Overview
This article underscores the critical importance of determining the appropriate sample size for clinical trials involving medical devices. A well-calculated sample size is not merely beneficial; it is essential for achieving statistically meaningful results and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Factors such as:
- Anticipated effect size
- Variability
- Statistical power
- Dropout rates
significantly influence sample size calculations. By detailing these elements, the article provides best practices for researchers, guiding them to optimize study design and enhance the reliability of clinical evaluations. In the complex landscape of Medtech, understanding these dynamics is imperative for successful clinical research.
Introduction
In the realm of clinical trials, the importance of sample size is paramount. It forms the foundation of any study, influencing its capacity to detect treatment effects and ensuring the validity of the results. Given the high stakes, particularly in the Medtech sector where patient safety is of utmost concern, comprehending how to calculate and justify an appropriate sample size is essential.
This article explores the critical elements of sample size planning, examining its regulatory implications, best practices, and real-world examples that highlight its impact on trial outcomes. By navigating these complexities, researchers can bolster the reliability of their findings and ultimately enhance the efficacy of medical devices within the healthcare landscape.
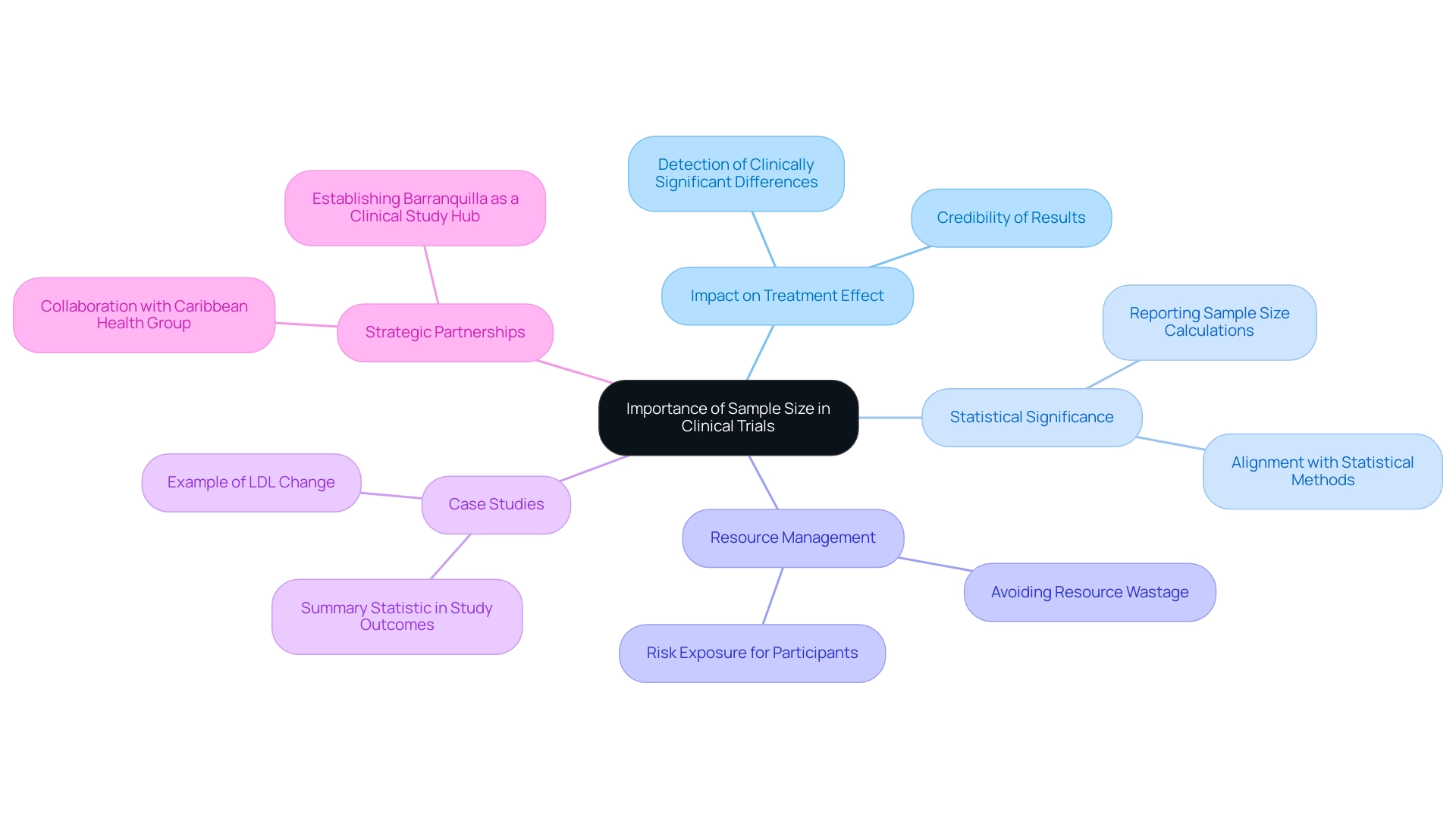
Understanding the Importance of Sample Size in Clinical Trials
The clinical trial sample size for devices, defined as the number of participants in a clinical study, is a crucial element that significantly impacts the research's ability to identify a treatment effect, should one be present. A carefully determined clinical trial sample size for devices ensures that the study possesses sufficient strength to yield statistically meaningful outcomes, thereby enhancing the credibility of the results. With over 20 years of experience in the Medtech sector, bioaccess® recognizes that an inadequate clinical trial sample size for devices can lead to inconclusive results, potentially delaying the approval process and jeopardizing patient safety.
Understanding the significance of clinical trial sample size for devices is essential for creating successful clinical studies. For instance, when a trial aims to demonstrate that a new device surpasses an existing one, a larger clinical trial sample size for devices is often necessary to detect minor yet clinically significant differences in results. Conversely, employing an excessively large clinical trial sample size for devices can result in resource wastage and increase risk exposure for participants without yielding additional valuable insights.
Recent discussions in the field underscore the importance of reporting the clinical trial sample size for devices in research manuscripts to mitigate potential biases. This practice is vital, as it allows for a clear evaluation of the design and its implications. The selection of data quantity is influenced by various study results, including correlation, association, agreement, sensitivity, or specificity.
This multifaceted approach to determining the clinical trial sample size for devices is critical for ensuring that clinical studies produce reliable and practical outcomes. Practical examples illustrate the impact of participant quantity on the clinical trial sample size for devices and study results in the Medtech field. For example, an analysis that based its participants on the ability to identify a clinically significant difference in LDL percent change between groups highlighted how essential this element is for obtaining meaningful outcomes. As noted by Smith, "Calculation of the sample size was based on the ability to detect a clinically relevant difference in the percent change LDL (primary outcome) of 5% between the two study groups."
Such case studies emphasize the importance of aligning study design with statistical methods to optimize outcomes and enhance the overall effectiveness of clinical evaluations for medical devices, including considerations for the clinical trial sample size for devices. Furthermore, bioaccess®'s partnership with Caribbean Health Group aims to establish Barranquilla as a premier location for clinical studies in Latin America, supported by Colombia's Minister of Health. This initiative underscores the significance of strategic site selection and comprehensive management services in achieving successful results.
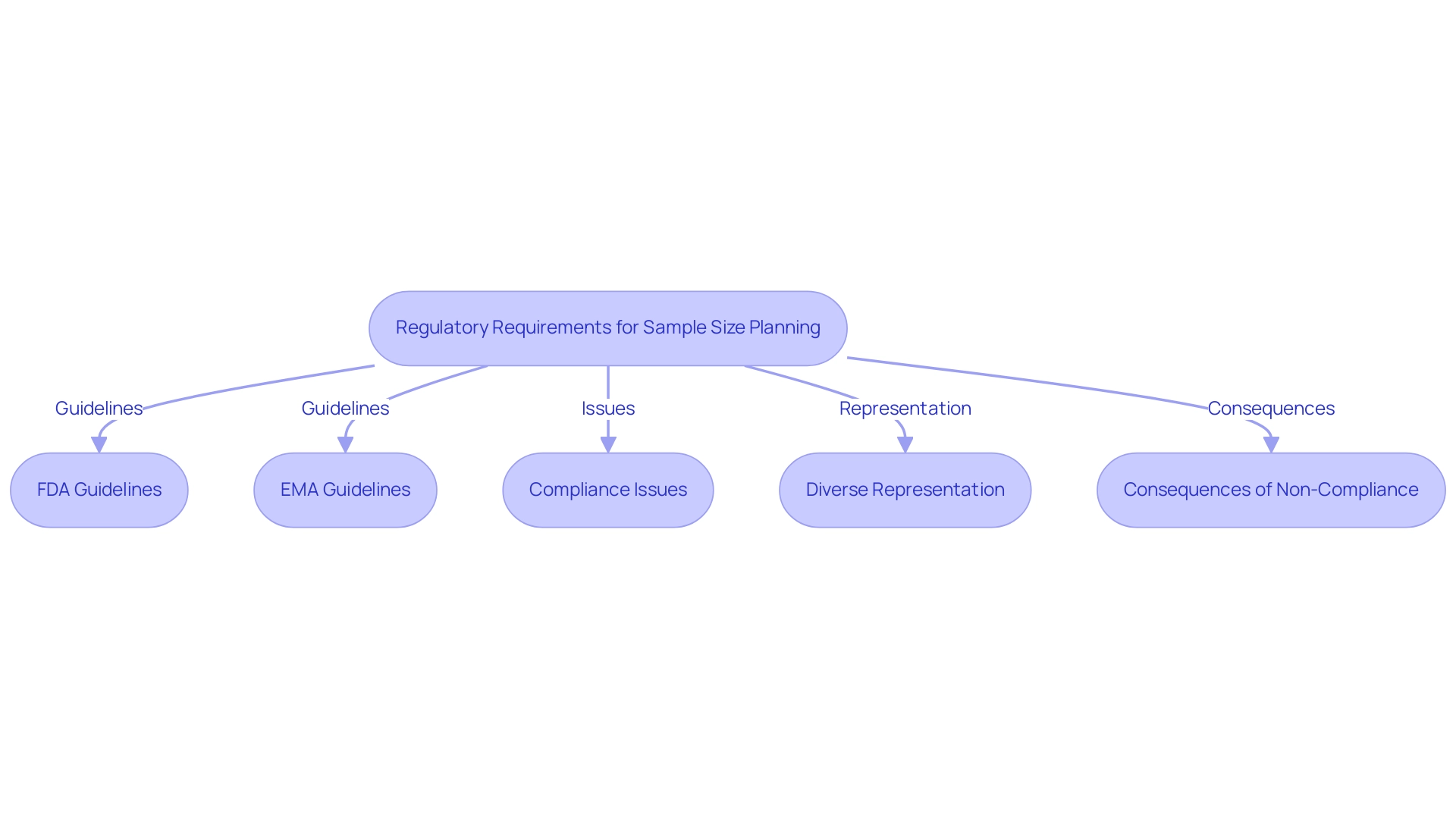
Regulatory Requirements for Sample Size Planning in Medical Device Trials
Regulatory organizations such as the FDA and EMA have established comprehensive guidelines for determining the clinical trial sample size for medical devices. These guidelines underscore the necessity of a scientifically justified sample size that effectively addresses the study's objectives. For example, the FDA advises that group sizes should be calculated based on the anticipated effect magnitude, data variability, and a desired statistical power, typically set at 80% or higher.
Significantly, only 37% of device approval documents have provided adequate information on participant numbers, highlighting a substantial area for improvement in compliance.
Furthermore, the European Medical Device Regulation (MDR) mandates that the clinical trial sample size for devices be thoroughly justified in the clinical evaluation report. This requirement ensures that studies are designed to yield reliable evidence regarding the safety and performance of the device. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in considerable delays in the approval process or outright rejection of results.
To enhance compliance and improve outcomes, it is imperative to establish incentives for manufacturers to address representation and bias mitigation in their submissions.
At bioaccess, our service capabilities encompass:
- Feasibility assessments
- Selection of research locations and principal investigators
- Review and feedback on project documents to ensure compliance with country requirements
- Facilitation of setup, start-up, and approval processes involving ethics committees and health ministries
- Management of import permits and the nationalization of investigational devices
- Comprehensive project management and monitoring services to guarantee thorough reporting on research status, inventory, and adverse events, all in line with regulatory standards
Historical context illustrates the critical importance of diverse representation in clinical trials. For instance, previous research on cholesterol-lowering medications predominantly involved male participants, raising concerns about the effectiveness of these treatments in women. This lack of demographic diversity has prompted calls for more inclusive research practices, as evidenced by the approval of specific drugs tailored for particular ethnic groups.
Such developments highlight the necessity for diverse representation in clinical studies to ensure safety and efficacy across various populations. As Tobi Olatunji noted, "These authors jointly supervised this work: Roxana Daneshjou, Tobi Olatunji," emphasizing the collaborative effort in addressing these critical issues.
Moreover, recent data indicates that despite the increasing number of market-approved medical devices, FDA reporting remains inconsistent, with underreported demographic and socioeconomic characteristics contributing to algorithmic bias and health disparity. As we approach 2025, compliance with FDA and EMA guidelines regarding clinical trial sample sizes for devices will be essential for medical device studies. Regulatory requirements are evolving, and understanding these changes will be crucial for clinical researchers aiming to optimize their study designs and enhance the likelihood of successful outcomes.
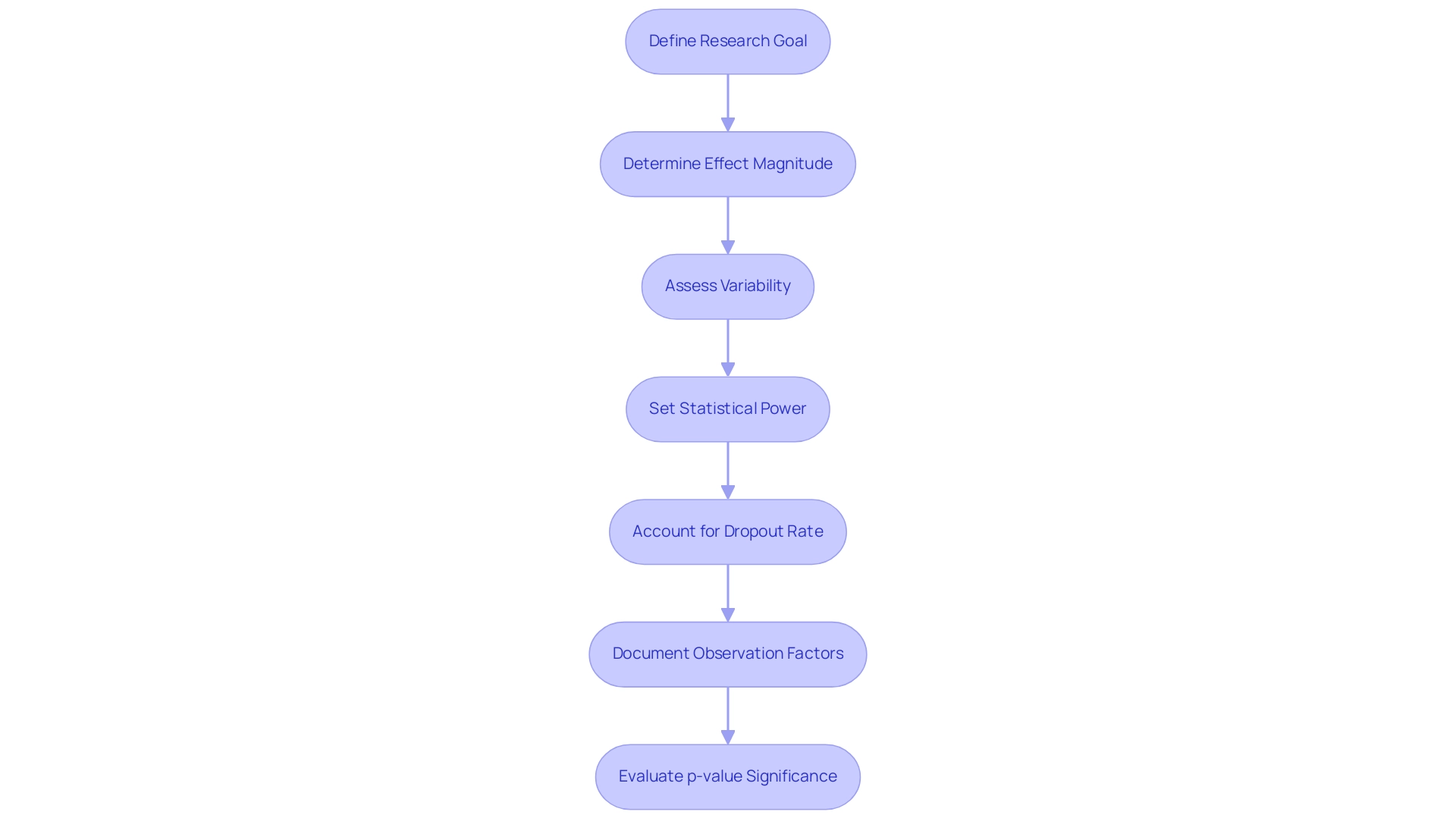
Key Questions for Effective Sample Size Calculation
When determining the sample size for clinical trials, researchers must address several pivotal questions to ensure robust and reliable outcomes:
- What is the primary goal of the research? Clearly defining the main goal is essential, as it directs the determination of the clinical trial sample size for devices needed to achieve statistically significant results. A well-articulated objective aligns the research design with the expected outcomes.
- What is the anticipated effect magnitude? This parameter reflects the magnitude of the difference the study aims to detect. A larger anticipated effect magnitude generally permits a smaller group in the clinical trial sample size for devices, whereas a smaller effect magnitude requires a larger group to attain the desired statistical power.
- What is the variability in the outcome measures? Greater variability in the data necessitates a larger clinical trial sample size for devices to ensure that the results are statistically dependable. Grasping the anticipated variability aids in making informed choices regarding the amount required to identify significant differences.
- What is the desired level of statistical power? Researchers generally aim for a power of 80% or 90% when determining the clinical trial sample size for devices, which indicates the likelihood of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis when it is indeed false. Greater power levels require larger groups, especially in research with smaller effect magnitudes.
- What is the anticipated dropout rate? It is crucial to account for potential dropouts when determining the clinical trial sample size for devices, as they can significantly impact the validity of the study results. Modifying the group dimensions to accommodate an expected dropout rate—ideally less than 10%—ensures that the final cohort remains sufficient throughout the trial.
- What factors are utilized in determining the number of observations? All parameters utilized in participant count calculations must be documented for reproducibility, which is crucial for scientific rigor.
- What is the significance of the p-value? A statistically significant result arises when the p-value is below the selected alpha threshold, usually < 0.05, emphasizing the importance of the number of observations in attaining meaningful outcomes.
By systematically addressing these questions, researchers can establish a well-justified group that adheres to both scientific rigor and regulatory standards, particularly regarding the clinical trial sample size for devices. This approach not only enhances the credibility of the research but also facilitates the successful advancement of medical devices by optimizing the clinical trial sample size for devices.
Furthermore, it is essential to take into account the expected reduction in data set due to factors such as non-response and incomplete information. Researchers should aim for less than 10% loss in the clinical trial sample size for devices to maintain the validity of their results, as highlighted in the case analysis titled 'Anticipated Loss in Clinical Trial Sample Size for Devices Calculations.' This emphasizes the importance of assessing potential losses derived from previous experiences and modifying calculation methods accordingly.
Moreover, the expertise of organizations like bioaccess®, which has over 15 years of experience in Medtech and emphasizes various types of studies, reinforces the importance of the clinical trial sample size for devices in clinical study design. As mentioned by Yuwadi Thein Naing, who aided in the creation of software for determining group numbers, the incorporation of these components is essential for improving the credibility and clarity of the content.
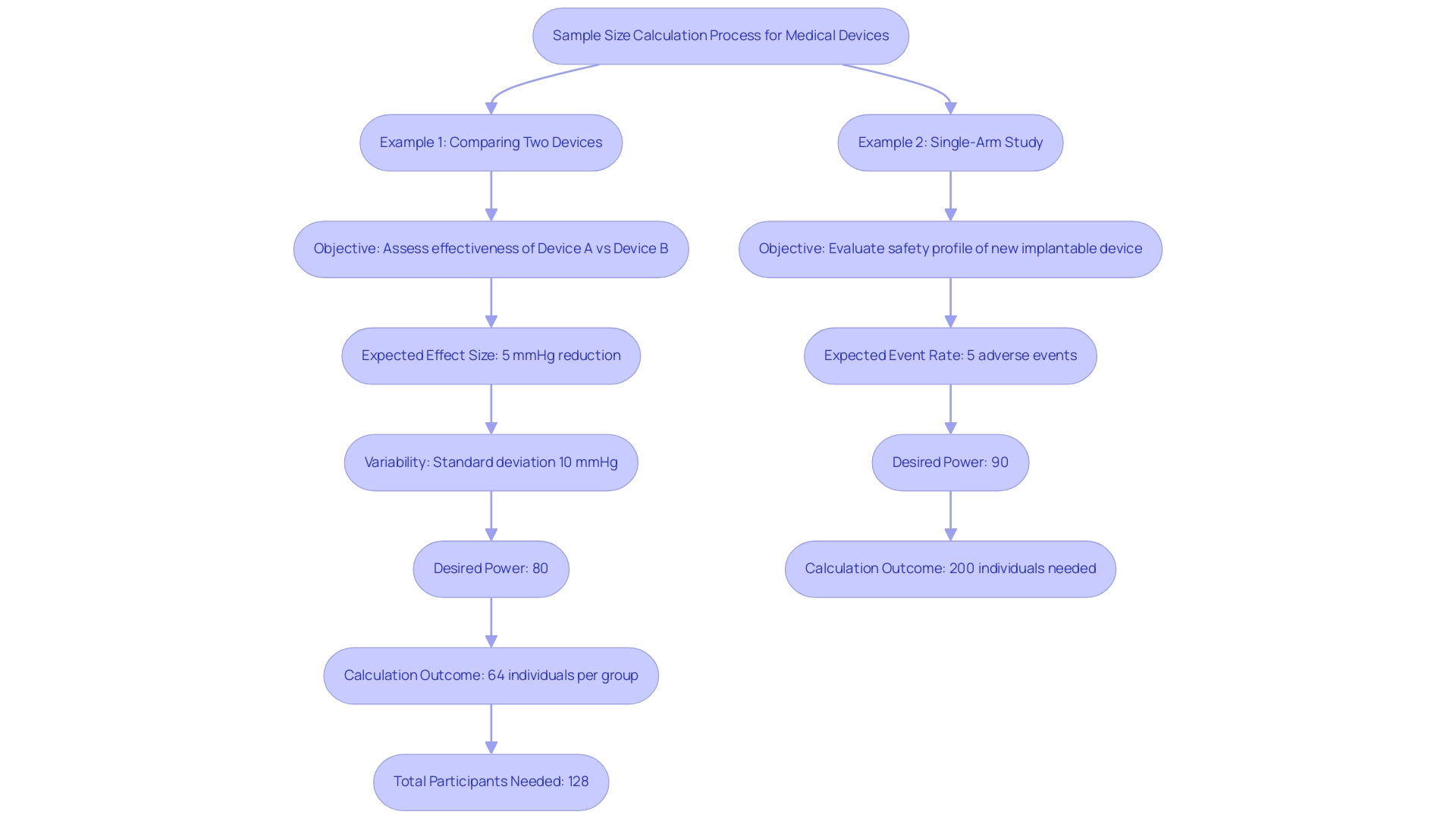
Practical Examples of Sample Size Calculations for Medical Devices
To illustrate the intricacies of sample size calculation in clinical trials for medical devices, consider the following detailed examples:
-
Example 1: Comparing Two Devices
- Objective: Assess the effectiveness of Device A versus Device B in lowering blood pressure.
- Expected Effect Size: A targeted reduction of 5 mmHg.
- Variability: Standard deviation is estimated at 10 mmHg.
- Desired Power: Set at 80% to ensure reliable results.
- Calculation Outcome: Using a participant calculator, it is established that 64 individuals are needed for each group. Considering a 10% dropout rate, the total number of participants required is 128.
-
Example 2: Single-Arm Study
- Objective: Evaluate the safety profile of a new implantable device.
- Expected Event Rate: Anticipated adverse events are projected at 5%.
- Desired Power: Aiming for 90% power to confidently identify any significant safety concerns.
- Calculation Outcome: The participant count calculation indicates that 200 individuals are essential to effectively identify possible safety concerns.
These examples emphasize the essential role that various factors play in determining the clinical trial sample size for devices and highlight the need for careful planning in clinical trial design. It is crucial to consult a seasoned biostatistician for precise calculations of the clinical trial sample size for devices, as highlighted by Francesca Botta, a Senior Biostatistician, who observes, "Although methods for participant number calculation are outlined in various statistical texts, executing these calculations can be intricate, and it is preferable to consult a knowledgeable biostatistician to assess this important research parameter."
Furthermore, the qualified body cannot permit a clinical trial if no systematic analysis and participant planning, particularly regarding the clinical trial sample size for devices, has been conducted, emphasizing the significance of these calculations in regulatory situations. By systematically addressing these calculations and considering the key questions for the clinical trial sample size for devices, researchers can enhance the reliability and effectiveness of their clinical studies. With more than 20 years of experience in Medtech, bioaccess® offers the knowledge necessary to oversee different types of clinical studies, including Early-Feasibility, First-In-Human, Pilot, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Research.
This extensive experience enables researchers to navigate the complexities of study design and regulatory compliance more effectively, ultimately contributing to the advancement of medical devices.
Summary and Best Practices for Sample Size Planning in Clinical Trials
Efficient participant planning is essential to the success of clinical studies for medical devices, particularly when determining the clinical trial sample size for devices. Utilizing the extensive clinical study management services provided by bioaccess®, which boasts over 20 years of experience in Medtech, can significantly enhance the reliability and validity of outcomes related to clinical trial sample size for devices. Here are key strategies to consider:
- Initiate Early Calculations: Begin calculations for the clinical trial sample size for devices during the initial planning phase. This proactive approach ensures that all study components are cohesively aligned from the outset, supporting the determination of the clinical trial sample size for devices, in line with bioaccess®'s focus on Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS) and First-In-Human Studies (FIH).
- Adhere to Regulatory Standards: Familiarize yourself with the specific requirements established by regulatory authorities, including those related to clinical trial sample size for devices. Compliance with these guidelines is crucial for the acceptance of trial results, particularly concerning the clinical trial sample size for devices, a principle that bioaccess® emphasizes in its trial setup and compliance reviews.
- Utilize robust statistical methods to determine the clinical trial sample size for devices by employing statistical software or partnering with a biostatistician to accurately ascertain the quantities adapted to your research design. For example, for a cohort of n = 100 with a 2:1 ratio between test and placebo groups, the calculations would result in n1 = 150 and n2 = 75. This guarantees that calculations regarding the clinical trial sample size for devices are based on solid statistical principles, which is essential for the success of crucial research.
- Adjust for Participant Dropouts: Anticipate potential dropouts by modifying the clinical trial sample size for devices accordingly. This adjustment is vital to maintain the integrity and power of the research, particularly regarding the clinical trial sample size for devices, ensuring that the results remain valid, especially in post-market clinical follow-up investigations (PMCF).
- Ongoing Review and Adjustment: Be ready to revisit and refine the clinical trial sample size for devices as new data arises or as the research evolves. This flexibility can lead to more accurate and relevant outcomes, reflecting the adaptive approach that bioaccess® employs in managing the clinical trial sample size for devices.
A case study on conditional performance score evaluation emphasizes the significance of design choice based on anticipated effect magnitudes. It shows that two-stage designs are optimal for effect magnitudes below 0.4, while three-stage designs excel for larger effect levels. This highlights the importance of customizing participant strategies to the particular context of the clinical trial sample size for devices.
As Tushar Vijay Sakpal, Principal Statistician at PharmaNet Clinical Services, observes, "Best practices in planning the clinical trial sample size for devices are essential for ensuring the success of clinical studies."
By adhering to these best practices and leveraging the expertise of bioaccess® in Latin America, researchers can not only enhance the robustness of their clinical trials but also contribute to the advancement of medical devices, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Effective sample size planning stands as a cornerstone of successful clinical trials, particularly in the Medtech sector where patient safety and regulatory compliance are paramount. This article has delved into the multifaceted aspects of determining an appropriate sample size, emphasizing its critical role in ensuring that trials can detect meaningful treatment effects while maintaining statistical validity. By addressing key questions regarding study objectives, expected effect sizes, variability, and dropout rates, researchers can establish well-justified sample sizes that align with both scientific rigor and regulatory standards.
Moreover, adherence to regulatory requirements set forth by bodies like the FDA and EMA is essential for the acceptance of trial results. The necessity for comprehensive justifications in sample size calculations cannot be overstated, as non-compliance can lead to significant delays or rejections in the approval process. By integrating robust statistical methodologies and consulting with experienced biostatisticians, researchers can navigate the complexities of sample size planning more effectively.
Ultimately, the successful execution of clinical trials hinges on meticulous sample size calculations that reflect the unique context of each study. As demonstrated through real-world examples and best practices, a proactive and adaptable approach to sample size planning not only enhances the reliability of trial outcomes but also contributes to the advancement of medical devices. By prioritizing these principles, researchers can significantly impact patient care and safety, reinforcing the importance of high-quality clinical research in the healthcare landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the importance of clinical trial sample size for medical devices?
The clinical trial sample size for devices is crucial as it impacts the research's ability to identify a treatment effect, ensuring that the study has sufficient strength to yield statistically meaningful outcomes, which enhances the credibility of the results.
What can happen if the clinical trial sample size is inadequate?
An inadequate clinical trial sample size can lead to inconclusive results, potentially delaying the approval process and jeopardizing patient safety.
Why is it necessary to have a larger clinical trial sample size in certain studies?
A larger clinical trial sample size is often necessary to detect minor yet clinically significant differences in results, particularly when demonstrating that a new device surpasses an existing one.
What are the consequences of using an excessively large clinical trial sample size?
Using an excessively large clinical trial sample size can result in resource wastage and increase risk exposure for participants without providing additional valuable insights.
Why is reporting the clinical trial sample size important in research manuscripts?
Reporting the clinical trial sample size is important to mitigate potential biases and allows for a clear evaluation of the study design and its implications.
What factors influence the selection of clinical trial sample size?
The selection of clinical trial sample size is influenced by various study results, including correlation, association, agreement, sensitivity, and specificity.
What guidelines have regulatory organizations established regarding clinical trial sample size for medical devices?
Regulatory organizations like the FDA and EMA have established guidelines that emphasize the necessity of a scientifically justified sample size that effectively addresses the study's objectives.
What does the FDA recommend for calculating group sizes in clinical trials?
The FDA advises that group sizes should be calculated based on the anticipated effect magnitude, data variability, and a desired statistical power, typically set at 80% or higher.
What is the compliance status regarding clinical trial sample sizes in device approval documents?
Only 37% of device approval documents have provided adequate information on participant numbers, indicating a significant area for improvement in compliance.
What are the implications of non-compliance with the European Medical Device Regulation (MDR)?
Non-compliance with MDR can result in considerable delays in the approval process or outright rejection of study results.
What services does bioaccess provide to enhance compliance and improve outcomes in clinical trials?
Bioaccess provides services including feasibility assessments, selection of research locations, review of project documents, management of ethics committee processes, and comprehensive project management and monitoring services.
Why is diverse representation in clinical trials important?
Diverse representation in clinical trials is essential to ensure safety and efficacy across various populations, as historical research has often lacked demographic diversity, raising concerns about treatment effectiveness.
What recent trends have been observed regarding FDA reporting of demographic data in clinical trials?
Recent data indicates inconsistent FDA reporting, with underreported demographic and socioeconomic characteristics contributing to algorithmic bias and health disparities, highlighting the need for compliance with evolving regulatory guidelines.




