Overview
Mastering randomized clinical trials (RCTs) for medical devices is essential in today's clinical research landscape. Understanding key concepts such as:
- Randomization
- Control groups
- Blinding
is crucial for minimizing bias and ensuring valid outcomes. Effective design and execution of RCTs, supported by comprehensive management services, are critical for advancing medical device development. This approach not only enhances patient outcomes but also ensures adherence to regulatory and ethical standards. As the Medtech landscape evolves, collaboration and adherence to these principles will be pivotal in overcoming key challenges.
Introduction
In the realm of medical research, randomized clinical trials (RCTs) represent the gold standard for evaluating the efficacy and safety of new treatments and devices. These meticulously designed studies are crafted to eliminate bias, ensuring that results are both reliable and applicable to real-world scenarios. At their core, RCTs utilize randomization to provide a robust framework for comparing treatment effects while safeguarding the integrity of the data collected.
However, the journey from trial conception to market approval is fraught with challenges, including:
- Recruitment hurdles
- Regulatory complexities
- The ongoing necessity for ethical oversight
As the landscape of clinical trials continues to evolve, it becomes increasingly crucial for stakeholders to understand the phases of these studies, the significance of randomization, and the importance of post-market surveillance in advancing medical innovations. This article delves into the essential components of RCTs, offering insights into best practices and emerging trends designed to enhance the reliability and impact of clinical research within the medical device sector.
Understanding Randomized Clinical Trials: Key Concepts and Definitions
Randomized Clinical Trials (RCTs) are essential scientific experiments meticulously designed to minimize bias in evaluating new treatments. In RCTs, individuals are randomly assigned to either the treatment group or the control group, a critical step for ensuring comparability between the groups. This randomization process is fundamental in eliminating selection bias, thereby enhancing the validity of the trial's outcomes.
Key concepts in RCTs include:
- Randomization: This cornerstone of RCTs involves the chance assignment of participants to different groups. By doing so, it mitigates the risk of bias that could skew results, ensuring that the treatment effects can be attributed to the intervention rather than pre-existing differences among individuals.
- Control Group: This group does not receive the experimental treatment and serves as a benchmark against which the treatment's effectiveness can be measured. The presence of a control group is vital for establishing a causal relationship between the treatment and observed outcomes.
- Blinding: This technique involves keeping individuals and/or researchers unaware of group assignments to prevent bias in treatment administration and outcome assessment. Blinding can be single (only participants are blinded) or double (both participants and researchers are blinded), significantly enhancing the integrity of the study results.
Grasping these concepts is essential for interpreting RCT results and their implications in medical practice. Recent research indicates that a significant percentage of medical trials, approximately 70%, utilize randomization to ensure robust findings. Moreover, a recent study published in NEJM Evidence concluded that RCT reports in prominent medical journals often lack adequate information for readers to evaluate the importance of results, recommending clear reporting of primary outcomes, sample size delta values, and discussions on significance.
For instance, the sample size delta value was observed to be a 4% absolute difference over a 3.5-year period in the same research.
Furthermore, a case study named "Assessment of Reporting Standards in High-Impact Journals" disclosed that essential elements required for understanding significance in a medical context were frequently underreported. This necessitates better compliance with reporting standards to improve the clarity and usefulness of RCT findings for medical practice. As research expert Andreas Laupacis stated, "Our findings demonstrate that the reports of RCTs published in major general medical and internal medical journals do not provide consistently the authors' interpretation of the significance of their results."
At bioaccess®, we understand that reducing bias in randomized clinical trials for devices is paramount for advancing medical device development and ensuring that innovations translate effectively into improved patient outcomes. Our comprehensive clinical study management services encompass feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, setup, import permits, project management, and reporting, ensuring that your clinical studies are conducted with the utmost expertise and efficiency. With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, we are well-equipped to guide you through Early-Feasibility, First-In-Human, Pilot, Pivotal, and Post-Market Follow-Up Studies, navigating the complexities of regulatory environments such as INVIMA in Latin America to ensure successful outcomes.
Phases of Clinical Trials: From Initial Testing to Market Approval
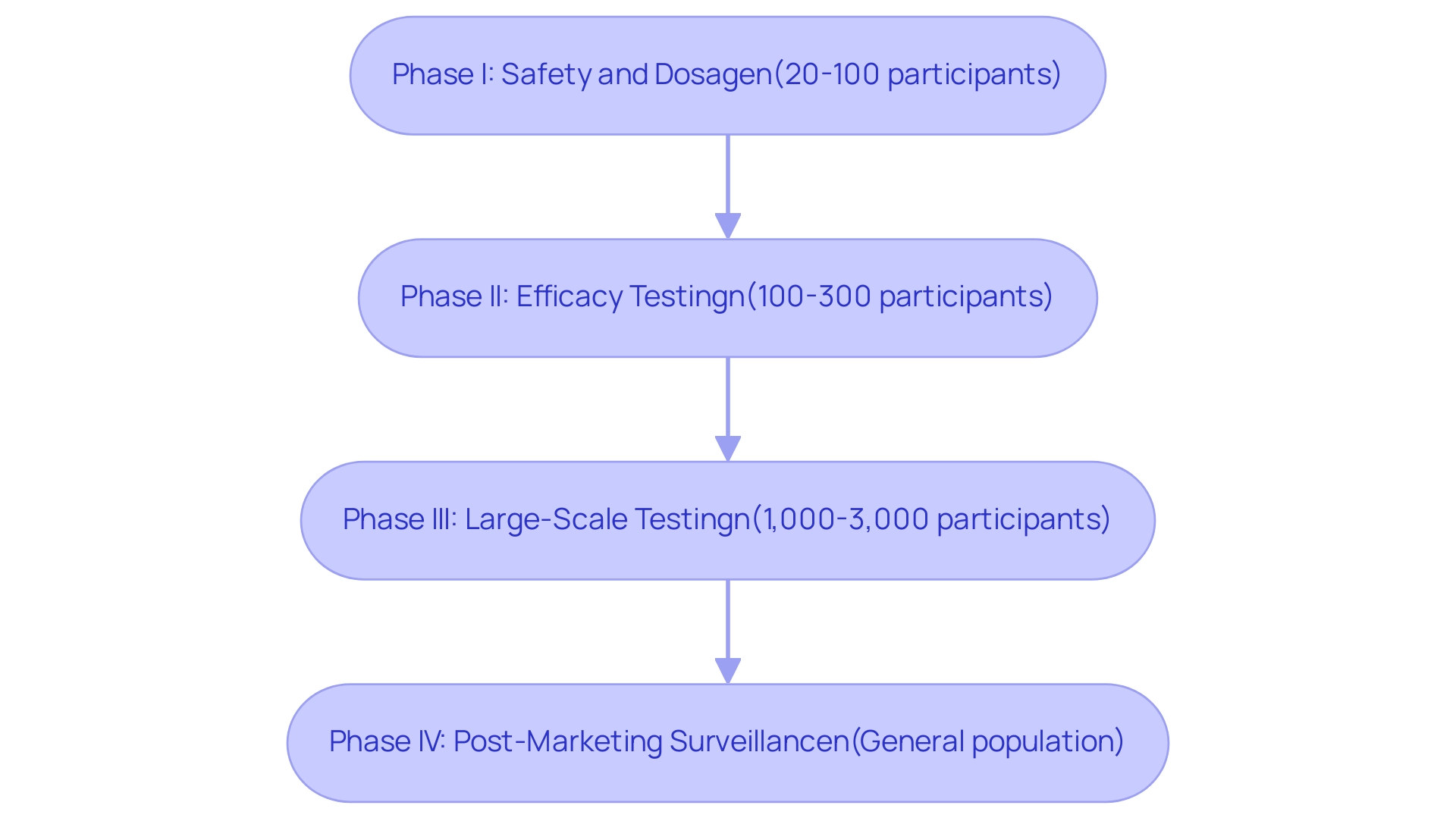
Clinical trials are systematically categorized into four primary phases, each serving a distinct purpose in the evaluation of medical devices.
- Phase I: This initial phase is critical for assessing safety and dosage. It typically involves a small group of individuals, ranging from 20 to 100, to establish the treatment's safety profile and identify any potential side effects.
- Phase II: Building on the findings from Phase I, this phase tests the treatment's efficacy in a larger group of individuals, usually between 100 and 300. Safety continues to be monitored closely, ensuring that any adverse effects are documented and addressed.
- Phase III: Characterized by large-scale testing, this phase often involves 1,000 to 3,000 participants. The primary goal is to confirm the treatment's effectiveness, monitor side effects, and compare the new treatment against standard therapies. Successful completion of Phase III is essential for regulatory approval.
- Phase IV: Conducted post-approval, Phase IV studies concentrate on the long-term effects and safety of the treatment within the general population. This phase is vital for ongoing monitoring and can provide insights into the treatment's performance in real-world settings, which is particularly important in the context of randomized clinical trials for devices. Understanding these phases is essential for navigating the lifecycle of medical devices.
Recent statistics indicate that the completion rates for research phases have shown improvement, with Phase III studies achieving a completion rate of approximately 70% in 2025. This statistic is backed by bioaccess®, highlighting their participation in all research phases I-IV, thereby enhancing the credibility of these findings.
Moreover, insights from medical researchers emphasize a rising trend towards sponsors managing data internally for randomized clinical trials for devices, which improves control and quality in research studies.
The average number of participants in each phase indicates the growing complexity and scale of studies, with Phase I typically involving 20-100 participants, Phase II expanding to 100-300, and Phase III reaching up to 3,000. As the environment of research studies evolves, the incorporation of technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning is anticipated to enhance operations, possibly decreasing study durations by up to 30% and expenses by as much as 20%. This shift not only enhances patient recruitment and retention but also results in more efficient and adaptable research studies, emphasizing the significance of optimizing study design for successful outcomes.
As Vivienne van der Walle, Founder and Medical Director, aptly noted, 'Anything that takes away time from patients is a pain point for a site, and anyone who resolves that is helping patient care.' This emphasizes the essential requirement for effective research study procedures. Furthermore, bioaccess® aims to advance medical devices sooner through their expertise and customized approach, specializing in Early-Feasibility Evaluations (EFS), First-In-Human Trials (FIH), and other pivotal assessments.
Their dedication to improving the research landscape is strengthened by extensive services that encompass feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, setup, import permits, project management, and reporting.
The Role of Randomization in Clinical Trials: Ensuring Validity and Reducing Bias
Randomization serves as a cornerstone of randomized studies, fulfilling several essential purposes that significantly enhance the integrity of medical research.
- Eliminating Bias: The random assignment of subjects is paramount in minimizing selection bias. This process guarantees that any observed differences in outcomes can be attributed to the treatment itself rather than pre-existing differences among individuals. Research indicates that RCTs employing proper randomization can reduce bias by over 80%, underscoring its critical role in achieving reliable results.
- Enhancing Validity: The comparability of treatment and control groups is vital for drawing valid conclusions. Randomization ensures that these groups are similar in all respects except for the intervention being tested. This comparability is essential for establishing causality and is a fundamental principle in study design.
- Facilitating Blinding: Effective blinding is achievable through randomization, where neither subjects nor researchers are aware of group assignments. This further mitigates bias and upholds the objectivity of the study. The ability to obscure group assignments is associated with improved study results and subject retention, both critical for the success of any clinical investigation.
Understanding these facets of randomization is crucial for accurately interpreting RCT outcomes. For example, the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccine studies exemplified the successful implementation of randomization, achieving high minority representation through community engagement. This approach not only enhanced the validity of the findings but also established a precedent for future studies striving for diverse participant cohorts.
The community engagement strategies applied in these studies illustrate how effective recruitment can yield more representative samples, addressing disparities highlighted by experts like Brandon Turner, who noted that the largest disparities in health outcomes are often observed in Black Americans.
As we look ahead to 2025, expert opinions continue to underscore the necessity of minimizing bias through robust randomization techniques. Current discussions emphasize that a proportion of less than 5% missing outcome data is considered 'small', while over 20% is regarded as 'large'. This statistic illustrates the importance of meticulous study design, as high levels of missing data can jeopardize the integrity of results.
By adhering to these best practices, researchers conducting randomized clinical trials for devices can ensure that their studies yield credible and actionable insights, ultimately advancing the field of medical technology. Bioaccess® aims to expedite the development of medical devices through its expertise in extensive research management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, setup, import permits, project management, and reporting. These services are crucial for conducting randomized clinical trials for devices in the research landscape.
Navigating Regulatory Requirements: Compliance and Ethical Considerations in RCTs
Conducting randomized research studies (RCTs) necessitates navigating a complex regulatory environment that is crucial for ensuring the integrity and ethical validity of medical research. Key components include:
- Ethics Committees: These review boards play a critical role in protecting individuals' rights and ensuring that studies conform to ethical standards. Recent data shows that a notable percentage of medical studies fulfill informed consent standards, demonstrating a dedication to subject protection. Moreover, it is essential for investigators to inform the ethics committee within five working days after the emergency use of an investigational product, highlighting the significance of prompt communication in research studies.
- Informed Consent: It is vital that participants are completely educated about the study's objectives, procedures, potential risks, and benefits before their involvement. This process not only nurtures trust but also adheres to regulatory mandates that underscore the importance of informed consent in research. As emphasized by ethics committee members, the significance of informed consent cannot be exaggerated, as it is fundamental to ethical research practices.
- Regulatory Bodies: Organizations such as the FDA and NIH are crucial in supervising research studies, ensuring adherence to established safety and efficacy standards. In 2025, revised guidance from these organizations has been pivotal in addressing challenges presented by external factors, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, to uphold participant safety and study integrity. Guidance issued by the FDA and NIH for clinical studies affected by COVID-19 highlights the evolving nature of regulatory requirements and their impact on study integrity.
Understanding these regulatory requirements is crucial for conducting ethical and compliant clinical research. For instance, a recent analysis of 150 site activations revealed that study characteristics, including the phase of the study and the mutual acceptance of ethics approvals, significantly influenced the time taken for ethics and governance approvals. This emphasizes the need for streamlined processes to enhance efficiency in testing.
The extensive services provided by bioaccess, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, experiment setup, import permits, project management, and reporting (such as study status updates and adverse event reporting), are intended to streamline this process efficiently.
Furthermore, ethical considerations in randomized research extend beyond informed consent. They encompass the necessity for transparency and fairness in participant selection, as well as the obligation to minimize risks while maximizing potential benefits. The procedure for obtaining research study approval in Colombia involves critical steps such as IRB/EC approval, INVIMA approval, and MinCIT import permits, which are essential for ensuring compliance with local regulations.
In summary, navigating the regulatory landscape of randomized clinical trials for devices involves a comprehensive understanding of ethics committees, informed consent processes, and the oversight of regulatory bodies. By following these principles and utilizing the expertise of bioaccess, researchers can guarantee that their studies are not only compliant but also ethically sound, ultimately aiding in the advancement of medical devices that enhance patient outcomes. Furthermore, as highlighted by Benlidayi IC, the use of engaging formats, such as cartoons in scholarly publishing, can improve communication and engagement, transforming complex scientific concepts into visually appealing and easy-to-understand formats.
Challenges in Conducting Randomized Clinical Trials for Medical Devices
Executing randomized clinical trials for devices necessitates navigating a landscape filled with complex obstacles that can significantly impact results and schedules.
- Recruitment Difficulties: Identifying suitable participants remains a significant hurdle, particularly for devices aimed at specific medical conditions. Data suggest that recruitment difficulties are common, with research revealing that almost 80% of medical studies do not achieve their enrollment goals. This issue is exacerbated for underrepresented populations, who historically have lower participation rates in clinical studies. However, by 2025, underrepresented study populations will have more choices for onboarding and visitations, potentially enhancing recruitment efforts. Engaging these communities through targeted outreach and utilizing technology to streamline participation can improve participation rates, as shown in the case analysis titled '[[[[Diversity in Clinical Trial Recruitment Statistics](https://antidote.me/blog/25-useful-clinical-trial-recruitment-statistics-for-better-results)](https://antidote.me/blog/25-useful-clinical-trial-recruitment-statistics-for-better-results)](https://antidote.me/blog/25-useful-clinical-trial-recruitment-statistics-for-better-results)](https://antidote.me/blog/25-useful-clinical-trial-recruitment-statistics-for-better-results),' which highlights how engaging diverse communities can lead to better outcomes. Notably, bioaccess™'s partnership with Caribbean Health Group aims to establish Barranquilla as a premier location for trials in Latin America, with the backing of Colombia's Minister of Health, potentially enhancing participant diversity and recruitment success.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The regulatory environment for medical devices is intricate, with diverse requirements that vary by region. The recent proposal by the FDA to mandate a single Institutional Review Board (IRB) review for FDA-regulated research seeks to simplify this process, potentially reducing duplicative reviews and expediting study initiation. Nevertheless, exceptions will still be made for local expertise and product-specific pathways, necessitating a thorough understanding of both local and international regulations. Staying informed about these regulatory changes is crucial for research teams. Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for medical devices and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, emphasizes the importance of navigating these complexities effectively, particularly in light of the challenges posed by varying regulatory requirements.
- Ethical Concerns: Balancing the rigorous demands of medical testing with ethical considerations poses another challenge. The use of placebo controls, for instance, raises ethical questions, particularly when effective treatments are available. Clinical researchers must navigate these dilemmas carefully to maintain participant trust and uphold ethical standards. Bree Burks, Vice President of Site Strategy at Veeva, emphasizes that "Sponsors will step up to solve site capacity issues," highlighting the importance of addressing recruitment challenges.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for the successful execution of randomized clinical trials for devices. By employing creative hiring methods, remaining updated on regulatory alterations, and emphasizing ethical factors, research teams can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their studies. bioaccess®'s expertise in managing Early-Feasibility Studies, First-In-Human Studies, Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies positions them as a valuable partner in advancing medical devices sooner, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Effective Patient Recruitment Strategies: Ensuring Diverse and Representative Samples
To ensure successful patient recruitment in medical device clinical trials, implementing the following strategies is essential:
- Utilize Digital Platforms: Harness the power of social media and online registries to expand your reach. Recent data indicates that approximately 60% of clinical studies in 2025 are utilizing digital platforms for recruitment, showcasing their effectiveness in engaging diverse populations.
- Engage Community Organizations: Collaborate with local community groups to raise awareness about the trial and encourage participation. This grassroots approach not only builds trust but also fosters a sense of community involvement.
- Simplify the Enrollment Process: Streamline the enrollment process to minimize barriers to participation. A straightforward approach can significantly enhance recruitment rates, as evidenced by studies showing that the best recruitment groups have a median of 0.0 modifications, compared to 2.0 for the worst. This statistic highlights the significance of simplifying enrollment to draw more individuals.
- Personalized Communication: Tailored messaging can resonate more effectively with potential participants. For instance, a lead gastroenterologist (AL) recently sent personalized letters to patients, stating, "Your involvement in this research could greatly contribute to advancements in medical technology." This approach proved to be an effective recruitment strategy.
- Flexible Monitoring Options: Incorporate flexible and remote monitoring solutions, such as telemedicine and wearable devices, to reduce the burden of frequent visits. This approach not only improves patient retention but also encourages ongoing participation in clinical trials. A case analysis titled 'Strategies for Enhancing Patient Retention' emphasized that implementing such strategies can cultivate loyalty and commitment among individuals.
- Incentives for Participation: Offering incentives can motivate individuals to join and remain in the study. This strategy has been shown to foster loyalty and commitment among participants.
Additionally, new mathematical measures have been developed to assess the cost-effectiveness of recruitment methods, including the enrollment rate and efficacy index. The efficacy index allows for a clear comparison of recruitment methods, helping to identify the most cost-effective strategies.
By adopting these best practices, research teams can significantly improve their recruitment efforts, ensuring that studies are not only successful but also inclusive and representative of the populations they aim to serve.
Data Management and Analysis: Turning Trial Results into Actionable Insights
Data management and analysis are crucial in the success of randomized clinical trials for devices, directly affecting the integrity and relevance of results.
- Data Collection: Implementing systematic and consistent data collection methods throughout the study is essential. This ensures that the data gathered is reliable and can be effectively analyzed. The resurgence of Medical Device Regulation (MDR) emphasizes the necessity for stringent data standards in both research design and data collection processes, reinforcing the importance of meticulous data management practices to comply with regulatory requirements. At bioaccess, our extensive research management services encompass feasibility studies, site selection, and compliance reviews, ensuring that all data collection methods meet the highest standards.
- Statistical Analysis: Utilizing appropriate statistical methods is crucial for analyzing data from experiments, as it guarantees the validity and reliability of the results. Current trends suggest that more than 85% of top pharmaceutical firms are embracing real-world evidence (RWE) initiatives, highlighting the increasing focus on strong statistical frameworks in research. Techniques such as regression analysis, survival analysis, and Bayesian methods are increasingly being employed to derive meaningful insights from complex datasets. Our project management services at bioaccess ensure that statistical analysis is integrated seamlessly into the trial process, enhancing the overall quality of the research.
- Reporting Results: Effectively communicating findings to stakeholders is vital, encompassing both positive and negative outcomes. Transparency in reporting fosters trust and facilitates informed decision-making. As research evolves, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is transforming data handling processes. A case analysis titled "The Rise of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Healthcare Data Management" illustrates how these technologies enhance accuracy and reduce the labor involved in managing healthcare information. By 2025, it is expected that Research Management services will heavily rely on AI to identify patterns in complex datasets and predict outcomes, potentially decreasing study timelines by up to 20%. This technological advancement allows for more nuanced analysis and reporting, further enriching the data management landscape. Additionally, the FDA's Single IRB Requirement is anticipated to be enforced in 2025, which may affect data management practices in clinical studies. At bioaccess, we are committed to providing comprehensive reporting services that ensure all findings, including serious and non-serious adverse events, are communicated effectively.
Mastering these aspects of data management is essential for translating trial results into actionable insights from randomized clinical trials for devices, ultimately advancing the development of medical devices and improving patient outcomes. As noted by the Head of Clinical Data Engineering, "Traditionally, data management was outsourced to our CRO vendor partners. Part of the initiative is to bring all our research in-house so that our internal teams can start working on it. They can be more hands-on, and we operationalize studies in-house and we are able to take control of our data, and we deliver for our patients with high quality." This approach not only enhances data integrity but also contributes to local economies through job creation and healthcare improvements.
Post-Market Surveillance: Ensuring Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Medical Devices
Post-market surveillance is an essential component of the medical device lifecycle, involving the continuous monitoring of devices after they have received regulatory approval. This process is crucial for ensuring long-term safety and efficacy, as well as maintaining public trust in medical technologies.
Effective post-market surveillance begins with systematic data collection on device performance and any adverse events reported by users. This data is vital for identifying potential safety issues and understanding the real-world impact of medical devices.
In 2025, it is estimated that approximately 70% of medical devices will undergo some form of post-market surveillance, reflecting a growing commitment to patient safety. The FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) serves as a centralized global repository supported by over 150 countries, further enhancing the data collection process.
Compliance with regulatory requirements is paramount. In Colombia, the INVIMA (Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute), classified as a Level 4 health authority by PAHO/WHO, plays a vital role in overseeing the marketing and manufacturing of health products, including medical devices.
Manufacturers must adhere to guidelines set forth by authorities such as the FDA and the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which mandates a robust post-market surveillance system tailored to the risks associated with each device. This includes timely reporting of safety issues and performance data to ensure that any emerging risks are addressed promptly. The implementation of a post-market surveillance system in accordance with the MDR has proven essential for manufacturers seeking to obtain and maintain CE marking, which signifies compliance with safety and performance standards necessary for market access in the EU.
The data collected through post-market surveillance should inform future iterations of medical devices, enhancing their safety and efficacy. By analyzing trends and patterns in adverse events, manufacturers can implement design changes and improve user instructions, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. The performance goal of technical success of 85% or greater, based on SIR guidelines, underscores the importance of meeting performance standards. Continuous staff training is also vital to adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes and enhance device safety.
As noted by experts in Regulatory Affairs, including Katherine Ruiz, the evolving nature of many medical devices through continuous learning challenges the robust performance and sustainability of applications based on such models, highlighting the need for ongoing adaptation in post-market practices.
The importance of post-market surveillance cannot be overstated. It not only safeguards patient health but also supports manufacturers in meeting compliance standards. In summary, establishing an effective post-market surveillance system involves meticulous planning, comprehensive data collection, thorough analysis, and proactive actions based on findings.
By prioritizing these practices, medical device manufacturers, including those working with bioaccess®, which specializes in Early-Feasibility Studies, First-In-Human Studies, Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies, can ensure the long-term safety of their products and foster trust among healthcare providers and patients alike.
Conclusion
The landscape of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) is both complex and indispensable for the advancement of medical devices and treatments. Understanding the fundamental principles of RCTs—specifically the significance of randomization, the structured phases of clinical trials, and the regulatory requirements—empowers stakeholders to navigate this intricate field more effectively. Furthermore, the emphasis on ethical considerations and rigorous data management reinforces the integrity of clinical research, ensuring that outcomes are reliable and applicable to real-world settings.
As highlighted throughout the article, overcoming challenges such as recruitment difficulties and regulatory hurdles is crucial for the successful execution of clinical trials. Innovative strategies, including the use of digital platforms and community engagement, enhance participant diversity and retention, ultimately leading to more representative study samples. Moreover, the commitment to post-market surveillance underscores the importance of continuous monitoring to ensure the long-term safety and efficacy of medical devices.
In conclusion, the journey from trial conception to market approval is a multifaceted process that demands collaboration, transparency, and adherence to best practices. As the medical device sector evolves, embracing these principles will not only foster innovation but also enhance patient outcomes, paving the way for a healthier future. By prioritizing rigorous clinical research and ethical standards, stakeholders can contribute to a landscape where medical advancements are both effective and trusted by the communities they serve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Randomized Clinical Trials (RCTs)?
Randomized Clinical Trials (RCTs) are scientific experiments designed to minimize bias in evaluating new treatments by randomly assigning individuals to either a treatment group or a control group.
Why is randomization important in RCTs?
Randomization is crucial because it eliminates selection bias, ensuring that the treatment effects can be attributed to the intervention rather than pre-existing differences among participants.
What is the role of a control group in RCTs?
The control group does not receive the experimental treatment and serves as a benchmark to measure the treatment's effectiveness, helping to establish a causal relationship between the treatment and observed outcomes.
What is blinding in the context of RCTs?
Blinding is a technique that keeps individuals and/or researchers unaware of group assignments to prevent bias in treatment administration and outcome assessment. It can be single (only participants are blinded) or double (both participants and researchers are blinded).
What percentage of medical trials utilize randomization?
Approximately 70% of medical trials utilize randomization to ensure robust findings.
What are the key reporting issues identified in recent RCT studies?
Recent studies have found that RCT reports in major medical journals often lack adequate information for readers to evaluate results, particularly regarding primary outcomes, sample size delta values, and significance discussions.
What are the four primary phases of clinical trials?
The four primary phases of clinical trials are: 1. Phase I: Assessing safety and dosage with 20 to 100 participants. 2. Phase II: Testing efficacy with 100 to 300 participants while monitoring safety. 3. Phase III: Large-scale testing with 1,000 to 3,000 participants to confirm effectiveness and compare against standard therapies. 4. Phase IV: Post-approval studies focusing on long-term effects and safety in the general population.
What is the completion rate for Phase III studies?
The completion rate for Phase III studies is approximately 70% as of 2025.
How is technology impacting clinical trials?
The incorporation of technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning is expected to enhance operations in clinical trials, potentially decreasing study durations by up to 30% and costs by as much as 20%.
What services does bioaccess® provide for clinical studies?
bioaccess® offers comprehensive clinical study management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, project management, and reporting, with expertise in various phases of clinical trials.




