Introduction
The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) has emerged as a critical framework within the European Union, designed to enhance patient safety and ensure the effectiveness of medical devices. Since its enforcement in May 2021, this regulation has replaced the previous Medical Device Directive (MDD) and introduced rigorous requirements that manufacturers must adhere to. The MDR aims to elevate standards across the medical device market, promoting transparency and quality while safeguarding patients.
As manufacturers navigate this complex regulatory landscape, the importance of understanding the MDR's objectives, classification systems, and compliance requirements becomes increasingly evident. This article delves into key aspects of the MDR, exploring its implications for device manufacturers and the essential strategies needed to thrive in a rapidly evolving market.
Through a comprehensive examination of clinical data, the role of Notified Bodies, and the General Safety and Performance Requirements, the discussion highlights the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for stakeholders in the medical device industry.
Understanding the Medical Device Regulation (MDR): An Overview
The medical device MDR represents a crucial framework established by the European Union to safeguard patient safety and ensure the efficacy of medical devices. Enforced since May 2021, the medical device MDR replaces the Medical Equipment Directive (MDD) and introduces a series of stringent requirements for producers of medical devices. Its primary objectives include:
- Enhancing patient safety
- Increasing transparency in the medical device market
- Ensuring that all medical devices comply with the medical device MDR standards of quality and performance
This regulatory environment is essential for producers, particularly when taking into account the extensive clinical trial management services needed for regulations, such as:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
Notably, only 13% of companies view digital transformation as a high priority for 2024, emphasizing a significant challenge for producers in adapting to the evolving regulatory landscape. Additionally, improving data integration and sharing is cited as the top productivity measure companies are focusing on for the upcoming year, underscoring the importance of operational efficiency in compliance with the medical device MDR regulations.
For producers, a comprehensive understanding of the medical device MDR is essential, as non-compliance can lead to severe repercussions, including market withdrawal and significant financial penalties. This section examines the essential elements of the medical device MDR, clarifying its aims, range, and the significant effects it has on medical product producers navigating a complex regulatory environment. As illustrated in the case study 'Medical Device Outlook For 2024 and Beyond,' companies are not only navigating these regulatory challenges but are also committing to sustainability to thrive in a rapidly growing market.
Furthermore, awareness of INVIMA, Colombia's national food and drug surveillance authority, is vital, as it plays a significant role in the oversight and classification of medical instruments as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO. Additionally, it is imperative for manufacturers to engage in thorough reviews and feedback on study documents to ensure compliance with local regulations, as this process is critical to the successful setup and management of clinical trials.
Medical Device Classification: Key Categories and Requirements
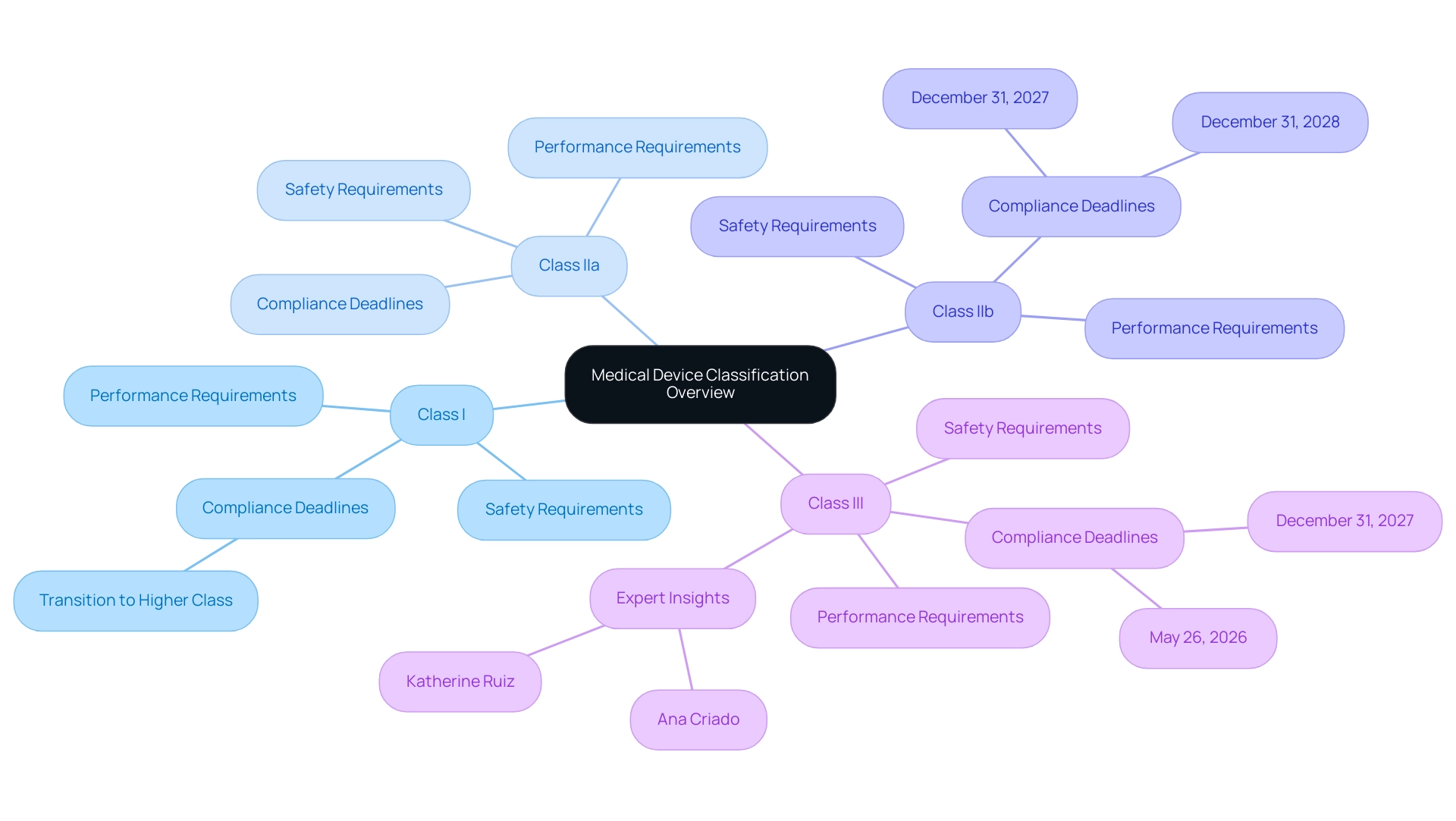
Under the medical device MDR, medical instruments are categorized into four primary classes: Class I, Class IIa, Class IIb, and Class III. Each class is subject to distinct safety and performance requirements, directly influenced by the associated risk levels. Class I items, such as bandages and non-invasive instruments, encounter the least stringent regulatory scrutiny.
In contrast, Class III products, including implantable items like pacemakers, undergo extensive evaluation due to their higher risk profiles. Manufacturers must meticulously assess their products to determine the appropriate classification, as this classification dictates the conformity assessment process and the necessary documentation for compliance. The participation of Notified Bodies becomes critical for higher-risk classifications, particularly for Class III products, where comprehensive clinical evaluation data is essential.
Recent guidance from MDCG 2019-15 rev.1 highlights that 70% of Class I items are expected to transition to higher classifications under the medical device MDR, illustrating significant shifts in regulatory expectations. Furthermore, the quote from Saint-Gobain, 'We’re here to help navigate, contact us if you have questions,' underscores the support available for manufacturers during this transition. Experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, who has extensive experience in Regulatory Affairs, biomedical engineering, and health economics, and Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, emphasize the importance of understanding these classifications.
This understanding is particularly vital considering the approaching deadlines for adherence to the medical device MDR:
- Class III custom-made implantable items must meet requirements by May 26, 2026.
- Class III and implantable Class IIb items have until December 31, 2027.
- Non-implantable Class IIb instruments and lower-risk products are required to meet compliance by December 31, 2028.
The ongoing public consultation initiated by the Commission on December 12, 2024, further underscores the evolving landscape of medical device regulation and its implications for producers.
A pertinent case study outlining the regulatory requirements for ventilators and their accessories, published in April 2020, illustrates the practical implications of these classifications, demonstrating the essential need for producers to navigate these requirements effectively. Understanding the nuances between Class I and Class III requirements is imperative for manufacturers to ensure adherence to the appropriate regulatory frameworks throughout the product lifecycle.
General Safety and Performance Requirements Under MDR
The medical device MDR outlines essential General Safety and Performance Requirements (GSPRs) that medical instruments must satisfy to ensure both safety and efficacy. These requirements mandate that devices are designed and manufactured to minimize associated risks while delivering adequate information to users. The adherence process is stringent; manufacturers are required to substantiate conformity through comprehensive testing and meticulous documentation.
Experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and founder of Mahu Pharma, bring invaluable insights into navigating these complex regulations. With her extensive background in biomedical engineering and her role as a consultant for global companies, she assists organizations in aligning their strategies with the medical device MDR. Mahu Pharma provides extensive clinical trial management services, including:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
This ensures that clients meet all regulatory requirements.
A recent analysis underscores the importance of understanding the differences between the EU's GSPRs and the US' Essential Principles of Safety and Performance, which are not as strictly enforced. This understanding is essential for companies navigating both markets, as it affects their regulatory strategies. Furthermore, risk assessments play a pivotal role in this landscape.
These assessments are not simply a regulatory box to tick; they are essential to clinical evaluations and crucial for post-market surveillance, enabling continuous monitoring of performance and safety. As noted by Emilia Niemiec, 'This work was supported by the Forskningsradet om Hälsa, Arbetsliv och Välfärd (grant no. 2020-01089),' emphasizing the importance of ongoing research in this field.
The article was received on 19 October 2021 and accepted on 6 March 2022, highlighting the relevance of staying informed about compliance rates among medical manufacturers and the latest methodologies for risk assessment under the medical device MDR to ensure that products meet the required safety and performance standards.
The Role of Notified Bodies in Achieving MDR Compliance
Notified Bodies are designated organizations responsible for evaluating the compliance of medical instruments under the medical device MDR. Their role is especially crucial for higher-risk items, such as Class IIa, IIb, and III, where thorough evaluation is essential. Manufacturers must carefully choose a Notified Body that possesses expertise in their specific product category.
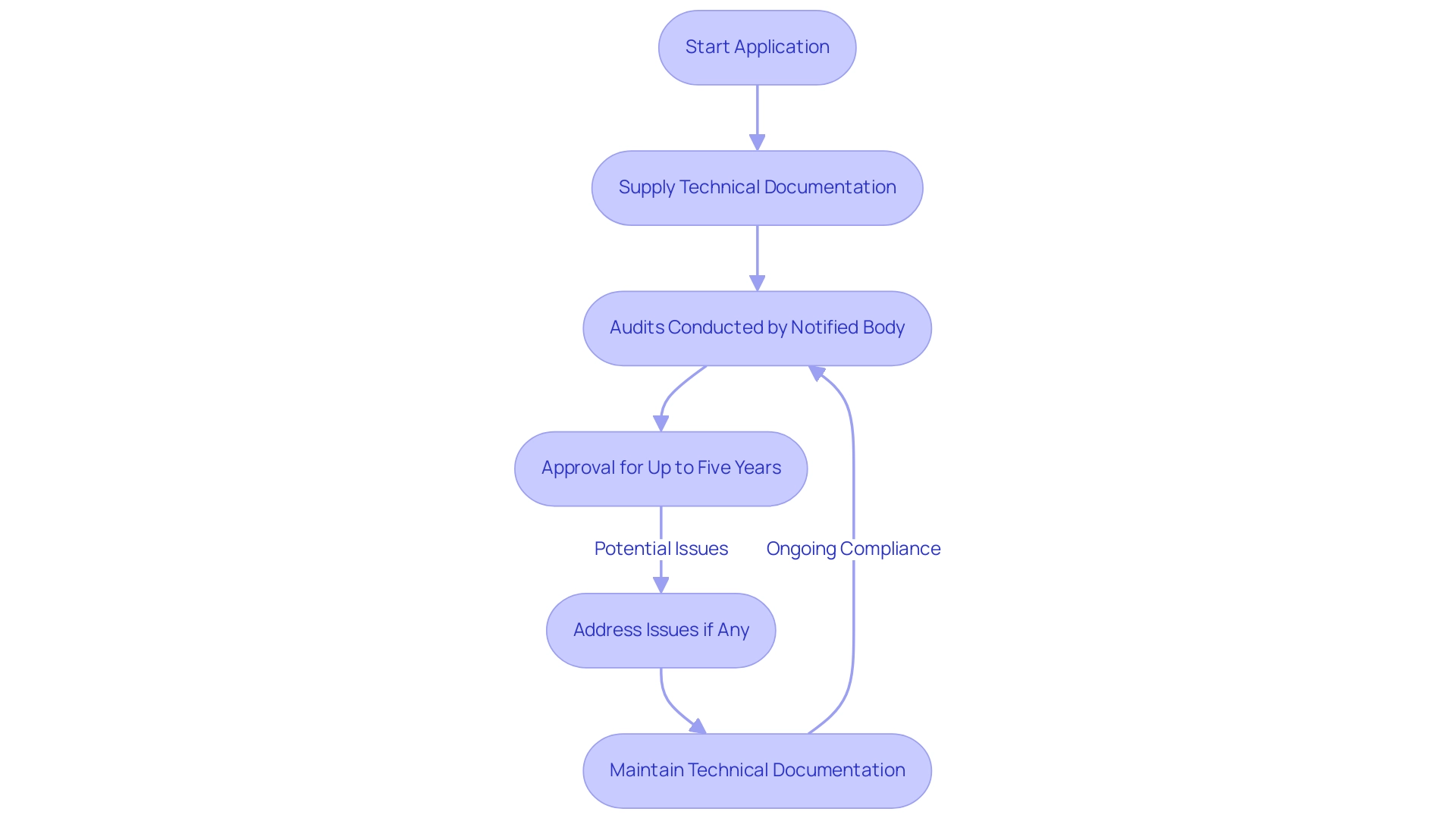
The process of collaborating with a Notified Body includes several essential steps:
- Manufacturers must start an application, supplying detailed technical documentation that shows adherence to the medical device MDR requirements.
- This documentation is crucial as it serves as the basis for audits conducted by the Notified Body.
- Significantly, equipment is approved for up to five years, but this is not automatic due to potential issues uncovered during audits, emphasizing the importance of compliance.
Recent trends indicate an increase in market surveillance by European Competent Authorities, particularly focused on self-declared Class I products, which underscores the importance of maintaining robust technical documentation. This trend includes heightened scrutiny and inspections, as noted in the case study regarding increased market surveillance. Furthermore, the Notified Body will typically require clinical data to validate that the product meets regulatory standards.
To prepare for audits, manufacturers should ensure their documentation is complete and easily accessible, as this can significantly aid the adherence process. Collaborating with seasoned experts, like Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in regulatory matters for medical devices and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, can offer invaluable assistance in navigating the intricacies of medical device MDR regulations. Katherine's expertise can also aid in the comprehensive clinical trial management services, including feasibility studies and site selection, ensuring that all regulatory reviews and trial setups align with expectations.
As noted by experts from Emergo by UL, 'We at Emergo will leverage our experience to review the drafted TDFs and assist with the notified body application.' This proactive method highlights the significance of thorough preparation and robust technical documentation to meet regulatory expectations. Understanding these steps and the role of Notified Bodies, along with the associated clinical trial management services, is essential for achieving successful audit outcomes and ensuring ongoing compliance in a landscape where scrutiny is poised to intensify.
Clinical Data and Monitoring: Essential Components for MDR Compliance
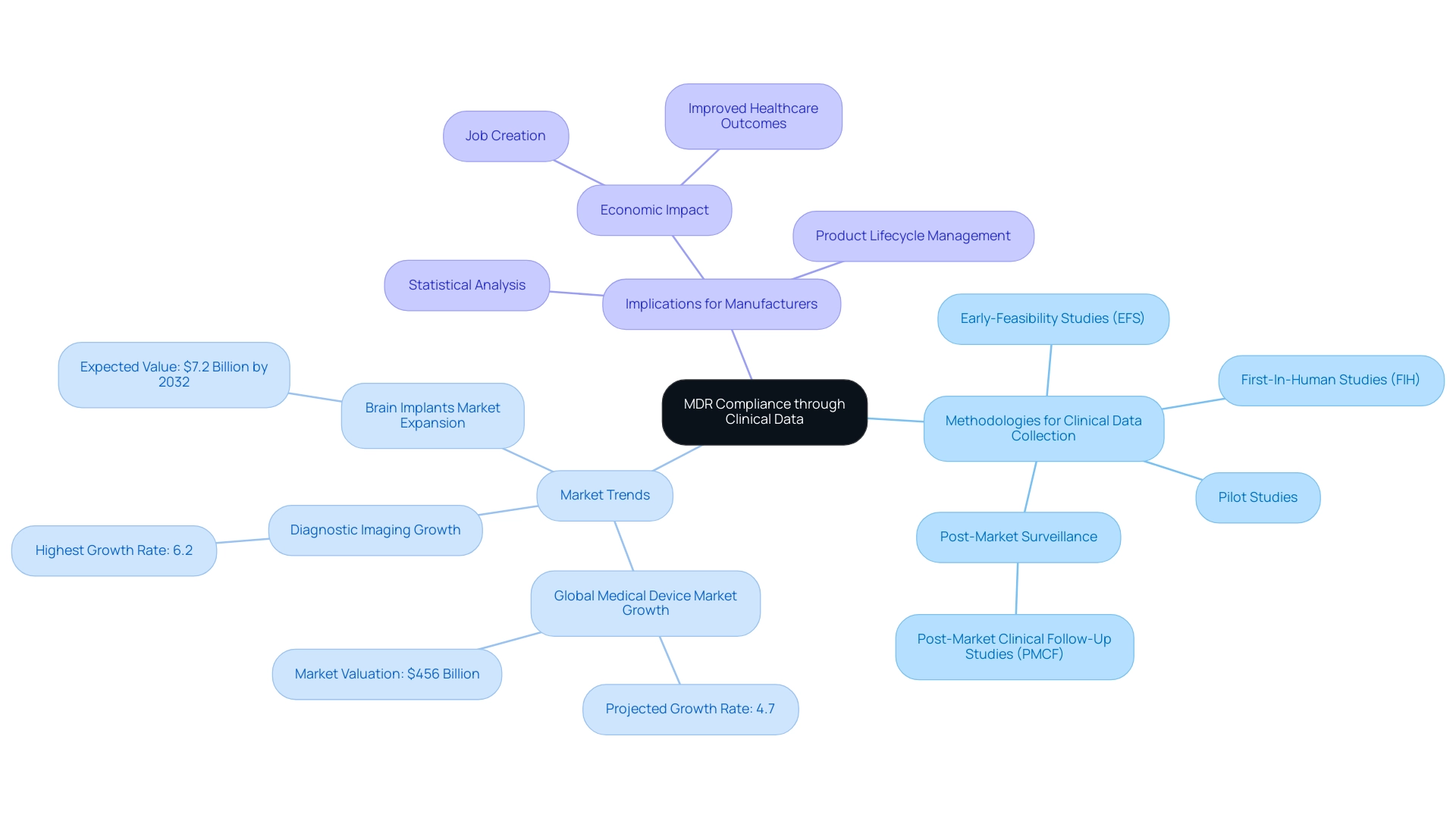
Clinical data is a cornerstone in verifying that a medical device adheres to the General Safety and Performance Requirements mandated by the medical device MDR. To achieve this, producers must systematically collect and analyze clinical data through diverse methodologies, including:
- Well-structured Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS)
- First-In-Human Studies (FIH)
- Pilot Studies
- Robust post-market surveillance, including Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF)
With bioaccess®'s comprehensive clinical trial management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, project management, and reporting, we are poised to support manufacturers in navigating these complexities effectively.
With over 20 years of experience in the Medtech field, bioaccess® offers a customized approach to help navigate your company towards successful acquisition. In 2023 and 2024, the global medical equipment market is projected to experience significant growth, attributed to advancements in technology, increased healthcare expenditure, and a rise in chronic diseases, with a notable growth rate of 4.7%, reaching a valuation of $456 billion. Importantly, 55% of stakeholders express optimism about Ai's future impact on the MedTech sector, indicating a trend towards innovation that can enhance clinical data collection and analysis.
Given this context, the design of clinical trials becomes paramount, where meticulous statistical analysis is essential to ensure the reliability and validity of the gathered evidence. The diagnostic imaging equipment sector has experienced the highest growth at 6.2%, illustrating specific trends within the broader market growth narrative. Furthermore, effective monitoring of equipment performance in real-world settings is crucial for ongoing safety evaluations.
Producers must also stay alert in refreshing clinical information as new insights arise, a practice that not only aids adherence but also improves the product's lifecycle management. This proactive approach is further supported by insights from experts in the field, such as Trishita Deb, who underscores the significance of robust clinical data in fostering confidence in new innovations, particularly as the brain implants market is expected to expand to US$ 7.2 billion by 2032. By adopting methodologies such as technology reuse, focusing on core competencies, and forming strategic partnerships, manufacturers can better navigate the complexities of medical device MDR regulations and ensure their devices meet evolving clinical data requirements.
This comprehensive approach not only aids in compliance but also contributes to job creation, economic growth, and improved healthcare outcomes within local economies.
Conclusion
The Medical Device Regulation (MDR) represents a pivotal shift in the regulatory landscape for medical devices within the European Union, focusing on patient safety, transparency, and quality. Enforced since May 2021, the MDR imposes stringent requirements that manufacturers must understand to successfully navigate this complex environment.
Medical devices are classified into distinct categories—Class I, IIa, IIb, and III—each with specific safety and performance standards. Accurate classification is crucial as it directly affects the conformity assessment process and the involvement of Notified Bodies, essential for ensuring compliance, particularly for higher-risk devices. The expected transition of many Class I devices to higher classifications further emphasizes the need for manufacturers to adapt their strategies.
Additionally, compliance with the General Safety and Performance Requirements (GSPRs) necessitates thorough risk assessments and robust clinical data collection. Collaborating with experienced professionals and utilizing clinical trial management services are vital for meeting these rigorous standards.
In conclusion, effective navigation of the MDR requires a proactive approach focused on compliance and adaptation to the evolving regulatory landscape. By prioritizing safety and performance, medical device manufacturers can overcome challenges and seize opportunities for innovation, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and contributing to a more resilient healthcare system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the medical device MDR and why is it important?
The medical device MDR is a regulatory framework established by the European Union to enhance patient safety and ensure the efficacy of medical devices. It replaces the Medical Equipment Directive (MDD) and introduces stringent requirements for producers, focusing on increasing transparency and compliance with quality and performance standards.
When was the medical device MDR enforced?
The medical device MDR has been enforced since May 2021.
What are the primary objectives of the medical device MDR?
The primary objectives of the medical device MDR include enhancing patient safety, increasing transparency in the medical device market, and ensuring compliance with standards of quality and performance.
What are some key clinical trial management services required under the medical device MDR?
Key clinical trial management services include feasibility studies, site selection, reviews, trial setup, import permits, project management, and reporting.
What challenges do producers face regarding digital transformation in relation to the medical device MDR?
Only 13% of companies view digital transformation as a high priority for 2024, indicating a significant challenge for producers in adapting to the evolving regulatory landscape.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with the medical device MDR?
Non-compliance with the medical device MDR can lead to severe repercussions, including market withdrawal and significant financial penalties.
How are medical instruments classified under the medical device MDR?
Medical instruments are categorized into four classes: Class I, Class IIa, Class IIb, and Class III, with each class subject to distinct safety and performance requirements based on associated risk levels.
What is the significance of Notified Bodies in the classification of medical devices?
Notified Bodies are critical for higher-risk classifications, particularly for Class III products, as they require comprehensive clinical evaluation data for compliance.
What recent guidance indicates changes in the classification of medical devices?
Recent guidance from MDCG 2019-15 rev.1 indicates that 70% of Class I items are expected to transition to higher classifications under the medical device MDR.
What are the key compliance deadlines for different classes of medical devices?
Class III custom-made implantable items must comply by May 26, 2026. Class III and implantable Class IIb items have until December 31, 2027. Non-implantable Class IIb instruments and lower-risk products must meet compliance by December 31, 2028.
Why is understanding the classifications of medical devices critical for manufacturers?
Understanding the classifications is vital for manufacturers to ensure adherence to appropriate regulatory frameworks throughout the product lifecycle, particularly given the approaching deadlines for compliance.




