Introduction
Navigating the complex landscape of FDA approval for medical devices is a critical endeavor for manufacturers aiming to bring innovative solutions to market. The financial implications of this process can be substantial, influenced by various factors such as registration fees, user fees, and clinical trial costs. Understanding these elements is essential for effective budget planning and strategic decision-making.
As organizations strive to comply with stringent regulatory requirements, the importance of a well-structured submission strategy becomes increasingly clear. This article delves into the multifaceted costs associated with FDA approval, offers insights into user fees and financial assistance for small businesses, and outlines best practices for estimating clinical trial expenses and post-approval considerations, ultimately guiding manufacturers toward a successful market launch.
Understanding the Costs of FDA Approval for Medical Devices
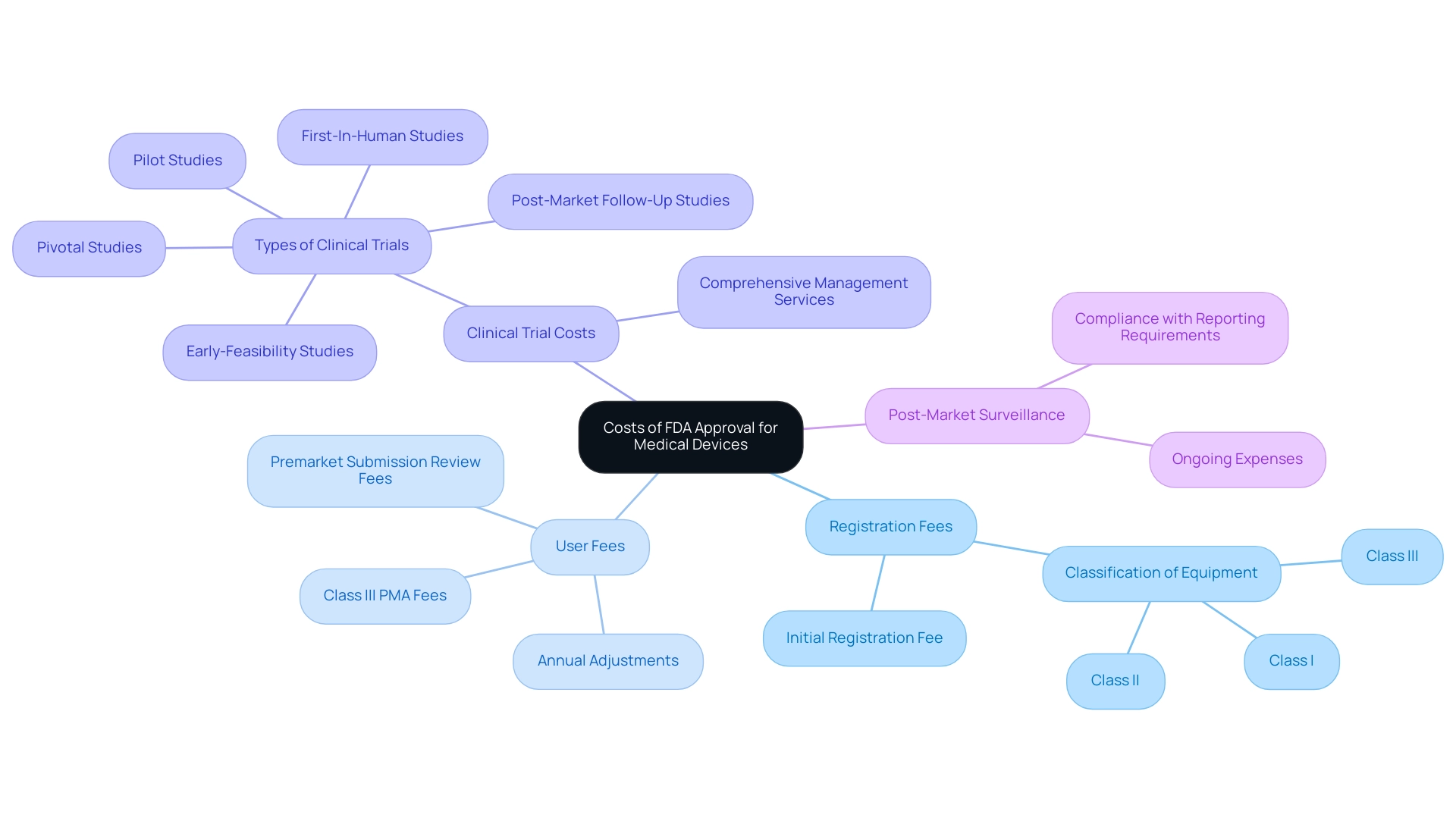
The expenses related to how much does FDA approval cost for medical devices can vary significantly depending on the type of instrument and the regulatory route chosen. Major components influencing these costs include:
- Registration Fees: Manufacturers are required to pay an initial registration fee to list their product with the FDA. This fee is contingent upon the classification of the equipment, which may fall into Class I, II, or III categories.
- User Fees: The FDA charges user fees for reviewing premarket submissions, which are adjusted annually. These fees can be particularly substantial for Class III products that necessitate a Premarket Approval (PMA).
- Clinical Trial Costs: Many medical devices must undergo clinical trials to establish their safety and efficacy, often representing one of the most significant expenses throughout the approval process. At bioaccess®, we leverage our 20+ years of experience in Medtech to provide comprehensive clinical trial management services in Latin America, specializing in Early-Feasibility, First-In-Human, Pilot, Pivotal, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies. Our adaptable and targeted method guarantees that all facets of trial preparation, site selection, compliance assessments, and project oversight are managed effectively, aiding in reducing expenses.
- Post-Market Surveillance: Following approval, manufacturers may face ongoing expenses related to post-market studies and compliance with mandatory reporting requirements.
In 2023, the FDA covered expenses for 72 individuals attending the Drug Information Association Global Annual Meeting, highlighting the financial commitments involved in the regulatory landscape. As Jim Welch, EY Global MedTech Leader, states, "Understanding these financial elements is crucial for manufacturers as it aids in effective budget planning and timeline management." This insight underscores the importance of being prepared for how much does FDA approval cost for medical devices and the financial obligations associated with it.
Furthermore, the FDA's 510(k) application process, the most prevalent regulatory route for low-to-moderate risk medical instruments, demonstrates these expenses in practice. The average time to receive a decision on 510(k) applications was 147 days in 2021, which can extend due to requests for additional information, further emphasizing the need for manufacturers to plan accordingly. By leveraging our expertise at bioaccess®, manufacturers can ensure they are adequately prepared for how much does FDA approval cost for medical devices, navigating the complexities of regulatory requirements and optimizing their clinical trial processes.
Navigating User Fees and Financial Assistance for Small Businesses
Navigating user fees presents unique challenges for small medical equipment manufacturers. Understanding the following key points can help streamline the process:
-
User Fee Structure: The FDA's user fee framework encompasses various submission types, including 510(k) submissions and Premarket Approvals (PMAs). Small businesses may be eligible for reduced fees based on specific criteria, which can significantly alleviate financial burdens. User fees support programs that strengthen input from patients and enhance product safety, underscoring their importance in the regulatory landscape.
-
Small Business Qualification: To be recognized as a small business by the FDA, manufacturers must adhere to outlined criteria, including revenue limits. Achieving this qualification is crucial, as it can lead to substantial reductions in user fees. As stated by the FDA,
The Organization ID Number (Org ID) uniquely identifies a business in the FDA User Fee System, underscoring the importance of proper registration. It is also important to note that if an application is submitted before the FDA qualifies a business as a small business, the standard fee must be paid, and the FDA will not refund the difference if the business later qualifies.
-
Financial Assistance Programs: The FDA provides various programs aimed at assisting small businesses with the costs associated with regulatory submissions. This includes grants and funding opportunities available through initiatives such as the Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program, designed to support innovation and reduce financial barriers.
-
Consultation Services: Small businesses should leverage FDA consultation services to gain critical insights into the approval process and understand potential financial implications. These consultations can serve as a valuable resource for navigating the complexities of user fees and regulatory requirements.
-
Case Study: For instance, the case study titled "Benefits of User Fee Programs" illustrates how user fees have expedited the accessibility of new medical instruments to the public. This program has resulted in improved patient-centered methods in medical product development, along with funding for FDA inspections to safeguard clinical trial participants.
By thoroughly grasping the user fee framework and actively investigating available financial aid options, small businesses can more effectively handle the expenses associated with FDA approval, paving the way for more successful outcomes in the medical device sector.
Estimating Clinical Trial Costs and Budgeting
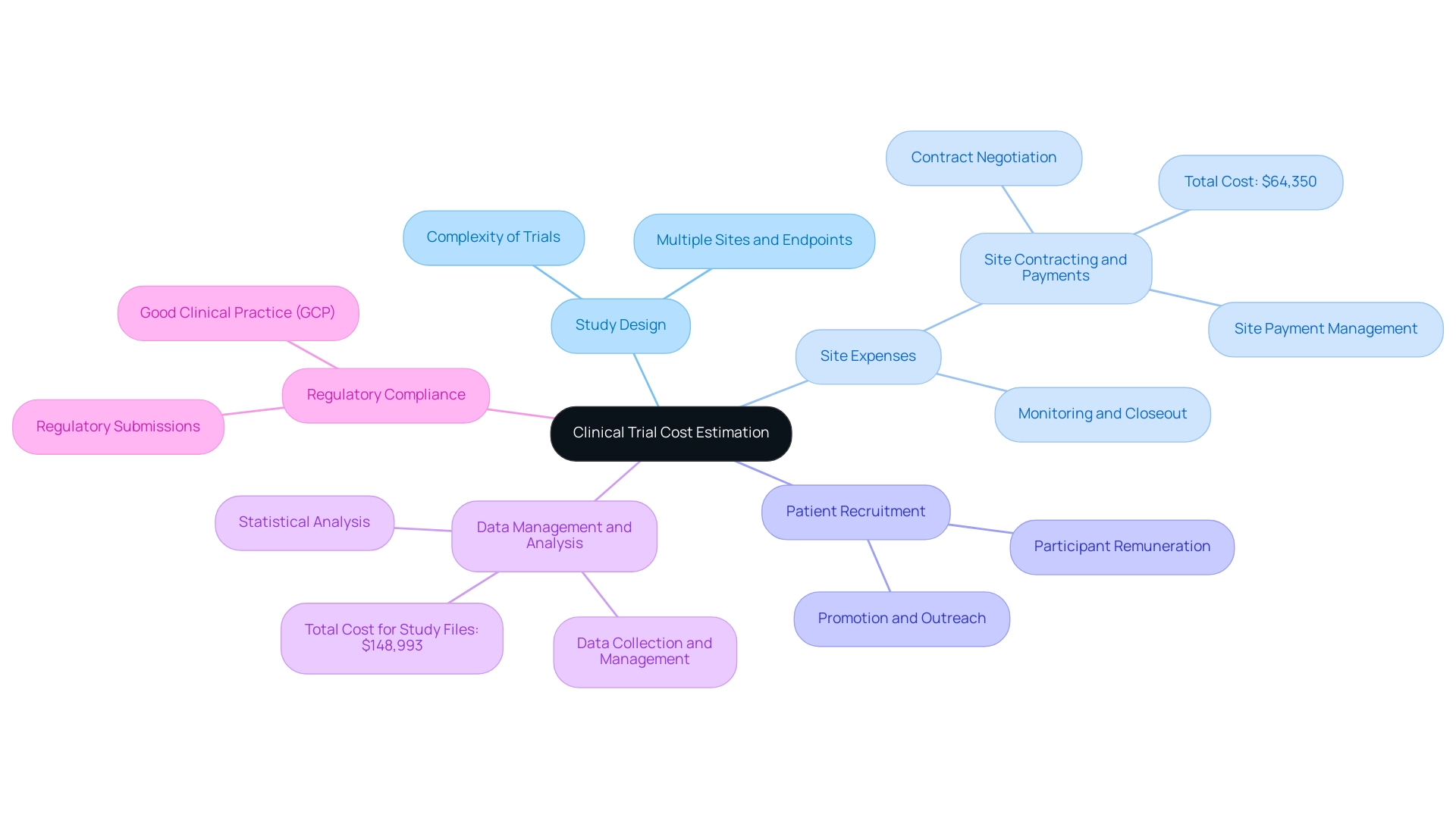
Estimating clinical trial expenses comprises several critical components that significantly influence the overall financial commitment. These include:
- Study Design: The intricacy of the research design is a pivotal factor; more complex trials, especially those involving multiple sites and endpoints, inherently incur higher expenses.
- Site Expenses: It is essential to budget for expenses related to site selection, initiation, monitoring, and closeout. This encompasses fees paid to clinical investigators and site staff, which can accumulate substantially. Notably, site contracting and payments involve contract negotiation and site payment management, totaling $64,350. Our service capabilities include feasibility and selection of research sites and principal investigators (PIs) to ensure optimal trial conditions.
- Patient Recruitment: Expenses associated with recruiting and retaining participants must be carefully considered. This may entail expenses for promotion, outreach initiatives, and participant remuneration to ensure sufficient enrollment and retention throughout the research period.
- Data Management and Analysis: Allocate funds for comprehensive data collection, management, and statistical analysis. This aspect is crucial for meeting regulatory requirements and ensuring the integrity of the findings. Indeed, the overall expense for research files and document management is projected to be $148,993, emphasizing the significance of this element. Our project management services support these efforts by monitoring study progress and reporting on study status, inventory, and both serious and non-serious adverse events.
- Regulatory Compliance: A thorough budget must also encompass expenses for regulatory submissions and adherence to Good Clinical Practice (GCP). These expenses are vital for obtaining necessary approvals from regulatory bodies like the FDA and Anvisa. Our compliance reviews ensure that research documents meet country requirements, facilitating smoother approval processes.
Furthermore, various elements influence clinical trial expenses, including trial size, locations, the number of clinical sites, therapeutic area, drug type, and specific tests and procedures. By meticulously assessing these expenses and constructing a detailed budget, manufacturers can adeptly navigate the complex financial landscape of clinical trials, including how much does FDA approval cost for medical devices. Furthermore, insights from the case study titled "Methodological Contributions to R&D Cost Estimation" suggest that employing a novel approach to estimate R&D costs—allocating total R&D spending across patient-months—can provide a clearer picture of expenses related to new drug development.
According to Stephanie Rennane, a PhD expert in the field, > Policymakers and researchers should consider median R&D costs and other nonparametric descriptive statistics... when considering the typical R&D costs per new drug. This perspective emphasizes the need for a nuanced approach to budgeting in clinical trials, ensuring that manufacturers are well-equipped for the financial challenges ahead.
Developing a Comprehensive FDA Submission Strategy
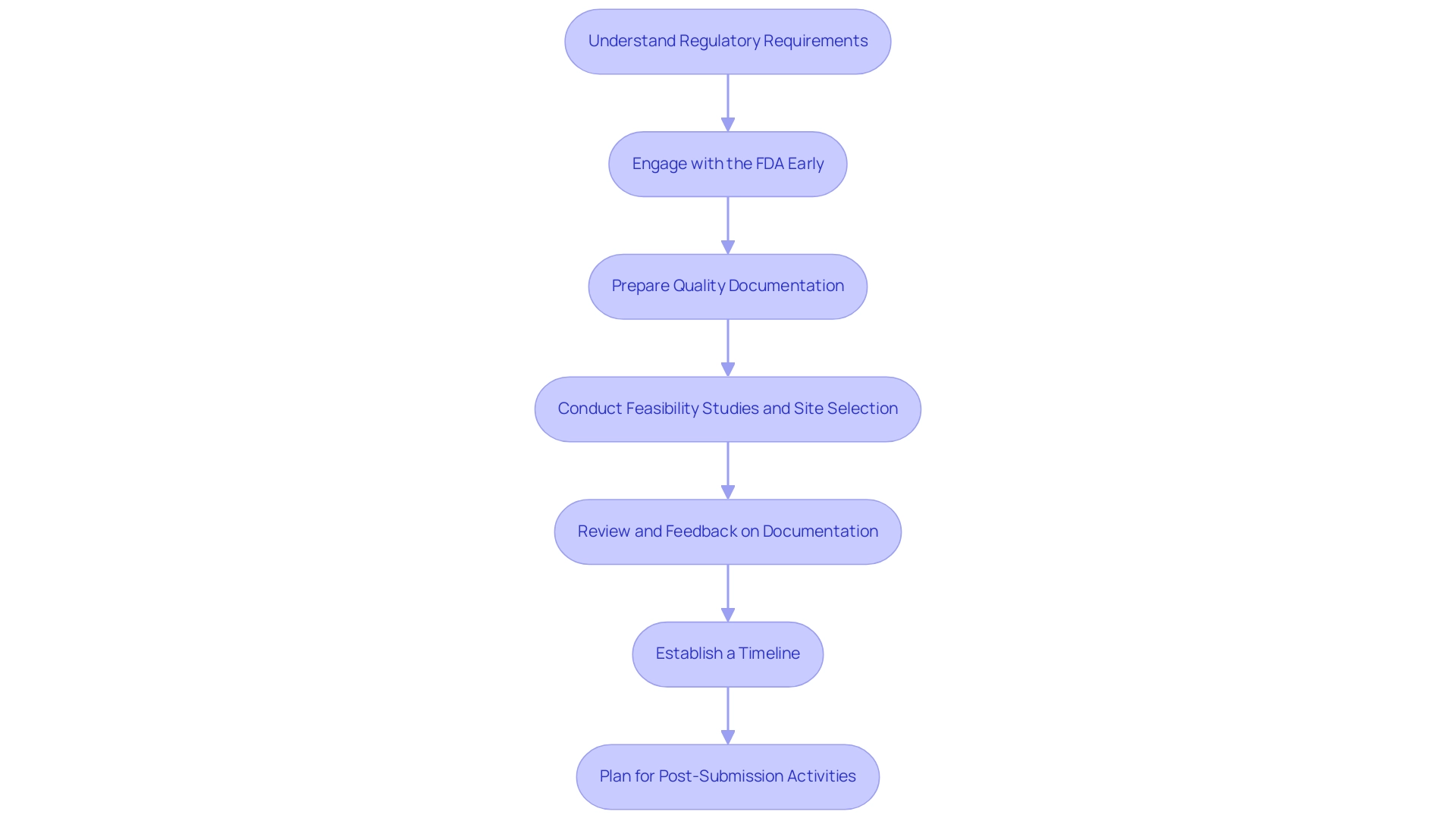
To develop a comprehensive FDA submission strategy, manufacturers should adhere to the following critical steps:
-
Understand Regulatory Requirements: It is essential to familiarize yourself with the specific requirements corresponding to your classification and the applicable FDA regulations. This foundational knowledge is vital for ensuring compliance throughout the submission process.
-
Engage with the FDA Early: Early engagement through pre-submission meetings and informational meetings, which are a type of Q-Sub, is invaluable. These meetings allow manufacturers to clarify expectations and gather crucial feedback on their submission plans. As noted by the FDA,
We are not able to answer this question before we fully understand the intended use of your product,
underscoring the need for clear communication and a thorough understanding of the product's intended use as a cornerstone of the submission strategy.
-
Prepare Quality Documentation: Quality documentation is paramount. Ensure that all necessary documentation—including clinical data, manufacturing information, and labeling—is meticulously prepared and adheres to FDA standards. This thoroughness not only enhances credibility but also streamlines the review process.
Engaging regulatory consultants, such as Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for medical devices and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, can optimize this aspect by providing expertise in documentation and compliance, ultimately helping to streamline timelines and budgets.
-
Conduct Feasibility Studies and Site Selection: Assessing the feasibility of potential research sites and selecting qualified principal investigators (PIs) are crucial steps in ensuring the success of clinical trials. This process assists in recognizing the most appropriate settings for carrying out research and recruiting participants effectively.
-
Review and Feedback on Documentation: Manufacturers should prioritize the review and feedback of documents to ensure compliance with country requirements. This step is essential for aligning the submission with regulatory expectations and minimizing the risk of delays.
-
Establish a Timeline: Create a detailed timeline that outlines key milestones. This should include submission dates, expected review periods, and follow-up actions, which are critical for maintaining momentum in the approval process. Additionally, our service capabilities, including trial setup and project management, can assist in adhering to these timelines effectively.
-
Plan for Post-Submission Activities: Manufacturers should anticipate potential requests from the FDA for additional information and prepare accordingly. Proactive planning can significantly reduce delays and facilitate a smoother review process. Our comprehensive services, which include reporting on study status and inventory management, can play a vital role in this phase.
By following these structured steps and leveraging the expertise of regulatory consultants and our clinical trial management services, including feasibility studies and document reviews, manufacturers can significantly improve their chances of a successful FDA submission and expedite the overall approval process, ultimately leading to more efficient market entry for their medical products.
Post-Approval Considerations and Market Launch
Upon obtaining FDA approval, manufacturers must navigate several essential post-approval factors to ensure the successful introduction of their medical products:
- Post-Market Surveillance: A robust plan for monitoring the product's performance in the market is crucial. This includes adhering to the FDA's requirements for adverse event reporting and conducting post-market studies. The finalized document titled 'Best Practices in Drug and Biological Product Postmarket Safety Surveillance for FDA Staff,' released in January 2024, emphasizes ongoing safety surveillance and outlines risk-based principles that manufacturers should integrate into their strategies. As Lauren K. Roth, Associate Commissioner for Policy, stated on January 23, 2024, 'Effective post-market surveillance is critical to ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical products in real-world settings.'
- Compliance with Labeling Requirements: It is imperative to ensure that all labeling and promotional materials strictly follow FDA regulations to prevent misleading claims that could jeopardize the product's market presence and reputation. The Cures Act has amended section 505(r)(2)(D) of the FD&C Act, eliminating the requirement for summary analyses for drugs, which highlights the evolving nature of compliance regulations and their implications for manufacturers.
- Quality Management Systems: Establishing a comprehensive quality management system is vital for continuously addressing manufacturing processes and ensuring product quality. This proactive approach is essential for maintaining compliance with FDA standards.
- Market Launch Strategy: Developing a detailed market launch strategy that includes pricing, distribution channels, and marketing plans is critical for maximizing the device's success in a competitive landscape, particularly in relation to how much does FDA approval cost for medical devices. Effective strategies often lead to smoother market entry and increased adoption rates among healthcare providers.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with healthcare professionals and key stakeholders is essential to gather valuable feedback and enhance the product based on real-world use. This iterative process can significantly enhance user satisfaction and product performance.
Additionally, utilizing comprehensive clinical trial management services offered by bioaccess®, which include Early-Feasibility Assessments, First-In-Human Trials, Pilot Trials, Pivotal Trials, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Trials, can streamline the processes of feasibility evaluations, site selection, compliance reviews, and trial setup. With over 20 years of experience in Medtech and expertise in Regulatory Affairs, bioaccess® ensures that manufacturers are well-equipped to navigate the post-approval landscape effectively. By meticulously addressing these post-approval considerations and integrating guidelines from the case study 'Best Practices for FDA Staff in Postmarketing Safety Surveillance,' manufacturers can facilitate a successful transition from development to market, ensuring regulatory compliance and positioning themselves favorably within the healthcare sector.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of FDA approval for medical devices requires a comprehensive understanding of the associated costs and strategic planning. Key financial components, such as:
- Registration fees
- User fees
- Clinical trial costs
can significantly impact a manufacturer's budget. By recognizing these elements, organizations can prepare more effectively for the financial obligations that accompany the approval process.
For small businesses, understanding the user fee structure and exploring available financial assistance can alleviate some of the financial burdens. Engaging with the FDA early and utilizing consultation services are essential steps in streamlining the submission process. Additionally, accurate estimation of clinical trial costs and a well-structured submission strategy are vital for facilitating a successful market launch.
Post-approval, manufacturers must focus on ongoing compliance and market strategies, including:
- Post-market surveillance
- Quality management systems
By addressing these considerations, manufacturers can not only ensure regulatory compliance but also enhance their product's success in the competitive healthcare landscape.
In conclusion, a thoughtful approach to budgeting, regulatory compliance, and strategic planning is crucial for medical device manufacturers aiming to navigate the FDA approval process successfully. By leveraging available resources and expertise, companies can optimize their pathways to market, ultimately leading to innovative solutions that benefit both healthcare providers and patients alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors influence the cost of FDA approval for medical devices?
The cost of FDA approval for medical devices can vary significantly based on the type of instrument and the regulatory route chosen. Major components influencing these costs include registration fees, user fees, clinical trial costs, and post-market surveillance expenses.
What are registration fees related to FDA approval?
Manufacturers must pay an initial registration fee to list their product with the FDA, which is contingent upon the classification of the equipment (Class I, II, or III).
How do user fees affect the FDA approval process?
The FDA charges user fees for reviewing premarket submissions, which can be substantial, particularly for Class III products that require a Premarket Approval (PMA). These fees are adjusted annually.
What are the clinical trial costs associated with FDA approval?
Many medical devices must undergo clinical trials to establish their safety and efficacy, which often represents one of the most significant expenses throughout the approval process.
What ongoing expenses might manufacturers face after FDA approval?
After approval, manufacturers may incur ongoing expenses related to post-market studies and compliance with mandatory reporting requirements.
What is the average time to receive a decision on 510(k) applications?
The average time to receive a decision on 510(k) applications was 147 days in 2021, but this can extend if additional information is requested.
How can small medical equipment manufacturers manage user fees?
Small manufacturers can manage user fees by understanding the user fee structure, qualifying as a small business to potentially benefit from reduced fees, and utilizing financial assistance programs provided by the FDA.
What criteria must a manufacturer meet to qualify as a small business?
Manufacturers must adhere to outlined criteria, including revenue limits, to be recognized as a small business by the FDA, which can lead to substantial reductions in user fees.
What financial assistance programs are available for small businesses?
The FDA offers various programs, including grants and funding opportunities through initiatives like the Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program, aimed at assisting small businesses with regulatory submission costs.
How can small businesses benefit from FDA consultation services?
Small businesses can leverage FDA consultation services to gain insights into the approval process and understand potential financial implications, which can help navigate user fees and regulatory requirements effectively.




