Overview
This article examines the intricacies and prerequisites involved in designing clinical trials for approval in Brazil, with a particular focus on the regulatory framework established by ANVISA and the essential ethical considerations for conducting research.
Understanding local regulations is paramount, as is the need for maintaining compliance and employing effective management strategies to successfully navigate the approval process.
Such efforts are vital in fostering trust and facilitating the advancement of medical research within the country.
Ultimately, the interplay of regulatory knowledge and ethical diligence serves as the foundation for robust clinical research practices.
Introduction
In Brazil, the landscape of clinical trials is shaped by a robust regulatory framework designed to ensure the safety and efficacy of medical research.
Governed primarily by the Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA), this framework emphasizes ethical guidelines, particularly regarding the protection of vulnerable populations and the necessity of informed consent.
Recent legislative reforms, such as Law No. 14.874, aim to streamline the approval process, enabling quicker access to innovative treatments.
As researchers navigate these complexities, understanding the interplay of regulatory bodies and the importance of compliance becomes crucial for fostering trust and advancing medical technology.
This article delves into the intricacies of conducting clinical trials in Brazil, highlighting the regulatory landscape, challenges faced, and strategies for success in this evolving field.
Understanding the Regulatory Framework for Clinical Trials in Brazil
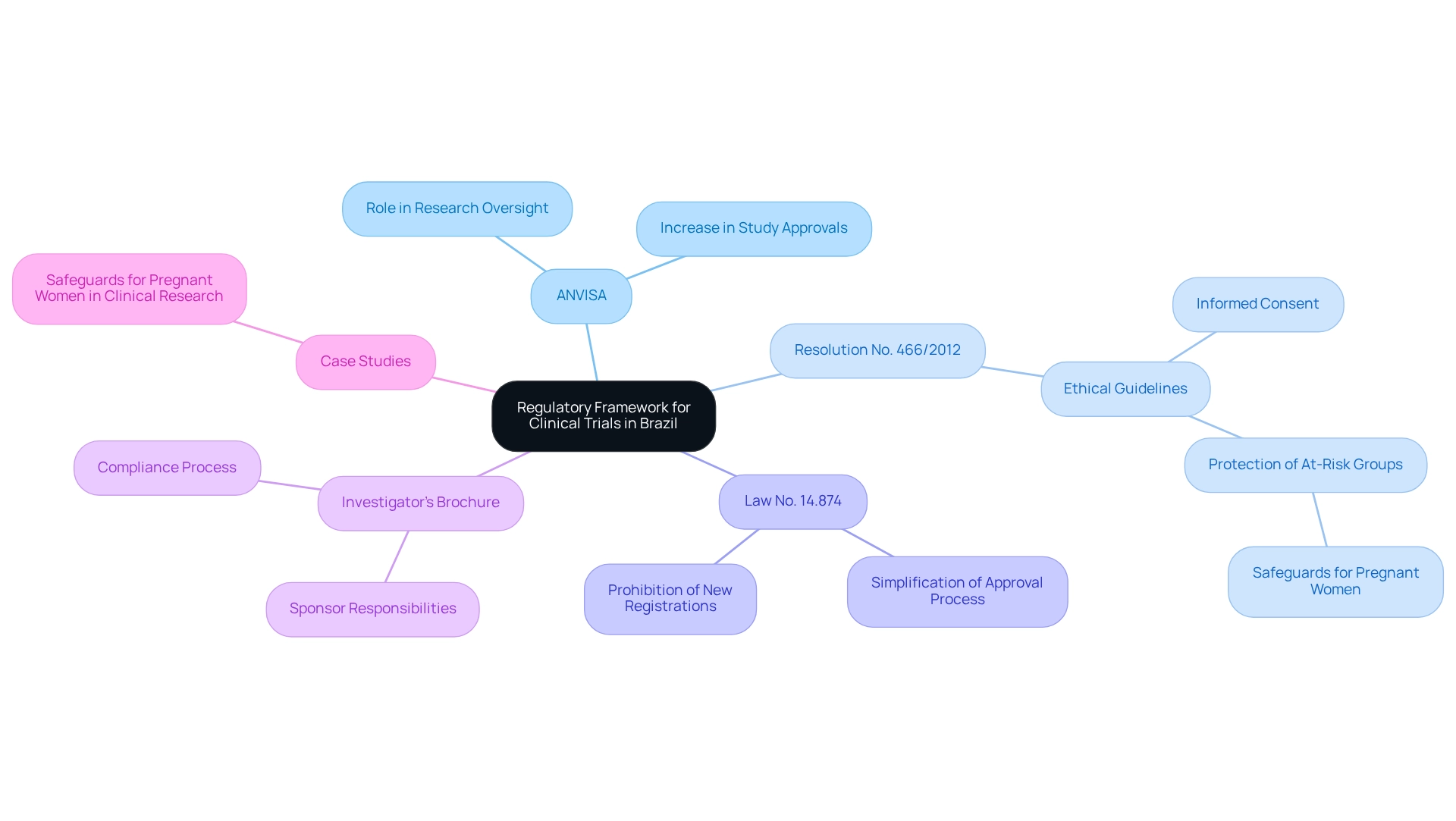
Brazil's regulatory system for research involving human subjects is primarily overseen by the Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA), responsible for the authorization and supervision of these investigations. A cornerstone of this framework is Resolution No. 466/2012, which establishes essential ethical guidelines for conducting research involving human subjects. This regulation underscores the importance of informed consent and the protection of at-risk groups, including expectant mothers, who require additional measures to ensure their safety and welfare during research studies. For instance, investigations involving pregnant women should only occur after examinations on non-pregnant women, and participants must retain the right to engage without mandatory contraceptives if they are not at risk of pregnancy.
In 2024, Brazil introduced Law No. 14.874, aimed at simplifying the research approval process. This law enhances efficiency by reducing bureaucratic hurdles, thereby facilitating quicker access to innovative treatments for patients. Furthermore, it is crucial to acknowledge that demands for new registration by supporting organizations are prohibited for a duration of 12 months following cancellation, emphasizing the necessity for adherence to guidelines.
Understanding these regulations is vital for researchers, as designing trials for approval in Brazil ensures that all investigations conform to local laws and ethical standards, ultimately fostering trust in the research process. Statistics reveal that the number of medical studies authorized by ANVISA has consistently increased, demonstrating the growing trust in Brazil as a suitable site for conducting research. In 2024, ANVISA reported a significant rise in study approvals, showcasing the effectiveness of recent policy reforms.
Successful case studies, such as those involving medical devices and pharmaceuticals, underscore the importance of designing trials for approval in Brazil as a hub for clinical research. These studies not only comply with ANVISA regulations but also highlight the nation's commitment to advancing medical technology while emphasizing participant safety and ethical considerations. Moreover, sponsors are responsible for providing researchers with an Investigator’s Brochure (IB) that addresses multiple aspects concerning the experimental drug, which is an essential component of the compliance process.
By leveraging the expertise of bioaccess®, researchers can adeptly navigate the complexities of Brazil's compliance environment, ensuring comprehensive management services for studies that encompass feasibility assessments, site selection, adherence reviews, setup, import permits, project oversight, and reporting. This strategic approach not only contributes to the development of innovative therapies that benefit patients locally and globally but also stimulates economic growth and healthcare improvement through international collaboration and innovation in Medtech.
Key Regulatory Bodies and Their Roles in Clinical Research
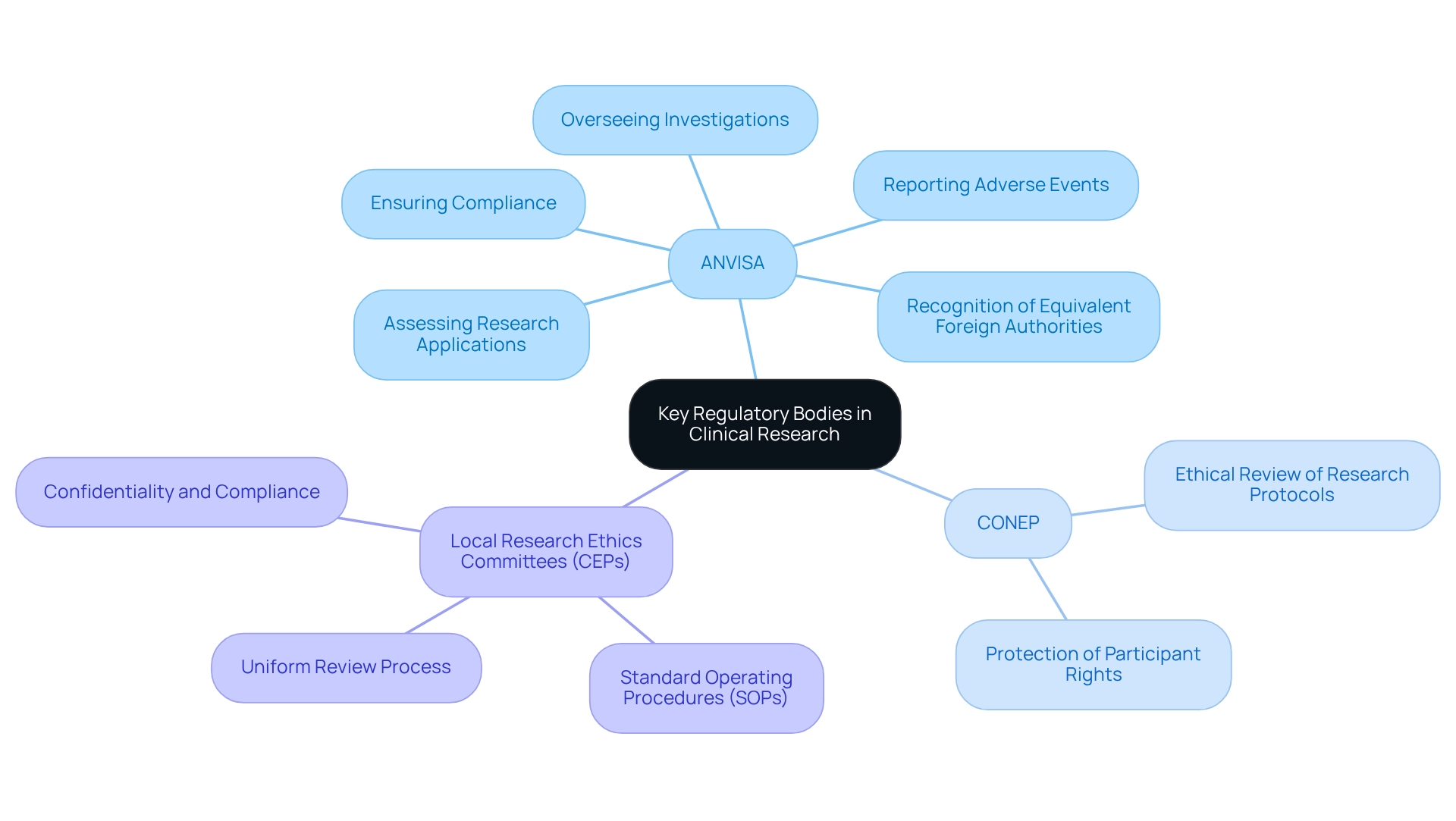
In Brazil, the design of trials for approval is overseen by the Agencia Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA), the primary governing body supervising studies for medications and medical apparatus. This agency plays a crucial role in ensuring that medical research adheres to stringent safety and efficacy standards. ANVISA's responsibilities include:
- Assessing research application submissions
- Overseeing ongoing investigations
- Ensuring compliance with regulatory standards
Importantly, sponsors are mandated to maintain investigation records for a minimum of two years following the final approval of a marketing application, underscoring the necessity of comprehensive documentation in the trial process. Furthermore, ANVISA provides an online system for reporting unexpected serious adverse events related to drugs and vaccines, which significantly enhances the agency's capacity to monitor participant safety effectively.
In addition to ANVISA's functions, the National Research Ethics Commission (CONEP) and local Research Ethics Committees (CEPs) are integral to the ethical oversight of clinical trials. CONEP is responsible for the ethical review of research protocols, ensuring alignment with established ethical standards and the protection of participant rights. Each CEP must maintain written standard operating procedures (SOPs) detailing their review processes, meeting schedules, and evaluation criteria for research studies.
These SOPs facilitate a systematic and transparent review process, ensuring that all research protocols are assessed uniformly and ethically, while safeguarding confidentiality and compliance with standards.
Recent developments indicate that ANVISA has recognized several foreign oversight agencies as Equivalent Foreign Oversight Authorities (AREE). This designation streamlines the assessment of research applications, potentially expediting the approval process for international sponsors conducting trials in Brazil. Understanding this acknowledgment is vital for international sponsors, as it may simplify their application process and enhance collaboration with Brazilian oversight authorities.
The interaction among ANVISA, CONEP, and local CEPs is essential for ensuring that research studies not only meet regulatory standards but also uphold ethical principles. As bioaccess® emphasizes, their expertise in managing Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF) positions them as a valuable partner in navigating these complexities. With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, bioaccess® offers a flexible and personalized approach to managing research, ensuring that each project is tailored to meet specific requirements.
As Christopher Holstege noted, "Medical surveillance involves performing observational studies of individuals or populations and includes the collection, collation, analysis, and dissemination of data in an effort to identify conditions or factors that pose an increased risk of adverse health effects." This statement highlights the importance of ethical considerations in research studies, particularly regarding participant safety and data management. As the landscape of medical research evolves, understanding the roles and functions of these entities, alongside the capabilities of bioaccess®, will be crucial for researchers designing trials for approval in Brazil and efficiently managing the complexities of conducting studies.
Navigating the Clinical Trial Approval Process in Brazil
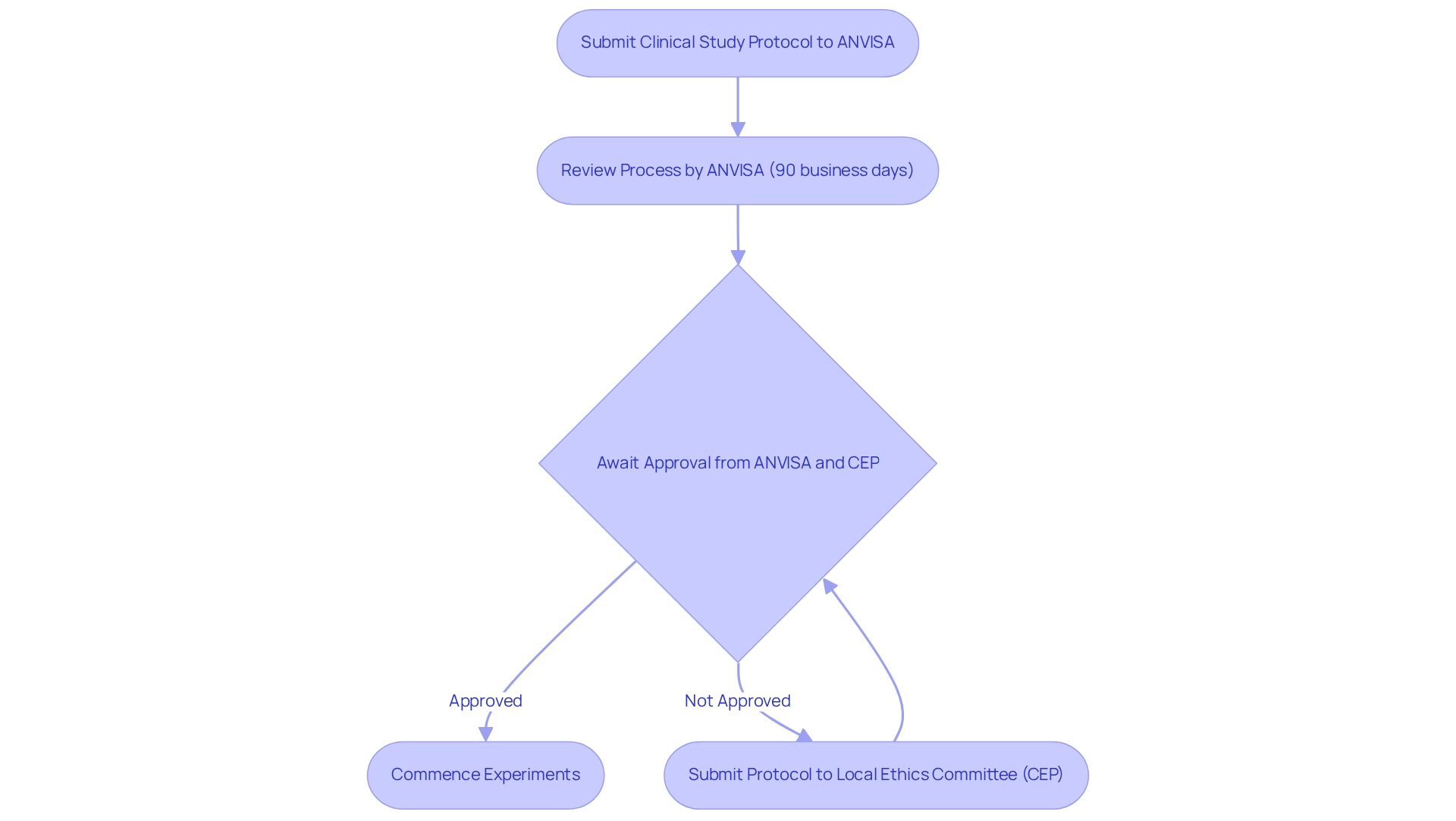
The research study approval process in Brazil is a structured pathway that scientists must navigate to ensure compliance and efficacy. Initially, researchers are required to submit a comprehensive clinical study protocol to ANVISA, accompanied by documentation demonstrating adherence to ethical standards. This submission is subjected to a review process that typically spans 90 business days.
Concurrently, the protocol must be submitted to a local Ethics Committee (CEP) for ethical evaluation. Only upon receiving approvals from both ANVISA and the CEP can researchers commence their experiments.
As of 2025, the approval process has gained heightened significance, with a notable 62.4% of stakeholders reporting limited knowledge of trial procedures. This underscores the urgent need for clear guidance and education in navigating the compliance landscape. Additionally, special attention is mandated when conducting studies involving indigenous populations, ensuring that ethical compliance is upheld and that the benefits of the research extend to these communities.
Recent developments have prompted ANVISA to implement an optimized analysis procedure for submissions, allowing for the incorporation of documentation from equivalent foreign authorities (AREEs). This innovation markedly enhances the efficiency of the oversight process, facilitating quicker approvals while upholding rigorous safety and efficacy standards. Consequently, the average duration for research approval in Brazil has improved, reflecting a commitment to promoting medical studies in the region.
Moreover, it is crucial to adhere to informed consent form (ICF) requirements, which stipulate that the ICF must be presented in a language comprehensible to the participant. In cases where the participant is illiterate, an impartial witness must be present during the consent process to ensure ethical compliance. As Carlos H Barrios from Grupo Oncoclínicas stated, "The approval process is an increasingly critical point in Brazil."
Understanding these stages and the regulatory landscape is vital for researchers designing trials for approval in Brazil, as they seek prompt authorizations and effective study implementation. bioaccess® excels in facilitating these processes, offering comprehensive management services that include feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance evaluations, setup, import permits, project oversight, and reporting. This ensures that researchers can adeptly navigate the complexities of the Latin American Medtech landscape.
Challenges in Conducting Clinical Trials in Brazil
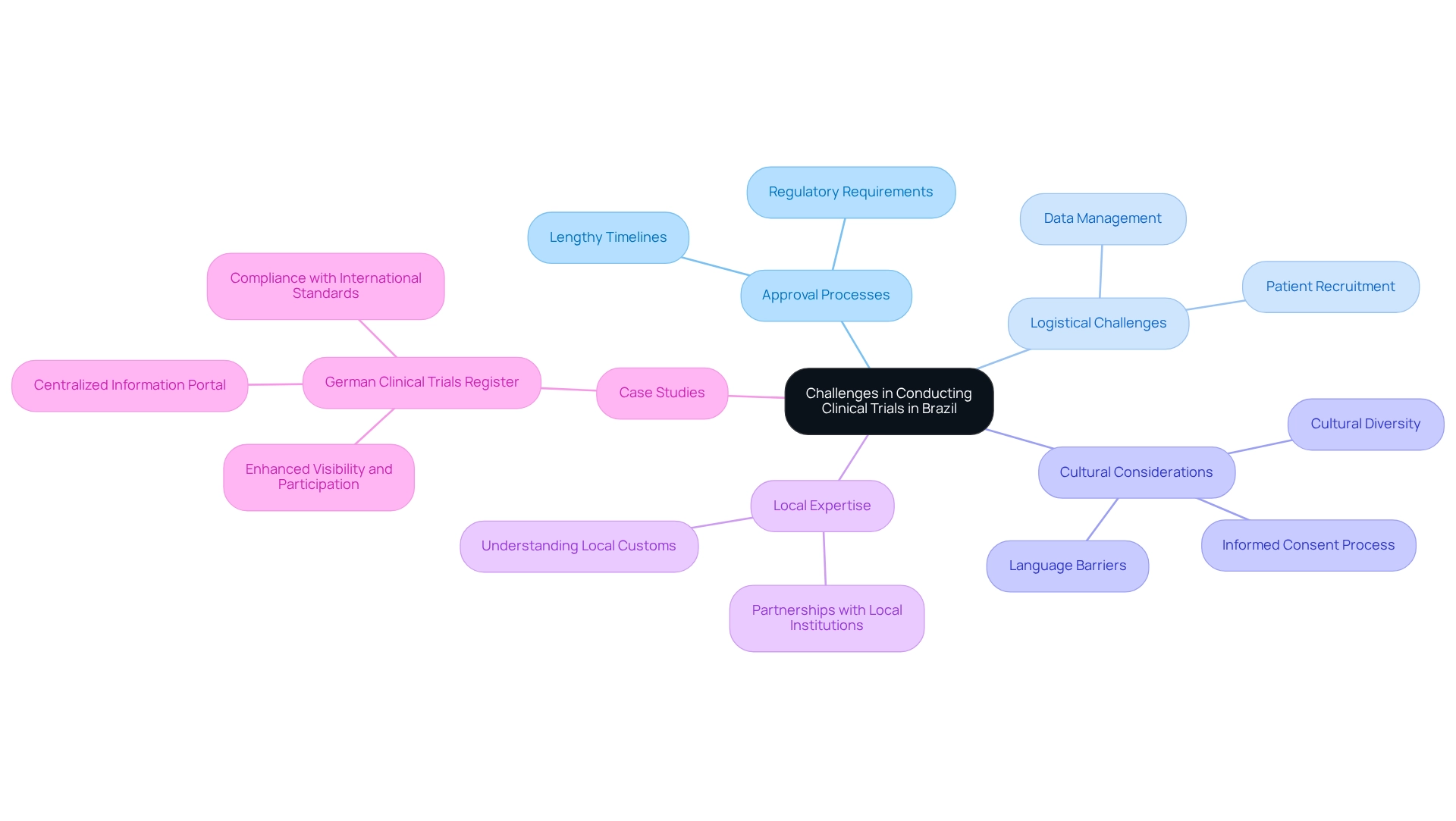
Designing trials for approval in Brazil necessitates conducting clinical studies while navigating a landscape filled with significant obstacles. Lengthy approval processes and intricate regulatory requirements can impede the initiation of studies, often extending timelines beyond initial projections. Additionally, logistical challenges, particularly in patient recruitment and data management, present further barriers.
For example, while 75% of the Brazilian population is covered by the Public Health System (SUS), effectively reaching and engaging potential participants remains a pivotal challenge. The cultural and linguistic diversity of Brazil introduces another layer of complexity. Understanding local customs and languages is essential for successful execution, as it directly impacts the informed consent process and overall participant engagement. Local supervisors, who possess a deeper understanding of these nuances, can significantly enhance the effectiveness of research studies by ensuring compliance with ethical board standards and fostering trust among participants.
Respecting local culture, traditions, and language is crucial for success in Latin American research studies. To illustrate these challenges, consider the establishment of the German Research Register, which aimed to centralize information on studies in Germany. Launched in 2008, this initiative has improved visibility and participation in clinical studies by adhering to international standards.
A comparable approach, such as designing trials for approval in Brazil, could heighten awareness and streamline processes, ultimately benefiting both researchers and participants. By drawing parallels between the challenges encountered in Brazil and the solutions implemented in Germany, we can gain a clearer understanding of the potential for improvement in Brazilian judicial processes. Strategies to surmount these logistical hurdles include leveraging local expertise and cultivating partnerships with local institutions.
Collaborating with experienced researchers can enhance the credentials of study locations and elevate the overall quality of experiments. Bioaccess®, with over 20 years of experience in Medtech, specializes in managing Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF). Our tailored approach equips you with the expertise required to navigate these challenges effectively.
Engagement in initial research studies can bolster the expertise and credentials of researchers and study locations, further contributing to successful outcomes. By proactively addressing these challenges, researchers can facilitate smoother study operations, which is vital for designing trials for approval in Brazil and advancing medical technology. For further information on how bioaccess® can assist with your study needs, please reach out to us today.
The authors wish to express gratitude to Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Switzerland, for their support of this research.
Choosing the Right CRO for Your Clinical Trials
Choosing a contract research organization (CRO) for designing trials for approval in Brazil requires a thorough evaluation of various essential elements. First and foremost, the CRO's experience in the medical technology sector is paramount. A CRO with a robust background in Medtech, such as bioaccess®, possesses the necessary expertise and specialized knowledge to navigate the complexities of clinical trials effectively.
With over 20 years of experience overseeing diverse research projects—including Early-Feasibility Assessments (EFS), First-In-Human Trials (FIH), Pilot Trials, Pivotal Trials, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Assessments (PMCF)—bioaccess® exemplifies the level of expertise required in this field.
Understanding local regulations is another essential element. A CRO that comprehends the intricate oversight landscape can significantly assist in designing trials for approval in Brazil, ensuring adherence to all necessary guidelines. For instance, sponsors must maintain records detailing the shipment, receipt, disposition, return, and destruction of investigational products, underscoring the importance of compliance in CRO selection.
Furthermore, evaluating the CRO's performance in overseeing successful experiments is crucial. This involves reviewing their history of adhering to timelines and budgets, which can greatly influence the overall success of a project. The absence of clear guidelines in certain areas, as demonstrated in the case study on local accreditation in Mali, may hinder the development of strong ethical oversight in research—a challenge that could mirror the governance environment in Brazil.
Additionally, the CRO's capabilities in patient recruitment and data management are vital for study efficiency. Effective patient recruitment methods are essential for prompt enrollment, while strong data management systems ensure the integrity and precision of study results. Adherence to regulations is also a critical aspect, as upholding ethical standards and compliance is essential for the integrity of the research.
In summary, selecting a well-qualified CRO like bioaccess® not only enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of studies but also leads to improved results. By prioritizing these factors—experience in Medtech, compliance knowledge, successful study management, patient recruitment, data administration, adherence, flexibility, and a tailored approach—researchers can make informed decisions that will ultimately benefit their research studies.
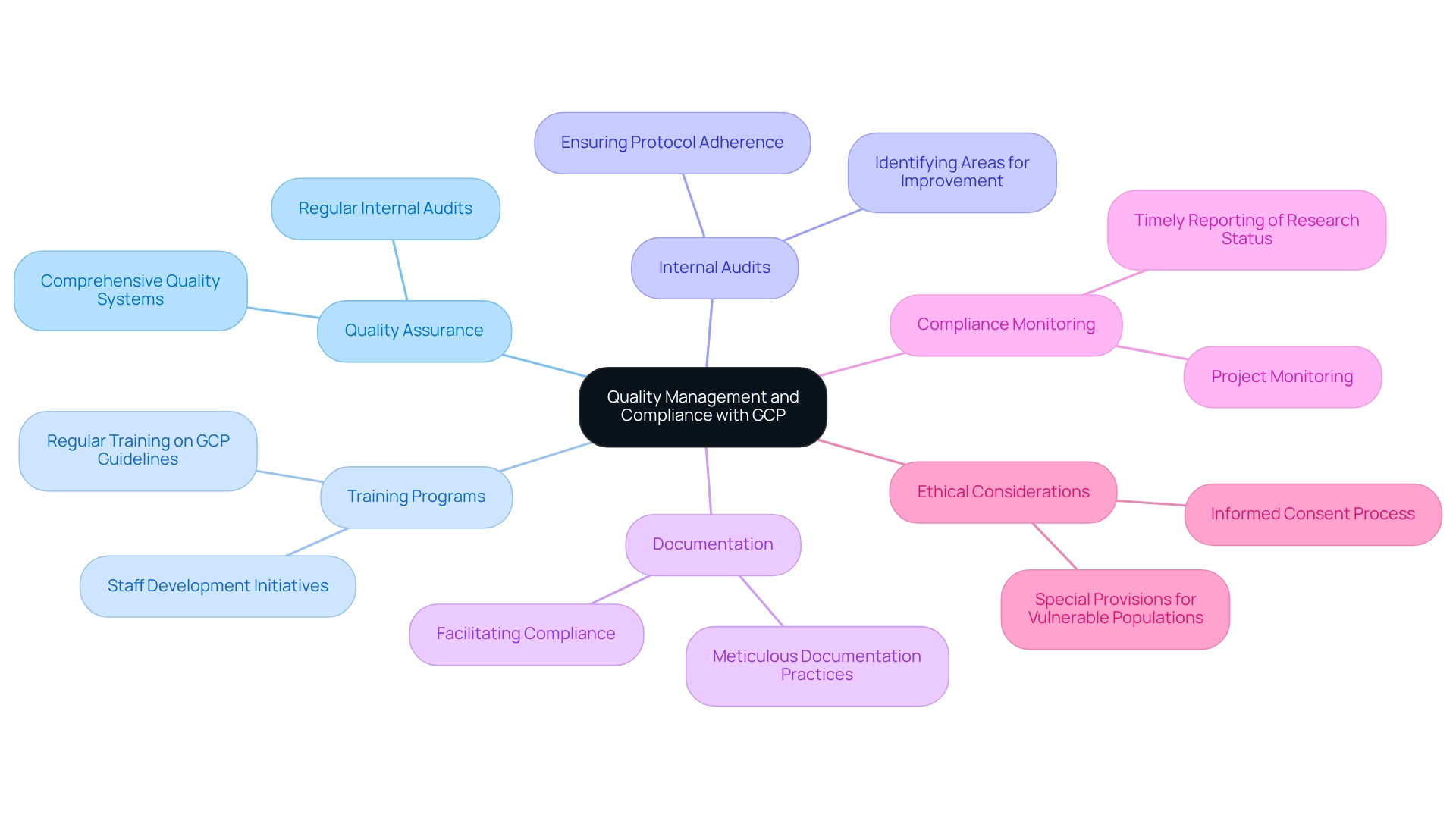
Ensuring Quality Management and Compliance with GCP
To achieve efficient quality management and ensure compliance with Good Clinical Practice (GCP) in research studies, investigators must establish comprehensive quality assurance and quality control systems. Regular training programs for staff on GCP guidelines are essential for designing trials for approval in Brazil, particularly in light of the evolving regulatory landscape and the new laws that will come into effect 90 days after their publication. Conducting internal audits is another critical practice that identifies areas for improvement and ensures adherence to established protocols.
In Brazil, where Plataforma Brasil serves as a national registry for research studies, designing trials for approval necessitates meticulous documentation that not only facilitates compliance but also enhances the credibility of the research. This platform oversees the review and approval procedures of both CEP and CONEP, guaranteeing that all studies are properly registered and tracked. By prioritizing quality management, researchers can significantly bolster the integrity of their experiments, ensuring adherence to both local and international compliance standards.
Moreover, bioaccess offers extensive management services for experiments, including feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance evaluations, setup, import permits, project oversight, and reporting. These services are crafted to streamline the clinical study process and enhance adherence to regulatory requirements. For instance, bioaccess conducts comprehensive viability analyses to assess the suitability of research locations and lead researchers, ensuring that experiments are organized efficiently and effectively.
Additionally, bioaccess is responsible for project monitoring to ensure compliance with protocols and timely reporting of research status, inventory, and adverse events. Statistics indicate that adherence to GCP guidelines can lead to a higher success rate in approvals, underscoring the importance of these practices. The successful implementation of GCP compliance strategies in Brazilian studies demonstrates that a structured approach to quality management in trial design can yield positive outcomes, fostering trust among stakeholders and participants alike.
It is also imperative to consider ethical aspects, such as the informed consent process, particularly for vulnerable populations like pregnant children, ensuring that all research adheres to ethical guidelines.
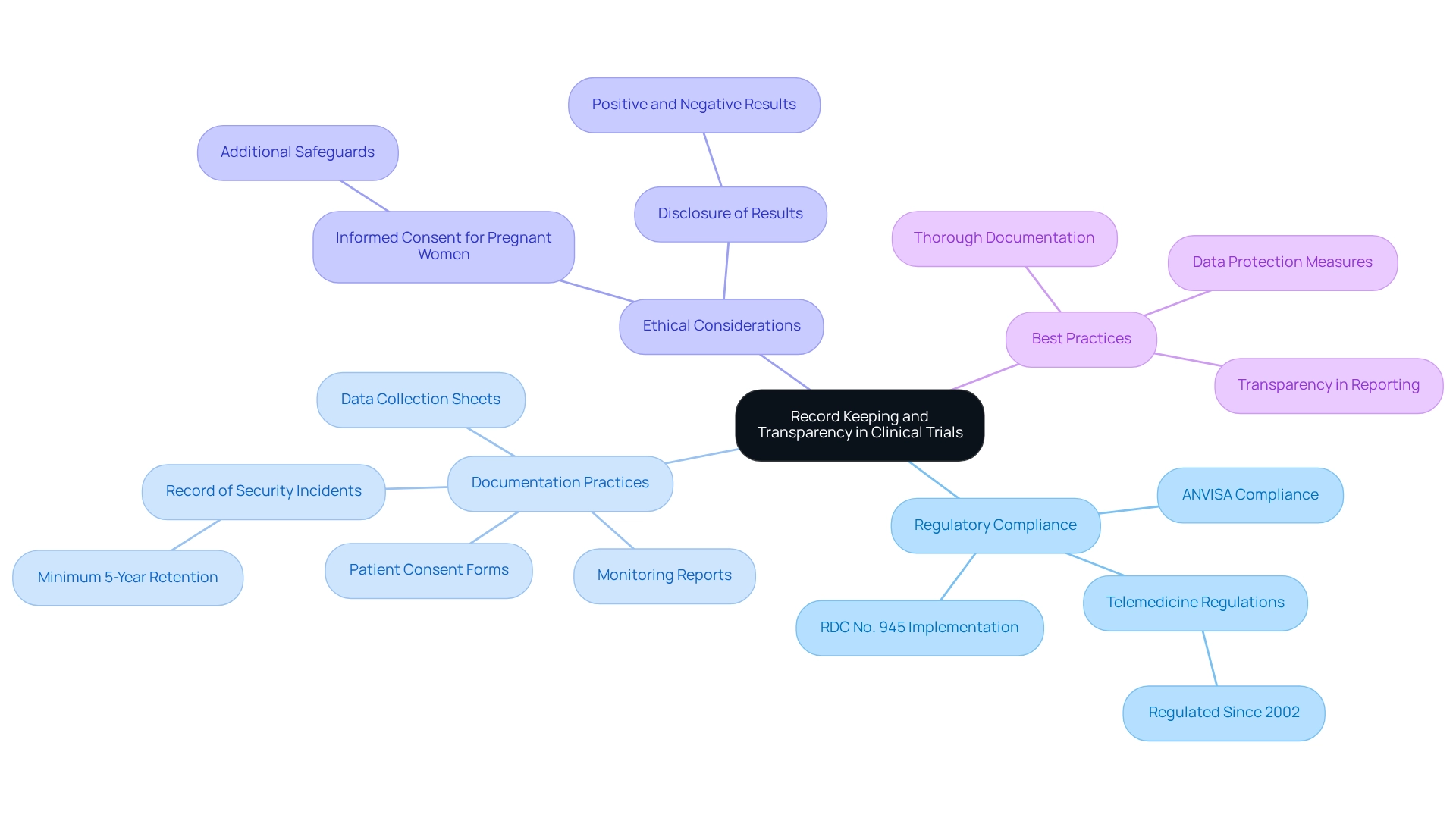
Record Keeping and Transparency in Clinical Trials
Efficient documentation in medical studies is paramount for ensuring compliance with legal standards and maintaining the integrity of the research process. This necessitates meticulous documentation of all trial-related activities, including patient consent forms, data collection sheets, and monitoring reports. Researchers must guarantee that all records are not only comprehensive but also easily accessible and securely stored, in accordance with the regulatory requirements established by authorities such as ANVISA.
As of January 1, 2025, the new clinical studies regulation RDC No. 945 will take effect in Brazil, superseding previous regulations. This transition highlights the imperative for researchers to remain informed about evolving compliance standards, particularly in the context of designing trials for approval in Brazil.
For instance, it is mandated that the controller must maintain a record of any security incidents for a minimum of five years from the date of registration, underscoring a long-term commitment to data integrity and participant safety.
Clarity in presenting results from experiments is equally essential. Researchers must disclose both positive and negative results to foster public trust and ensure adherence to regulations. The Brazilian regulatory framework emphasizes this openness, as illustrated by the case analysis concerning consent requirements for expectant women in research.
These regulations not only safeguard the health and rights of participants but also ensure that research is conducted ethically and responsibly. This case analysis demonstrates the additional protections established for at-risk groups, emphasizing the significance of ethical considerations in medical research.
Furthermore, expert opinions stress the importance of transparency in research study reporting. Negar Gharavi, Senior Director of Medical Writing & Regulatory Affairs, noted that 'BioPharma Services has successfully conducted several studies for the ANVISA submission, which involved designing trials for approval in Brazil,' reinforcing the importance of adhering to regulatory standards. By following best practices for record management and transparently sharing study results, researchers can foster a more reliable research environment.
This commitment to transparency and thorough documentation is vital for advancing medical technology and ensuring that research studies are conducted with the highest ethical standards. Moreover, it is essential to recognize that telemedicine has been regulated in Brazil since 2002, which may relate to broader compliance and ethical considerations in medical studies.
At bioaccess®, we offer comprehensive clinical study management services, including feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, study setup, import permits, project management, and reporting. Our commitment to data protection ensures that client information is handled with the utmost care, and our grievance procedures are established to address any concerns regarding compliance and transparency. For any inquiries or concerns about data protection, clients may reach out to our Grievance/Data Protection Officer at IMH ASSETS CORP (doing business as 'bioaccess®'), 1200 Brickell Avenue, Suite 1950 #1034, email: info@bioaccessla.com.
Additionally, we guarantee thorough documentation of serious and non-serious adverse events, ensuring adherence to established standards.
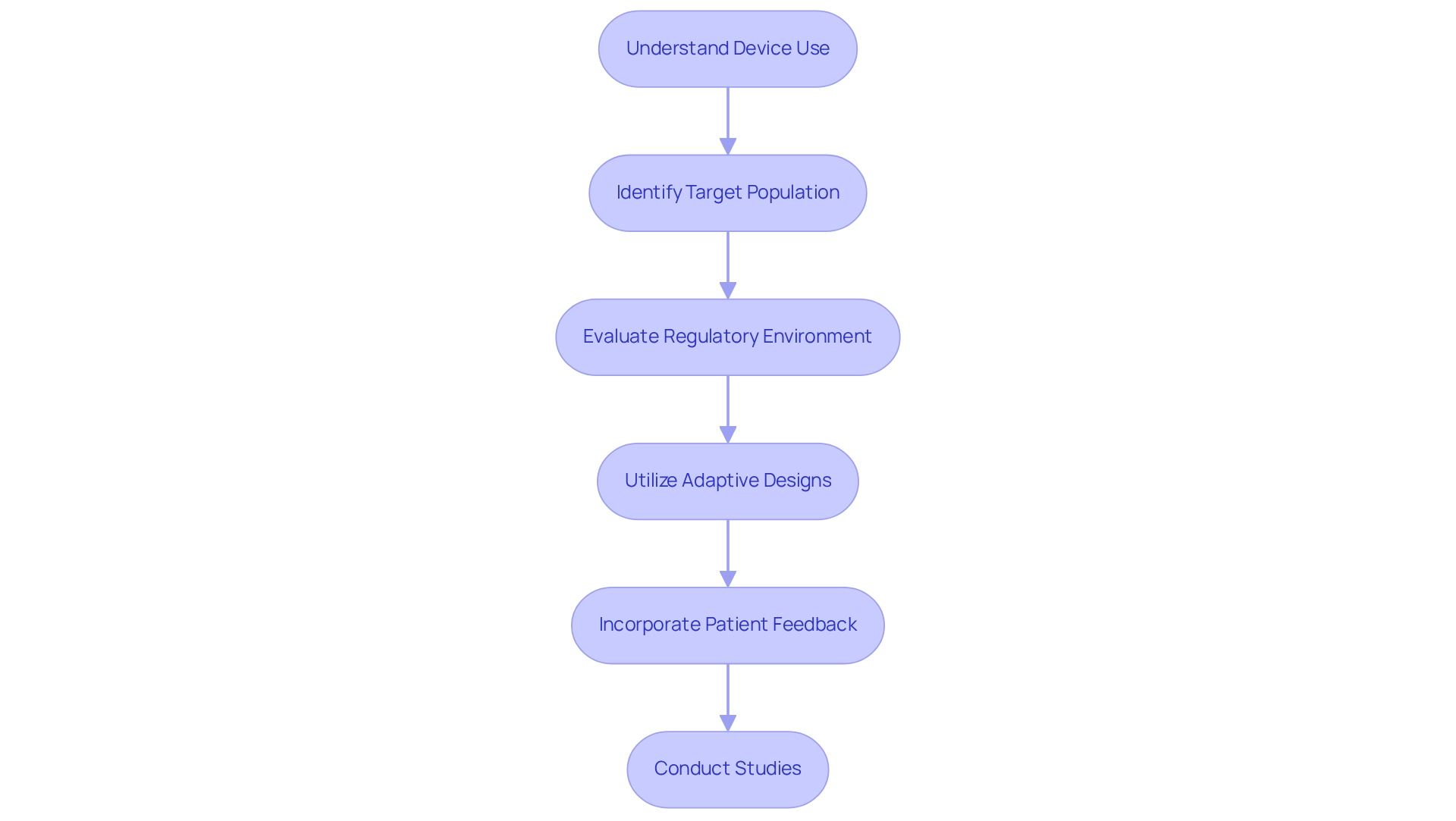
Design Strategies for Innovative Medical Device Trials
Designing trials for approval in Brazil necessitates a thorough evaluation of innovative medical devices, requiring a comprehensive understanding of several essential factors, including the device's intended use, target population, and regulatory environment. The utilization of adaptive study designs proves particularly beneficial, as these methodologies allow for adjustments based on interim outcomes, thereby enhancing both flexibility and efficiency in the research process. A recent study highlighted that out of 267 medical studies examining adaptive designs, 236 successfully applied them, showcasing a rising trend in this approach.
Moreover, incorporating patient feedback during the design stage is vital for improving relevance and participant involvement. This practice not only fosters a more patient-centered approach but also leads to more meaningful outcomes. The VICTAS study exemplifies this; it enrolled adults with sepsis-induced respiratory or cardiovascular dysfunction to evaluate the effects of vitamin C, thiamine, and hydrocortisone.
Although the experiment ultimately ceased due to shifts in funding priorities, it underscored the complexities associated with adaptive study designs, particularly concerning statistical significance and operational modifications.
As Brazil advances its research framework, the integration of adaptive study designs for medical devices is increasingly recognized. This shift is bolstered by expert opinions emphasizing the necessity for innovative design strategies that align with regulatory requirements while addressing the unique challenges of the medical technology sector. In this context, bioaccess® offers extensive clinical study management services, including Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF).
With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, bioaccess® provides the adaptability and expertise essential for effectively managing these challenges. Aaron S. Kesselheim notes that in their sample, 9% of adaptive studies evaluated medications sanctioned by the FDA through reliance on these designs, underscoring their significance in regulatory environments. However, international regulators have experienced mixed outcomes with adaptive studies, often necessitating revisions or alterations to research designs after extensive discussions with drug sponsors.
Thus, a careful evaluation of operating characteristics is imperative when incorporating multiple adaptive design features. By leveraging adaptive designs and the expertise of bioaccess®, researchers can adeptly navigate the complexities of trials, ultimately accelerating the market entry of innovative medical devices.
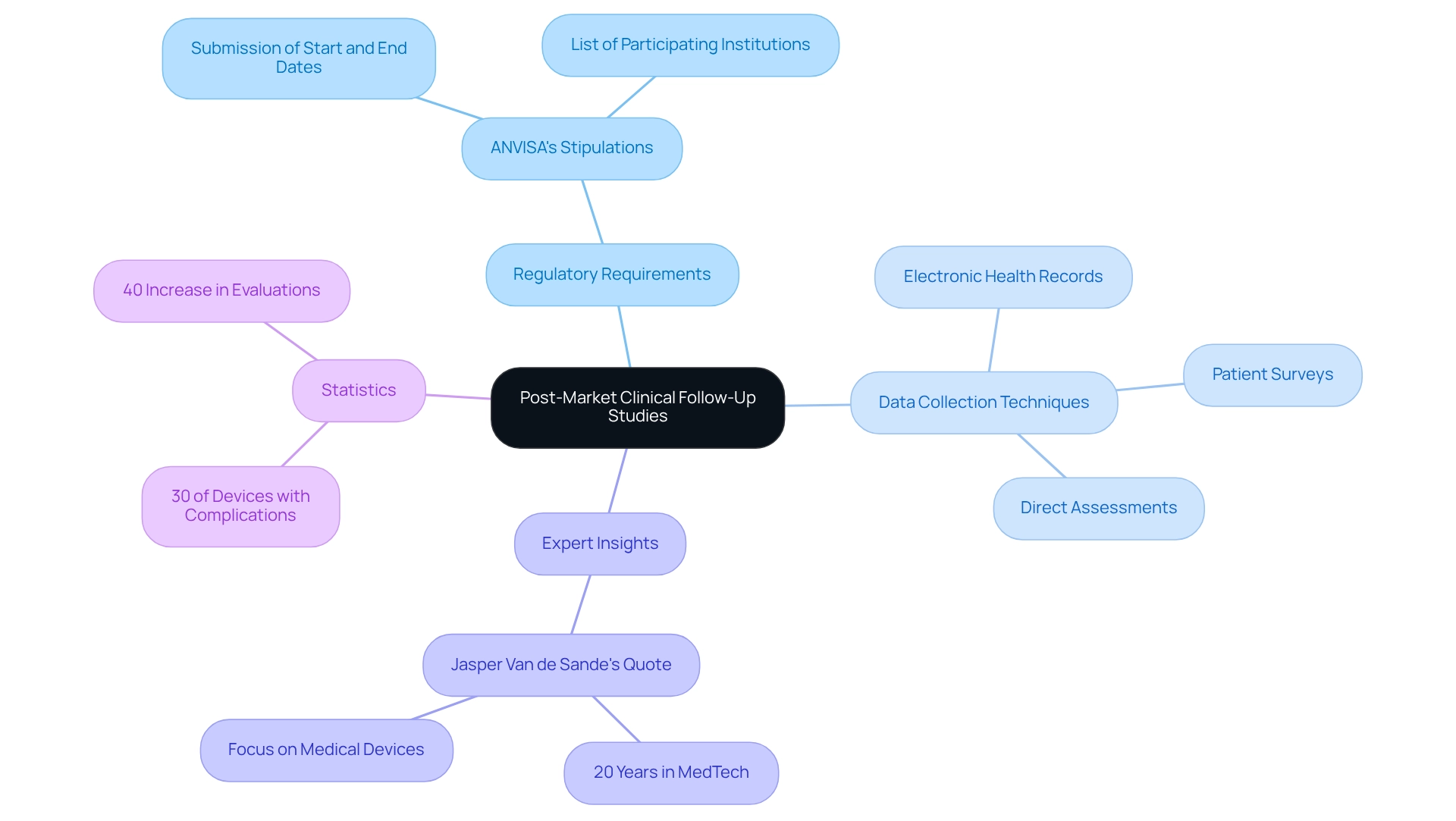
The Role of Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies
Post-market assessments are essential for determining the long-term safety and effectiveness of medical devices once they reach the market. These meticulously designed studies gather comprehensive data on device performance, adverse events, and patient outcomes in real-world environments. In Brazil, producers must conduct these assessments to comply with ANVISA's stipulations, which require submitting forms for the beginning and conclusion dates of studies within 30 calendar days of each occurrence.
Furthermore, the lead researcher is responsible for providing a list of participating institutions and related protocols for multicenter research trials, a vital aspect of the regulatory process.
The significance of post-market evaluations cannot be overstated. They not only help identify potential safety issues but also provide critical insights into the device's performance over time. For instance, a recent analysis revealed that approximately 30% of medical devices experience unanticipated complications post-approval, underscoring the necessity for ongoing monitoring.
Data collection techniques for these evaluations vary but typically include patient surveys, electronic health records, and direct assessments. These approaches enable researchers to capture a wide array of data, facilitating a thorough understanding of the device's impact on patient health.
Expert insights affirm that robust post-market health assessments are crucial for fostering innovation in the Medtech industry. They empower manufacturers to make informed adjustments to their products, enhancing safety and efficacy based on real-world evidence. Jasper Van de Sande, a seasoned expert in the Medtech field with two decades of experience, remarked, "Effective market opportunity evaluations and real-world evidence analyses significantly enhance strategic positioning and innovation in medical devices."
In Brazil, the design of trials for approval is evolving alongside the landscape for post-market clinical follow-up research, which increasingly emphasizes long-term safety evaluations. Statistics indicate that as of 2025, the number of registered post-market evaluations has surged by over 40%, reflecting a growing recognition of their importance in the medical device lifecycle. This trend not only benefits manufacturers but also enhances patient safety and trust in medical technologies.
At bioaccess®, we specialize in managing a comprehensive range of studies, including Early-Feasibility Studies, First-In-Human Studies, and Pilot Studies, alongside post-market evaluations. Our tailored approach ensures that clients can navigate the complexities of research project administration efficiently. For further information, ANVISA provides a clinical trials search tool for public access to authorized clinical trials.
Conclusion
Brazil's regulatory landscape for clinical trials is defined by a stringent framework designed to ensure the safety and efficacy of medical research. Governed primarily by ANVISA, this framework emphasizes ethical guidelines that prioritize informed consent and the protection of vulnerable populations. Recent reforms, including Law No. 14.874, have aimed to streamline the approval process, facilitating faster access to innovative treatments and enhancing Brazil's attractiveness as a clinical research hub.
Researchers must navigate a complex approval process that involves both ANVISA and local Ethics Committees, with compliance being crucial for successful study execution. The interplay between regulatory bodies, such as ANVISA and CONEP, is essential for upholding ethical standards and ensuring participant safety. Despite challenges such as lengthy approval timelines and logistical hurdles, the growing number of approved trials reflects increasing confidence in Brazil's clinical research capabilities.
Furthermore, selecting the right contract research organization (CRO) is pivotal for effective trial management. A CRO's experience in Medtech, regulatory knowledge, and successful trial track record can significantly impact the efficiency and outcomes of clinical studies. As the landscape continues to evolve, maintaining rigorous quality management and compliance with Good Clinical Practice (GCP) will be vital for researchers aiming to contribute to the advancement of medical technology in Brazil.
In summary, understanding Brazil's regulatory framework and the associated challenges is essential for researchers looking to conduct successful clinical trials. By leveraging local expertise and adhering to ethical standards, the potential for innovation in medical research is immense, paving the way for improved healthcare solutions both locally and globally.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary regulatory body overseeing research involving human subjects in Brazil?
The primary regulatory body is the Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA), which is responsible for the authorization and supervision of these investigations.
What are the key ethical guidelines established for conducting research involving human subjects in Brazil?
Key ethical guidelines are outlined in Resolution No. 466/2012, which emphasizes the importance of informed consent and the protection of at-risk groups, including expectant mothers.
What specific measures are required when conducting research involving pregnant women?
Research involving pregnant women should only occur after examinations on non-pregnant women, and participants must retain the right to engage without mandatory contraceptives if they are not at risk of pregnancy.
What does Law No. 14.874, introduced in 2024, aim to achieve in the research approval process?
Law No. 14.874 aims to simplify the research approval process by reducing bureaucratic hurdles, thereby facilitating quicker access to innovative treatments for patients.
How long are sponsors required to maintain investigation records after the final approval of a marketing application?
Sponsors are required to maintain investigation records for a minimum of two years following the final approval of a marketing application.
What roles do the National Research Ethics Commission (CONEP) and local Research Ethics Committees (CEPs) play in clinical trials?
CONEP is responsible for the ethical review of research protocols, while local CEPs oversee the ethical evaluation of studies, ensuring alignment with ethical standards and participant rights.
How has ANVISA streamlined the research approval process for international sponsors?
ANVISA has recognized several foreign oversight agencies as Equivalent Foreign Oversight Authorities (AREE), which streamlines the assessment of research applications and potentially expedites the approval process.
What is the significance of the informed consent form (ICF) in the research approval process?
The ICF must be presented in a language comprehensible to the participant, and if the participant is illiterate, an impartial witness must be present during the consent process to ensure ethical compliance.
What is the typical duration for the research approval process in Brazil?
The review process for research applications typically spans 90 business days, during which researchers must receive approvals from both ANVISA and the local Ethics Committee (CEP) before commencing their experiments.
How can bioaccess® assist researchers in navigating Brazil's compliance environment?
Bioaccess® provides comprehensive management services, including feasibility assessments, site selection, compliance evaluations, setup, import permits, project oversight, and reporting, helping researchers navigate the complexities of conducting studies in Brazil.




