equipment clinical trials, focusing on safety, scientific validity, and ethical conduct.
In Colombia, the regulatory pathway for medical equipment comprises two distinct routes:
- Uncontrolled items can receive automatic approval.
- Controlled items require a comprehensive review of registration documentation by INVIMA.
This process demands the submission of detailed technical documentation, including evidence of quality management and clinical data, all of which must be provided in Spanish to comply with regulatory standards. As Julio G. Martinez-Clark observes, "Looking for a reliable Contract Research Organization (CRO) in Latin America? Explore Colombia's INVIMA criteria for the authorization of first-in-human medical equipment clinical studies."
Class I and II in vitro diagnostic (IVD) registration renewals are now processed automatically, although additional information may still be requested. Understanding these nuances can significantly enhance the efficiency of the procedure. Effective navigation of INVIMA regulations has been demonstrated in various case studies, illustrating the potential for prompt and compliant clinical research when designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia.
At bioaccess®, we are dedicated to addressing any client concerns regarding data protection and compliance, ensuring transparency and adherence to applicable laws. Should you have any inquiries or concerns about the processing of your information, please reach out to our Grievance Officer at IMH ASSETS CORP (doing business as "bioaccess®"), 1200 Brickell Avenue, Suite 1950 #1034, email: info@bioaccessla.com. We will respond to your concerns in accordance with applicable law.
Our services encompass preparation, project oversight, and supervision, ensuring a comprehensive approach to advancing medical equipment evaluations.
Best Practices for Optimizing Wearable Device Integration in Clinical Trials
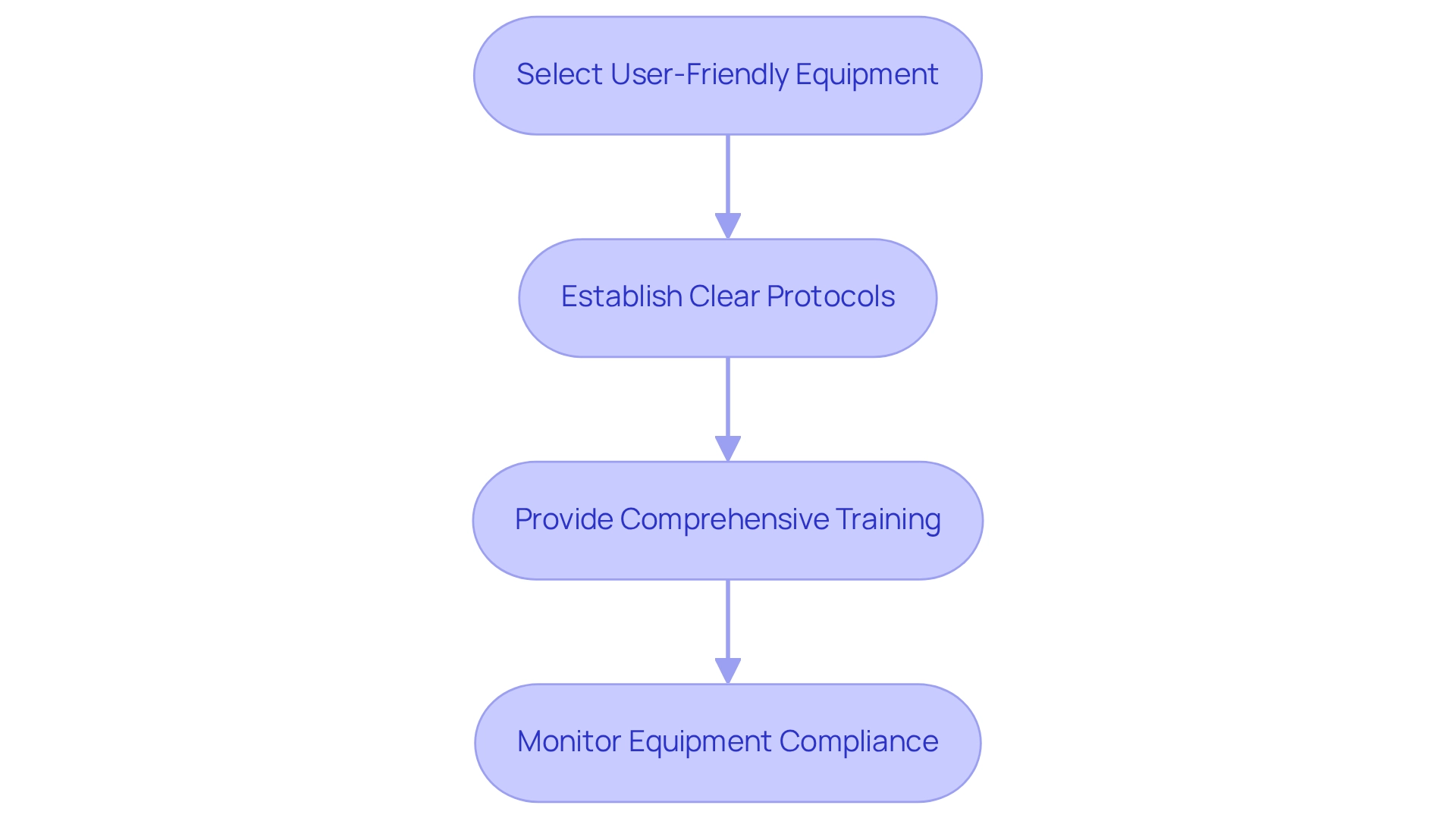
To effectively incorporate personal technology into clinical trials, researchers should adhere to several best practices:
-
Select User-Friendly Equipment: Opt for tools that are intuitive and easy for participants to operate, thereby minimizing the learning curve and enhancing user engagement. Designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia is essential, as these devices have the potential to assist cancer survivors in increasing and maintaining their activity levels, underscoring their significance in clinical trials.
-
Establish Clear Protocols: Develop detailed procedures for information gathering and management to uphold data integrity throughout the study. This includes specifying how information will be captured, stored, and analyzed. Quanticate’s Clinical Data Management group is engaged in designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia, focusing on integrating wearable technology into clinical trials for precise information gathering and analysis, highlighting the necessity for organized protocols.
-
Provide Comprehensive Training: Ensure that both participants and site staff receive thorough training on the use of wearable technology. This training should encompass equipment operation, troubleshooting, and information reporting to enhance compliance and minimize errors. Christine Guo, PhD, advises that researchers prioritize platforms emphasizing stability and backward compatibility over frequent updates, even if it necessitates delaying the adoption of the latest technology.
-
Monitor Equipment Compliance: Regularly assess equipment usage and adherence among participants, addressing any issues as they arise. For instance, a diabetes management study that implemented these best practices experienced an impressive 40% increase in compliance rates, demonstrating the effectiveness of a structured approach. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the acceptance of smart devices for remote patient monitoring, illustrating their essential role in contemporary healthcare and the importance of strategic planning, particularly in designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia for enhanced data collection.
By adhering to these recommendations, researchers can enhance the reliability of information gathered through smart technology, ultimately leading to more successful study outcomes and improved patient experiences.
Enhancing Patient Engagement Through Wearable Technology
Improving patient involvement is crucial for the success of designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia. These devices provide participants with real-time feedback on their health metrics, fostering a sense of ownership over their health data. This immediate feedback not only encourages adherence to study protocols but also keeps participants actively engaged throughout the research process.
For instance, studies involving portable heart monitors revealed that individuals who received regular updates on their health metrics were 50% more likely to complete the study compared to those who did not receive such feedback.
Furthermore, the integration of these devices has demonstrated promising outcomes in enhancing patient engagement levels. A case study examining the data abstraction process in a scoping review showed that a standardized data abstraction form was utilized to capture relevant information from 46 articles, including patient experiences with wearable technology. This collaborative approach enabled precise and uniform documentation of results, facilitating a more thorough examination of trends in patient involvement.
The significance of devices in motivating patients during studies cannot be overstated. Insights from experts suggest that the use of real-time feedback significantly boosts participant motivation, resulting in higher completion rates. In fact, data indicate that studies employing wearable technology can experience completion rates increase by up to 50%, underscoring the effectiveness of these tools in enhancing patient commitment.
Additionally, Volcansek et al. noted that 100% of participants regarded continuous glucose monitoring device usage as generally positive and beneficial, further highlighting the potential of such technology in improving patient engagement. However, it is essential to acknowledge that 32-42% of participants in a study expressed feeling 'unenthusiastic' about the application of AI in healthcare, emphasizing the need for effective communication and feedback in experimental settings.
As the landscape of clinical investigation continues to evolve, designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia to bolster patient involvement will be vital for the successful implementation of studies.
Challenges and Considerations in Wearable Device Trials
Designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia presents distinct challenges that researchers must navigate effectively. Central to these challenges are ensuring equipment reliability, managing privacy concerns, and maintaining participant compliance. Notably, 58.1% of studies have highlighted validation, accuracy, and clinical certification as strengths of affordable wearables; however, variability in performance can lead to inconsistent data collection, potentially compromising study outcomes.
To mitigate these risks, researchers should implement stringent testing procedures for equipment prior to the commencement of the experiment. This involves comprehensive assessments of device reliability and performance metrics to ensure consistency throughout the study. Moreover, establishing clear communication channels with participants is crucial; addressing concerns promptly can significantly enhance adherence and engagement.
The design of trials for wearable devices in Colombia underscores that data privacy remains a paramount concern. Researchers must prioritize the protection of sensitive information by developing and enforcing robust privacy protocols. bioaccess® is committed to fostering client trust by adhering to regulatory standards and employing secure information management practices.
Our grievance and information protection procedures are designed to address client concerns transparently, ensuring that any queries regarding processing are handled in accordance with applicable laws. For any inquiries or concerns about the processing of your information, you may contact our Grievance Officer at IMH ASSETS CORP (doing business as "bioaccess®"), located at 1200 Brickell Avenue, Suite 1950 #1034, or via email at info@bioaccessla.com.
A case study titled 'Challenges & Considerations for Wearables in Clinical Studies' discusses the complexities of data flow from devices to research databases, particularly in the context of designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia. It emphasizes the necessity for careful planning regarding data ownership and privacy, as well as the importance of regulatory compliance. Furthermore, future advancements in portable technology are anticipated to include improved metrics, battery life, connectivity, and security frameworks, all while maintaining patient privacy and regulatory balance. By proactively addressing these challenges, researchers can enhance the reliability and integrity of their trials, ultimately facilitating the successful advancement of technology in clinical research.
The expertise and tailored approach of bioaccess® aim to expedite the development of medical products for firms in the Medtech sector, focusing on Early-Feasibility Studies, First-In-Human Studies, Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies.
Future Trends in Wearable Technology for Clinical Research
The future of personal technology in clinical research is exceptionally promising, driven by significant advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies are poised to transform data analysis capabilities, enabling researchers to derive deeper insights from the extensive volumes of information gathered through smart gadgets. This enhanced analytical power can lead to more personalized treatment approaches, tailoring interventions to individual patient needs.
Furthermore, designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia is expected to incorporate devices with telehealth platforms, enabling remote patient monitoring and enhancing the accessibility of clinical trials to various populations. This is especially pertinent in Latin America, where bioaccess® provides accelerated medical instrument clinical study services, utilizing over 20 years of experience in managing Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF). The potential for personal technology to bridge gaps in healthcare delivery is substantial, particularly as fewer than 1 in 5 heart disease patients currently utilize such tools, presenting a significant opportunity to enhance patient engagement and data collection through these innovations.
As Muhammad Shaalan Beg from the Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology at UT Southwestern Medical Center states, 'So you want to use personal monitoring devices in your clinical trial? What do you need to know?' This emphasizes the significance of comprehending the incorporation of personal technology into clinical workflows to maximize its advantages in patient care.
As these trends continue to evolve, it is crucial for researchers to remain adaptable and open to incorporating new technologies into their study designs. The partnership between software developers and statisticians is essential, particularly in tackling challenges like information cleanup and interpretation. For instance, information gathered from fitness trackers frequently necessitates careful arrangement to remove duplicates and address time zone inconsistencies, as highlighted in a case study on information cleanup and interpretation.
This coordinated effort ensures that the information is stored in a usable format for efficient analysis.
Looking ahead, the influence of AI and machine learning on device analysis is anticipated to expand, with future trends suggesting a rise in the complexity of these technologies. Expert opinions indicate that the process of designing trials for wearable devices in Colombia will not only enhance data quality but also improve patient outcomes, ultimately transforming the landscape of clinical studies in Latin America. Furthermore, the success of these clinical studies contributes to local economies by creating jobs, fostering economic growth, and improving healthcare access, which underscores the importance of bioaccess®'s customized approach in navigating these trials.
Conclusion
The integration of wearable devices into clinical trials represents a pivotal evolution in the research landscape, significantly enhancing data collection and patient engagement in ways previously unimagined. By facilitating continuous, real-time monitoring of health metrics, wearables provide researchers with a wealth of objective data that far exceeds traditional methods. This transformation not only bolsters the reliability of findings but also nurtures a more patient-centric approach, as participants receive immediate feedback that encourages adherence to study protocols.
However, despite these numerous advantages, challenges such as regulatory compliance, data privacy, and device reliability must be navigated with care. Researchers are urged to adopt best practices, which include selecting user-friendly devices and establishing clear data management protocols. By proactively addressing these considerations, the potential for achieving successful outcomes in clinical trials is significantly enhanced.
Looking ahead, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are poised to further revolutionize the role of wearables in research. As these technologies refine data analysis capabilities, they will enable more personalized treatment approaches and expand the accessibility of clinical trials. The collaboration between technology and healthcare professionals will be crucial in maximizing the benefits of wearable devices, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and a more efficient research process.
In conclusion, the transformative impact of wearable technology in clinical trials is profound, paving the way for more accurate data collection and enhanced patient engagement. As the clinical research landscape continues to evolve, leveraging these innovative tools will be essential for advancing healthcare solutions and enhancing the overall efficacy of clinical trials.
Frequently Asked Questions
How have wearable devices transformed clinical trials in Colombia?
Wearable devices have facilitated continuous, real-time monitoring of participants' health metrics, allowing researchers to collect extensive data beyond conventional clinical environments. This evolution enhances data quality and promotes a patient-centric approach to research.
What types of devices are used in clinical trials for health monitoring?
Devices such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and specialized medical sensors are employed to monitor health metrics in clinical trials.
What are some significant studies that demonstrate the utility of wearable devices in health research?
Significant studies include the Datenspende study and the Apple Heart Study, which highlight the capacity of wearable technology to enhance patient involvement and compliance with study protocols.
How do wearable devices improve patient compliance in clinical trials?
By providing participants with immediate feedback on their health, wearable devices foster greater compliance and motivation, leading to more reliable study outcomes.
Why is the preservation of raw data from wearable devices important?
Preserving raw data is crucial for maximizing insights during clinical development and ensures adherence to regulatory requirements regarding information integrity, verification, and validation.
What advantages do portable devices offer in clinical studies?
Portable devices provide objective data collection, reducing recall bias, and can lead to cost savings by decreasing the need for frequent face-to-face appointments, thereby enhancing patient engagement.
How have wearable devices impacted patient dropout rates in clinical trials?
The implementation of wearable devices in a cardiovascular trial achieved a 30% reduction in patient dropout rates, highlighting their effectiveness in maintaining participant engagement.
What is the broader potential of wearable devices in health research?
They can revolutionize the analysis of health patterns, especially in underrepresented groups and low-resource environments, emphasizing the need for future research to explore their usability in diverse contexts.
Can you provide an example of a study that showcased the health monitoring capabilities of wearable devices?
The Apple Heart Study demonstrated the ability of wearable devices to detect atrial fibrillation (AF) and sparked discussions among healthcare providers and researchers regarding their implications in healthcare.
What promise do physiological monitoring devices hold for neonatal outcomes?
Physiological monitoring through devices holds significant promise for improving neonatal outcomes, particularly in low- and middle-resource countries, emphasizing the importance of inclusivity in research related to these innovations.




