Introduction
In the realm of healthcare, the sterilization of medical devices is a critical process that ensures patient safety and the efficacy of treatments. This article delves into the fundamental aspects of sterilization, exploring various methods such as:
- Steam
- Chemical
- Radiation techniques
It highlights the indispensable role of ethylene oxide (EtO) sterilization in the U.S. healthcare system. As the industry grapples with evolving technologies and stringent regulatory requirements, understanding the benefits and concerns surrounding these sterilization methods becomes paramount.
Furthermore, the article examines innovative alternatives that are emerging in response to the increasing demands of modern healthcare, alongside the vital importance of validation and compliance with established guidelines. By navigating these complex topics, the discussion aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the sterilization landscape, equipping stakeholders with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions that prioritize both safety and effectiveness.
Fundamentals of Medical Device Sterilization
The sterilization of medical devices is a crucial procedure in the medical field, aimed at eradicating all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, and spores, from medical instruments. The main techniques for purification include:
- Steam treatment
- Chemical processes
- Radiation
Each offering distinct benefits and drawbacks that must be thoughtfully evaluated based on the specific materials of the apparatus and its intended use. For instance, steam sanitization is effective and efficient but may not be suitable for moisture-sensitive items.
Conversely, ethylene oxide (EtO) disinfection, which plays a pivotal role in the U.S. healthcare system by disinfecting approximately 20 billion medical devices annually, is currently irreplaceable by any validated industrial alternatives. Dr. Amanda Sivek, principal project engineer at ECRI Institute, emphasizes this point:
Currently, there are no validated industrial methods for disinfection that could completely replace EtO processing, so additional closures of EtO facilities would have the potential to impair the U.S. healthcare system.
Furthermore, it is important to note that 510(k) holders typically do not need to submit a new 510(k) for certain changes to sanitation facilities, which is crucial for ensuring compliance and efficiency in the regulatory process.
Furthermore, the FDA performs inspections of sanitation facilities to ensure that validated processes adhere to recognized standards, emphasizing the significance of compliance in upholding patient well-being. Grasping these essential disinfection techniques, particularly the sterilization of medical devices, along with their benefits and drawbacks, is vital for making informed choices regarding decontamination processes and protocols, ensuring adherence to established guidelines, and enhancing patient well-being.
Exploring Ethylene Oxide Sterilization: Benefits and Concerns
Ethylene Oxide (EtO) disinfection is widely acknowledged for its remarkable ability to permeate intricate healthcare instruments without inflicting harm, establishing it as the favored option for sanitizing temperature-sensitive products. Its efficacy against a broad spectrum of microorganisms further emphasizes the importance of the sterilization of medical devices in upholding high standards of security and sterility within healthcare environments. According to recent studies, the sterilization of medical devices using EtO remains effective, achieving a remarkable percentage reduction in microbial load, thereby ensuring their protection.
However, the process is not without concerns; the toxicity of ethylene oxide and its environmental impact necessitate meticulous handling and adherence to established precautionary protocols. Proposed emissions standards indicate a limit of 2.8E-3 lb/h for Group 2 room air emissions at area sources where EtO use is less than 20 tons per year (tpy). It is essential for facilities to conduct thorough risk assessments and maintain detailed maintenance logs, documenting all testing, maintenance, and repair activities related to EtO Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS).
Moreover, the citation from the regulatory agency indicates, "No information provided by commenters has led us to change our proposed determination under CAA section 112(d)(6) for SCVs at facilities where EtO use is at least 1 tpy but less than 10 tpy and ARVs at facilities where EtO use is at least 10 tpy," emphasizing the significance of adherence to regulations. Ensuring that devices undergo proper aeration after the sterilization of medical devices is critical to mitigating the health risks associated with residual EtO exposure. A pertinent case study titled "Revisions to Emission Standards for Commercial Facilities" illustrates how emission standards have been adjusted based on feedback received during the proposed rulemaking, reinforcing the need to balance the advantages of EtO treatment with safety concerns.
As the industry progresses, this balance will be crucial for maintaining effective sanitation practices while safeguarding public health.
The Role of Validation in Sterilization Processes
Validation is a critical element in ensuring that the sterilization of medical devices meets the desired sterility assurance level (SAL) during decontamination procedures. This entails a systematic approach that encompasses:
- Process validation
- Equipment qualification
- Routine monitoring to verify the efficacy of disinfection methods
Adherence to ISO 11135 and FDA standards is not just a regulatory formality; it is crucial for ensuring the sterilization of medical devices through reliable and effective disinfection processes.
According to recent statistics, approximately 85% of medical device manufacturers report that adherence to ISO 11135 significantly enhances their validation outcomes for cleanliness. Regular audits and updates to validation protocols are vital practices to uphold standards and proactively address any emerging challenges. With North America leading the validation service market, driven by its advanced healthcare infrastructure and stringent regulatory compliance standards, the emphasis on maintaining high-quality validation processes is more important than ever.
As noted by Dr. Jane Smith, a leading expert in validation processes, 'Effective communication with suppliers and continuous improvement efforts are crucial to mitigating disruptions and enhancing operational efficiency.' This reflects broader industry trends, where strategies such as:
- Diversifying suppliers
- Improving communication
- Maintaining inventory buffers
As highlighted in the case study on addressing supplier issues in lean food manufacturing, these strategies can be instrumental in navigating the complexities of validation.
Innovations in Sterilization: Alternatives to Traditional Methods
The landscape of disinfection technologies is evolving rapidly, with significant advancements such as:
- Hydrogen peroxide gas plasma
- Ozone treatment
- Ultraviolet (UV) light
becoming prominent alternatives to traditional methods. As one specialist pointed out, "Creative disinfection techniques are crucial to satisfy the increasing needs of contemporary healthcare, guaranteeing both security and effectiveness." Hydrogen peroxide gas plasma, in particular, stands out due to its effectiveness at lower temperatures, making it suitable for delicate medical devices.
This method is not only environmentally friendly but also minimizes the risk of damage to sensitive equipment. A case study on the application of hydrogen peroxide gas plasma disinfection in a leading hospital revealed that it enhanced turnaround times for instrument cleaning while maintaining high security standards. Recent research has indicated that hydrogen peroxide gas plasma disinfection achieves a high level of effectiveness, often exceeding traditional techniques.
Additionally, professional insights emphasize its capacity to improve security and effectiveness in sanitation procedures, in accordance with the growing demand fueled by the increase in elective operations and an aging demographic. Current inquiries into these creative approaches suggest a hopeful future, as they may provide enhanced results in the sterilization of medical devices in the field of healthcare equipment disinfection. As these technologies continue to develop, their real-world applications could significantly advance clinical practices and patient safety in 2024 and beyond.
It is essential to balance innovation with practicality in the design of healthcare tools to fully utilize the advantages of these advanced cleaning techniques.
Navigating Regulatory Requirements for Medical Device Sterilization
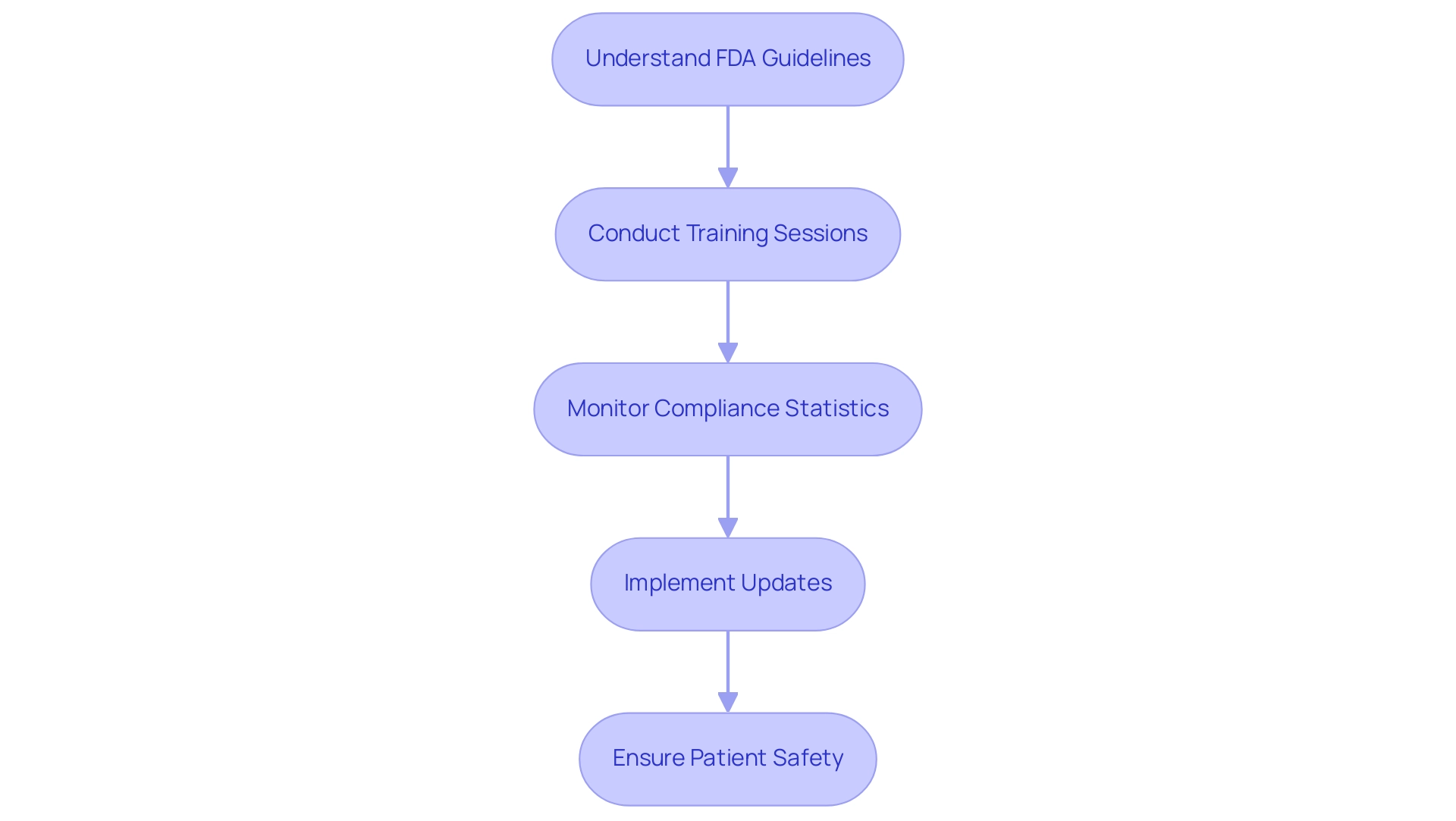
Adherence to regulatory authorities like the FDA and ISO is crucial for the purification of healthcare instruments, as these organizations create extensive protocols that regulate cleansing techniques, validation procedures, and required documentation. The COVID-19 pandemic significantly raised the demand for sterilization of medical devices and equipment due to increased hospitalizations, making it imperative for medical device manufacturers to stay informed about regulatory compliance statistics and updates. According to Cognitive Market Research, the disinfection instruments category is acknowledged as the fastest expanding segment within the Medical Device Disinfection industry, highlighting the urgent requirement for compliance with established standards.
Understanding FDA guidelines is crucial, as it guarantees that the sterilization of medical devices not only meets standards for effectiveness but also aligns with evolving industry expectations. Additionally, in response to possible shortages of healthcare equipment, FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb emphasized the Agency's proactive actions on March 26, 2019, which are still pertinent today. Consistent training sessions and updates on regulatory changes are essential for maintaining compliance and protecting patient well-being.
This proactive approach is underscored by industry experts such as Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, who emphasizes the importance of regulatory adherence in the rapidly evolving landscape of medical device manufacturing. Her expertise in biomedical engineering and health economics provides invaluable insights into navigating the complexities of FDA regulations, ensuring that organizations remain at the forefront of industry standards. For instance, staying updated on compliance metrics can lead to improved operational efficiencies and reduced risks associated with regulatory non-compliance, ultimately enhancing patient safety.
Conclusion
The sterilization of medical devices is a cornerstone of patient safety and treatment efficacy in healthcare. This article has explored the various methods of sterilization, including steam, chemical, and radiation techniques, emphasizing the unique advantages and limitations of each. Ethylene oxide (EtO) sterilization, in particular, stands out as a crucial method, particularly for heat-sensitive devices, despite its associated concerns regarding toxicity and environmental impact. The insights provided by industry experts underline the importance of balancing the benefits of EtO with stringent safety protocols to mitigate potential risks.
Validation plays a significant role in ensuring that sterilization processes consistently achieve the desired sterility assurance levels. Adherence to established standards such as ISO 11135 and FDA regulations is essential for maintaining the reliability and effectiveness of these processes. The evolving landscape of sterilization technologies, including innovative alternatives like hydrogen peroxide gas plasma and ozone sterilization, showcases the industry's commitment to enhancing safety and efficiency in response to modern healthcare demands.
Navigating the regulatory requirements is paramount for medical device manufacturers, especially in light of the increased need for sterilization services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Staying informed about compliance metrics and updates is vital for safeguarding patient safety and ensuring operational efficiency. As the healthcare sector continues to evolve, a proactive approach to sterilization practices, combined with a focus on innovation and regulatory adherence, will be critical in maintaining high standards of care and safety for patients. Ultimately, understanding and implementing effective sterilization methods is not only a regulatory obligation but a fundamental component of quality healthcare delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of sterilization of medical devices?
The sterilization of medical devices aims to eradicate all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, and spores, from medical instruments to ensure patient safety and uphold hygiene standards in healthcare environments.
What are the main techniques used for the sterilization of medical devices?
The main techniques for sterilization include steam treatment, chemical processes, and radiation, each with its own benefits and drawbacks depending on the materials of the devices and their intended use.
Why is ethylene oxide (EtO) disinfection significant in the healthcare system?
Ethylene oxide disinfection is significant because it effectively sanitizes intricate healthcare instruments without causing harm, making it the preferred option for temperature-sensitive products. It plays a crucial role in disinfecting approximately 20 billion medical devices annually in the U.S. healthcare system.
What are the concerns associated with ethylene oxide disinfection?
Concerns include the toxicity of ethylene oxide and its environmental impact, necessitating careful handling and adherence to established precautionary protocols to mitigate health risks associated with residual exposure.
What regulatory measures are in place for the use of ethylene oxide?
Regulatory measures include proposed emissions standards limiting ethylene oxide emissions and requirements for facilities to conduct thorough risk assessments and maintain detailed maintenance logs related to Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMS).
Do 510(k) holders need to submit a new application for certain changes to sanitation facilities?
Typically, 510(k) holders do not need to submit a new 510(k) for certain changes to sanitation facilities, which helps ensure compliance and efficiency in the regulatory process.
Why is proper aeration after sterilization important?
Proper aeration after the sterilization of medical devices is critical to mitigate health risks associated with residual ethylene oxide exposure, ensuring the safety of both patients and healthcare workers.
How do recent studies support the effectiveness of ethylene oxide sterilization?
Recent studies indicate that the sterilization of medical devices using ethylene oxide achieves a significant reduction in microbial load, reinforcing its effectiveness in maintaining high standards of security and sterility in healthcare settings.




