Introduction
Navigating the intricate landscape of medical device regulation is paramount for manufacturers aiming to bring innovative technologies to market. At the forefront of this process lies Premarket Approval (PMA), a rigorous pathway mandated by the FDA for Class III devices that ensures a comprehensive evaluation of safety and efficacy through extensive clinical trials. As the demand for advanced medical solutions grows, particularly in regions like Latin America, understanding the nuances of PMA becomes increasingly critical.
This article delves into the essential components of PMA submissions, contrasts the PMA process with the 510(k) pathway, and outlines best practices that can enhance the likelihood of successful approval. By exploring these elements, stakeholders can better navigate the regulatory framework, ultimately contributing to advancements that improve patient outcomes and foster innovation in the medical technology sector.
Understanding Premarket Approval (PMA): Definition and Importance
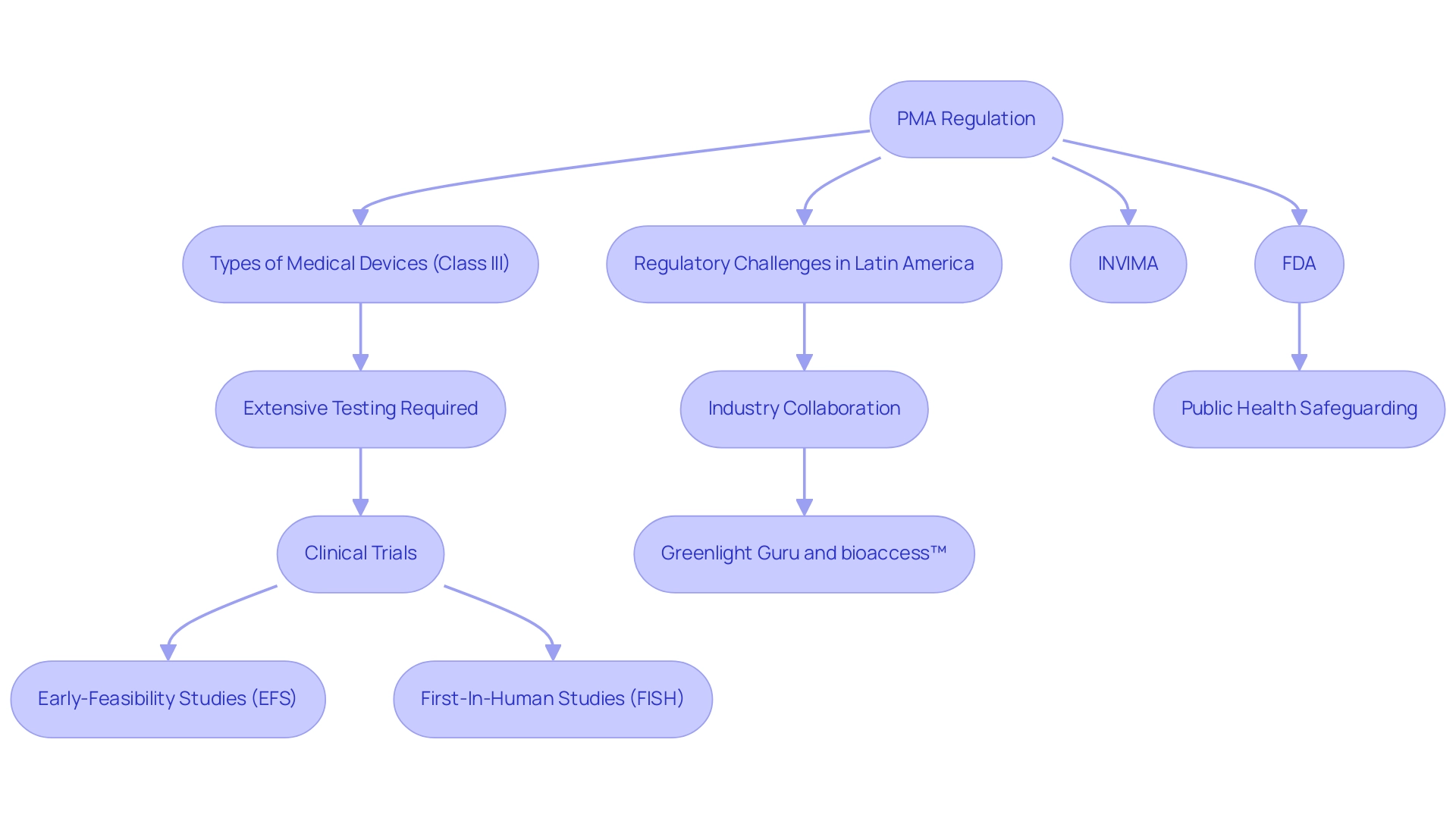
The PMA regulation functions as a vital regulatory route created by the FDA specifically for Class III medical items, which are categorized as high-risk products requiring extensive testing before market entry. The importance of PMA regulation is emphasized by its strong evaluation method, which carefully examines the safety and effectiveness of instruments through extensive clinical trials. This thorough scrutiny not only offers manufacturers the assurance that they meet stringent legal standards but also instills confidence in patients regarding the safety of the products they rely on.
In Latin America, Medtech companies encounter various challenges, including regulatory obstacles and resource fragmentation, which complicate the PMA regulation procedures. For example, collaboration between Greenlight Guru and bioaccess™ aims to bridge these gaps, enhancing clinical trial management services from feasibility studies to compliance reviews, ultimately accelerating innovation. Bioaccess® specializes in various clinical studies, including:
- Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS)
- First-In-Human Studies (FISH)
These studies are essential for advancing medical technology.
The recent involvement of companies like Cadence in the Costa Rica Medical Device Cluster illustrates the importance of industry collaboration in navigating regulatory pathways. Additionally, as emphasized by FDA officials, for FY 2024, there is no small business waiver for the annual establishment registration fee; all establishments pay the same fee, highlighting the regulatory landscape's implications for small enterprises in the medical sector. Additionally, after finishing registration, establishments must enter their DFUF order PIN and PCN to complete the procedure; this step is necessary for the registration to be acknowledged and handled by the FDA.
INVIMA, the Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, plays a crucial role in regulatory oversight, ensuring that medical equipment meets necessary standards before market entry. Ultimately, the PMA regulation plays a pivotal role in safeguarding public health while concurrently fostering innovation within the medical technology sector. A well-organized PMA regulation system is crucial for upholding high standards in equipment safety and effectiveness, thereby encouraging developments that can greatly improve patient outcomes.
Key Components and Requirements for PMA Submissions
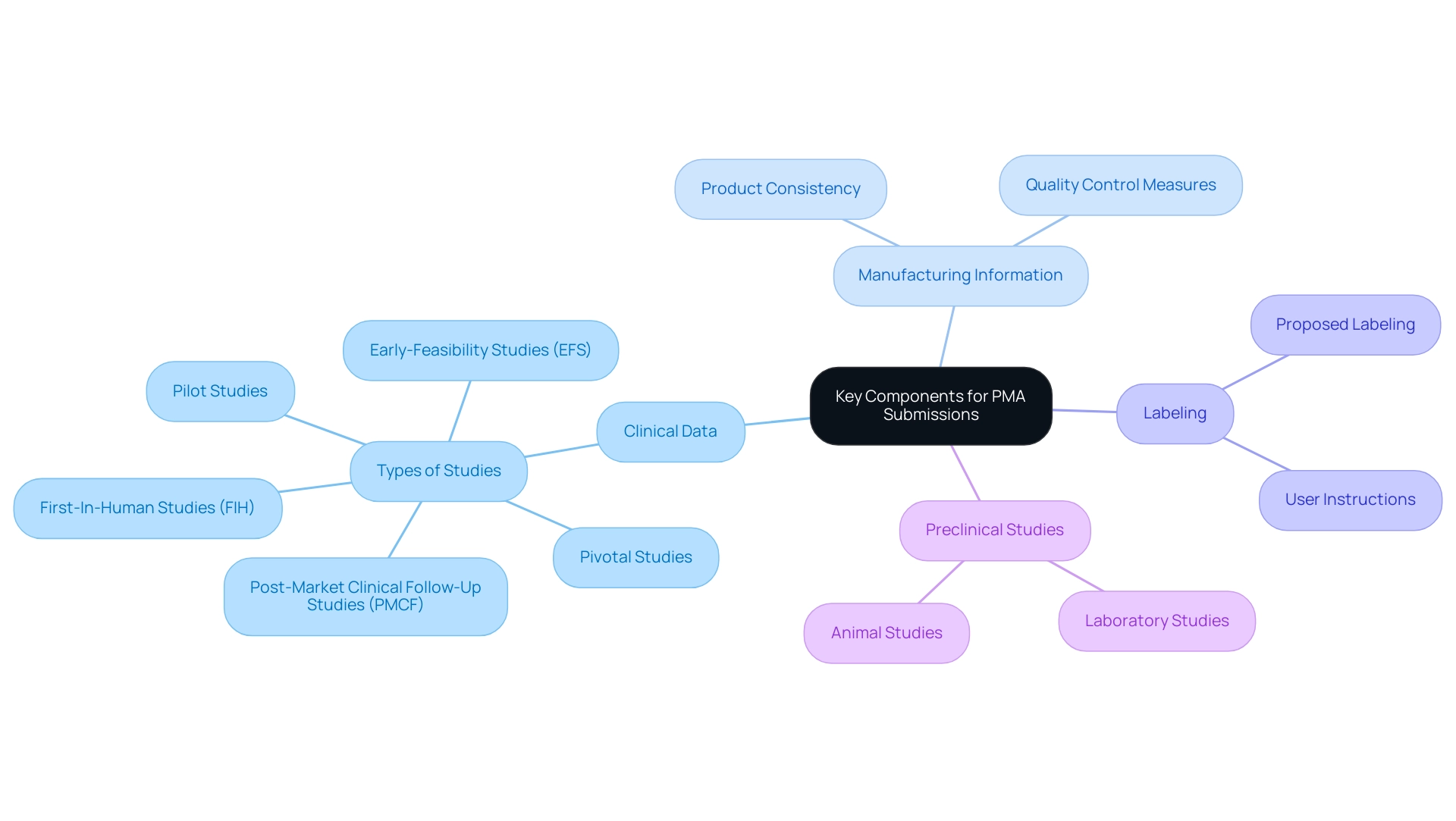
A comprehensive PMA regulation submission must encompass several essential components to effectively meet FDA guidelines. These include:
-
Clinical Data: Strong evidence demonstrating the safety and effectiveness of the medical instrument, derived from well-conducted clinical trials that adhere to regulatory standards.
In Latin America, bioaccess®, with over 20 years of experience in Medtech, specializes in managing critical studies such as Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF) to ensure thorough clinical data collection.
-
Manufacturing Information: Detailed insights into the manufacturing processes, including quality control measures that ensure product consistency and safety.
-
Labeling: Proposed labeling and user instructions that align with FDA regulations, providing clear guidance on the product's use.
-
Preclinical Studies: Data obtained from laboratory and animal studies that bolster the clinical findings and provide context for the device's performance.
Presenting all information clearly and concisely is crucial, as it not only facilitates the review but also enhances the likelihood of successful approval. Additionally, manufacturers will be required to submit annual post-approval reports starting one year from the date of PMA approval, emphasizing the ongoing commitment to safety and effectiveness.
The FDA explicitly states that they encourage applicants to contact them before submitting their PMA application to gain a better understanding of PMA regulation, requirements, guidance documents, and processes. Furthermore, the approval of a PMA application does not conclude FDA requirements; ongoing safety and effectiveness monitoring is mandated by PMA regulation, as demonstrated in the case study titled 'PMA Post-Approval Requirements.' Grasping these elements is essential for maneuvering through the regulatory environment efficiently, particularly with the knowledge of experts like Katherine Ruiz, who plays a crucial part in assisting companies with regulatory matters for medical products and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia.
PMA vs. 510(k): Understanding the Regulatory Pathways
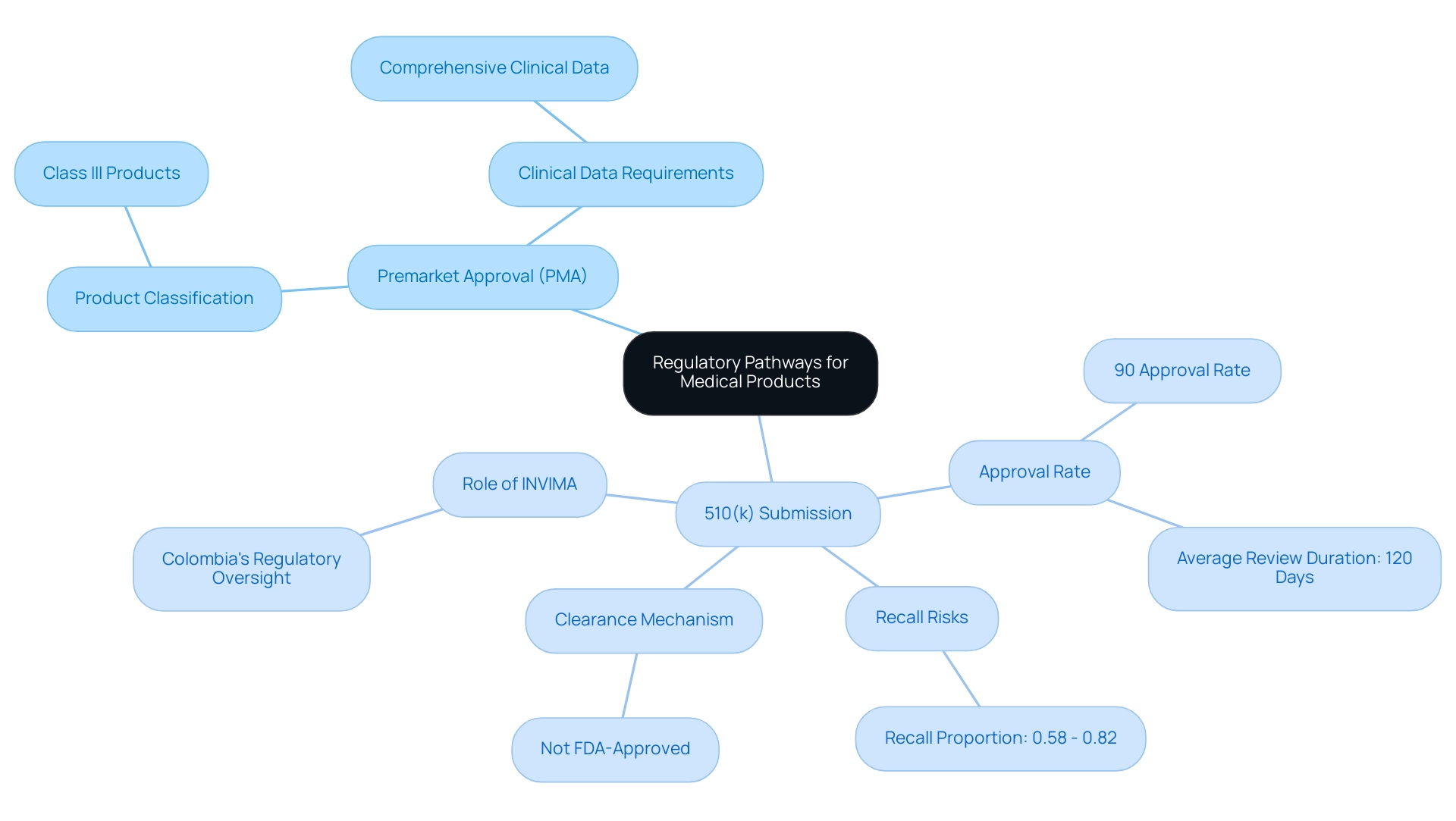
The pathways to market for medical products, namely Premarket Approval (PMA) and the 510(k) submission, serve distinct purposes based on the classification of the products involved. PMA regulation is required for Class III products, which are associated with higher risks and, therefore, necessitate comprehensive clinical data to substantiate their safety and efficacy. In contrast, the 510(k) pathway is designated for Class II products, allowing for a streamlined evaluation when a new item can be shown to be substantially equivalent to an already marketed product.
Significantly, the FDA evaluates roughly 10,000 510(k) submissions each year, attaining an impressive approval rate of about 90%, with an average review duration of 120 days. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that products cleared through the 510(k) pathway cannot be marketed as 'FDA-approved.' Furthermore, the proportion of recalls to approvals in the 510(k) system ranges from 0.58% to 0.82% of the 18,111 submissions, highlighting the recall risk associated with this pathway.
As observed by Dr. Akin Cil, the risk of recalls among medical products cleared through the 510(k) mechanism highlights the need for strong regulatory strategies in the development process. Strengthening postmarketing surveillance strategies and pivotal trials is essential to enhance safety of the product. Understanding these differences is vital for developers aiming to navigate the regulatory landscape effectively, including the PMA regulation, while leveraging comprehensive clinical trial management services from experts like bioaccess®, which specializes in Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), Pilot Studies, Pivotal Studies, and Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up Studies (PMCF) in Latin America.
Additionally, INVIMA, as Colombia's National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, plays a significant role in overseeing medical equipment regulation, and insights from experts like Katherine Ruiz in Regulatory Affairs can further enhance compliance and success in the clinical trial sector.
Navigating the PMA Submission Process: Steps and Timelines
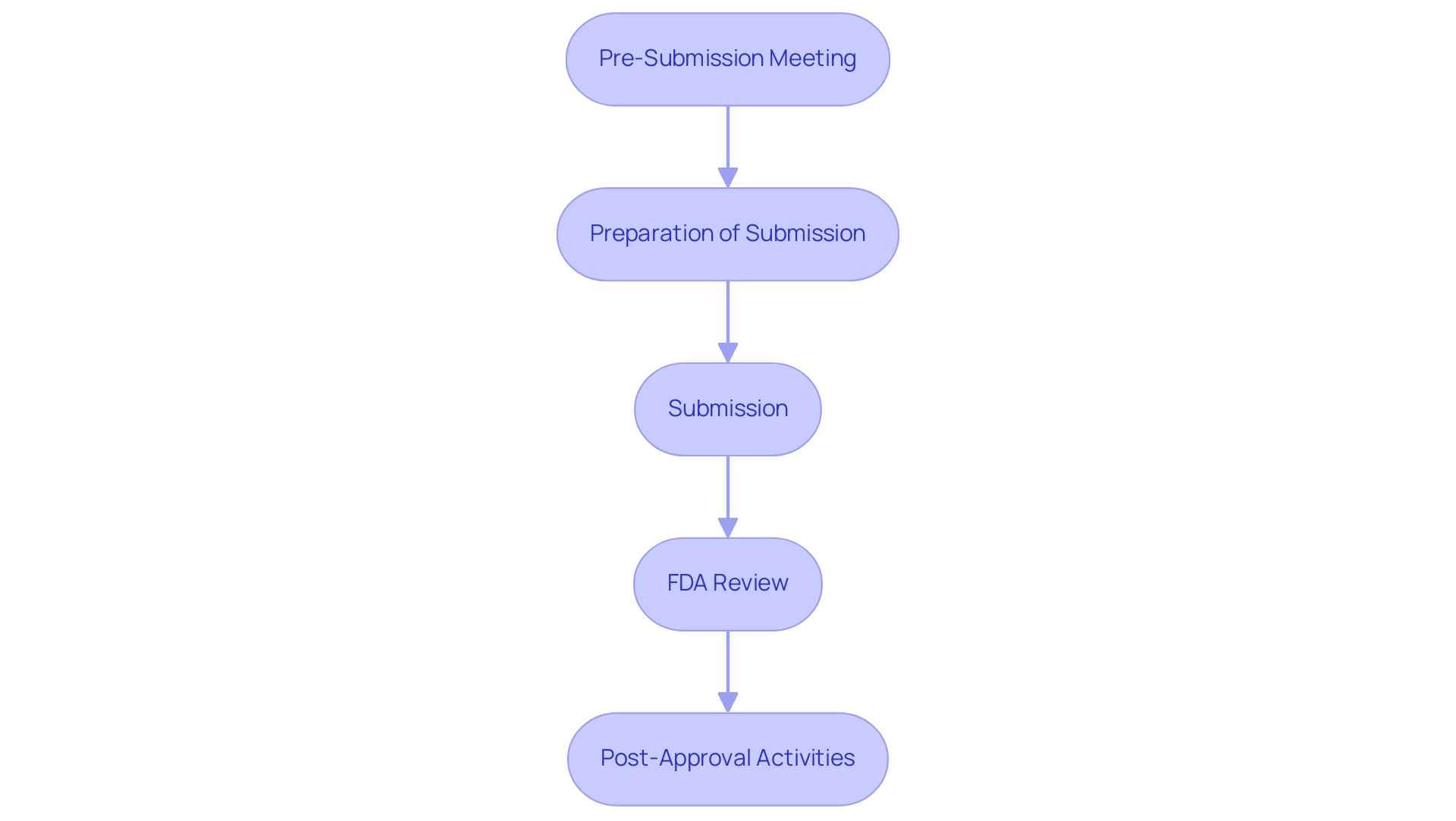
The pma regulation submission process is a critical pathway for bringing medical equipment to market and involves several key steps:
-
Pre-Submission Meeting: This initial engagement with the FDA allows manufacturers to discuss their proposed submission, seek guidance, and receive valuable feedback that can shape their application.
-
Preparation of Submission: This stage requires compiling comprehensive documentation, which includes clinical data, labeling information, and evidence of safety and efficacy of the instrument. Given that Class III devices pose the most significant risks to patients compared to Class I and Class II devices, thorough preparation is essential. This is where utilizing comprehensive clinical trial management services, such as those offered by bioaccess®, can significantly enhance the submission.
Their expertise in feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup, and project management ensures that all necessary components are meticulously addressed. With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, bioaccess® provides the credibility and knowledge needed for successful submissions.
-
Submission: The complete PMA application is formally presented to the FDA, initiating the regulatory review.
-
FDA Review: The length of the review can differ greatly, usually spanning from 180 days to multiple years, affected by the intricacy of the product and the thoroughness of the application submitted.
As highlighted in the recent case study on De Novo and Panel Track Approval Trends, understanding these timelines is crucial for manufacturers, especially as Panel Track approvals have declined by 6.6% year-over-year. This underscores the importance of a well-prepared submission in navigating the pma regulation landscape. Madris Tomes, CEO of Device Events, highlights this point by asking, 'How does the pre-market approval process protect manufacturers?'
This question highlights the critical nature of comprehensive submissions.
-
Post-Approval Activities: Once an item receives approval, ongoing compliance is essential.
This includes adhering to regulatory requirements and conducting post-market surveillance to ensure the product continues to meet safety standards. With INVIMA serving as Colombia's national authority for food and drug surveillance, understanding the regulatory framework is crucial for clinical research directors aiming to facilitate successful submissions under PMA regulation.
Best Practices for Successful PMA Submissions
To significantly enhance the likelihood of a successful submission under PMA regulation, it is crucial to implement the following best practices:
-
Thoroughly Understand FDA Requirements: Stay updated with the latest guidance documents and regulations, as the FDA's medical device approval procedures may vary based on the device's risk profile. Understanding these nuances is essential, especially considering that over 80% of Original PMAs and 67% of 510(k)s face deficiencies under PMA regulation, often requiring additional information requests.
-
Engage in Pre-Submission Meetings: These meetings are invaluable for establishing clear communication with the FDA, allowing developers to clarify expectations and align their submissions accordingly. As analyst Iseult McMahon states,
We think that this is a directional positive for the broader medical technology space as it provides both improving certainty to companies (and investors) as well as reduces cash burn during the interim period when a company is awaiting a decision.
-
Ensure Comprehensive Documentation: Providing complete and well-organized documentation is essential to facilitate the review, minimizing the risk of additional information requests. The case study titled "Challenges in Submission Approvals" highlights that many submissions encounter deficiencies, underscoring the importance of thorough preparation and adherence to PMA regulation guidelines.
-
Conduct Robust Clinical Trials: Leverage comprehensive clinical trial management services, such as those offered by bioaccess®, which specialize in feasibility studies, site selection, trial setup, project management, and compliance reviews. With over 20 years of experience in Medtech, bioaccess® ensures that trials are designed to thoroughly address safety and efficacy endpoints, providing all necessary data for review.
-
Plan for Potential Questions: Anticipate possible inquiries from the FDA and prepare comprehensive responses in advance, reinforcing the submission's credibility. By adhering to these practices and utilizing expert resources, including the extensive capabilities of bioaccess®, developers can adeptly navigate the complexities of the PMA regulation submission process and significantly enhance their chances of a successful outcome.
Conclusion
The Premarket Approval (PMA) process is a cornerstone of medical device regulation, especially for Class III devices, which demand rigorous scrutiny to ensure safety and efficacy. The comprehensive nature of PMA submissions, encompassing clinical data, manufacturing information, labeling, and preclinical studies, underscores the importance of meticulous preparation. As highlighted, leveraging expert resources such as clinical trial management services can significantly streamline the submission process, enhancing the likelihood of success.
Understanding the distinctions between PMA and the 510(k) pathway is critical for manufacturers navigating the regulatory landscape. While PMA is essential for high-risk devices, the 510(k) process offers a more streamlined approach for devices deemed substantially equivalent to existing ones. However, the higher approval rates associated with the 510(k) process do not diminish the necessity for robust regulatory strategies, particularly in mitigating post-market risks.
Successful navigation of the PMA process hinges on adherence to best practices, including engaging in pre-submission meetings, ensuring comprehensive documentation, and conducting thorough clinical trials. By anticipating potential inquiries and preparing accordingly, stakeholders can bolster the credibility of their submissions. Ultimately, a well-structured PMA process not only safeguards public health but also fosters innovation, paving the way for advancements that can significantly improve patient outcomes in the ever-evolving medical technology sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the PMA regulation and its purpose?
The PMA (Premarket Approval) regulation is a vital regulatory route established by the FDA for Class III medical devices, which are high-risk products requiring extensive testing before entering the market. Its purpose is to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of these devices through rigorous clinical trials.
Why is the PMA regulation important for manufacturers and patients?
The PMA regulation provides manufacturers with assurance that they meet stringent legal standards, while also instilling confidence in patients regarding the safety of the medical products they use.
What challenges do Medtech companies face in Latin America regarding PMA regulation?
Medtech companies in Latin America encounter challenges such as regulatory obstacles and resource fragmentation, which complicate the PMA regulation processes.
How do collaborations, such as between Greenlight Guru and bioaccess™, help with PMA regulation?
Collaborations like that between Greenlight Guru and bioaccess™ aim to bridge regulatory gaps by enhancing clinical trial management services, from feasibility studies to compliance reviews, thereby accelerating innovation in the medical technology field.
What types of clinical studies does bioaccess® specialize in?
Bioaccess® specializes in various clinical studies, including Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS) and First-In-Human Studies (FIH), which are essential for advancing medical technology.
What is the role of INVIMA in Colombia regarding medical devices?
INVIMA, the Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute, plays a crucial role in regulatory oversight by ensuring that medical equipment meets necessary standards before market entry.
What components are essential for a comprehensive PMA regulation submission?
A comprehensive PMA submission must include: 1. Clinical Data demonstrating safety and effectiveness from well-conducted clinical trials. 2. Manufacturing Information detailing processes and quality control measures. 3. Labeling that aligns with FDA regulations. 4. Preclinical Studies data from laboratory and animal studies.
What is the importance of presenting PMA submission information clearly?
Presenting information clearly and concisely is crucial for facilitating the review process and increasing the likelihood of successful approval.
What ongoing requirements must manufacturers fulfill after PMA approval?
Manufacturers are required to submit annual post-approval reports starting one year after PMA approval, demonstrating their ongoing commitment to safety and effectiveness.
How can applicants gain a better understanding of PMA regulation before submitting their application?
The FDA encourages applicants to contact them prior to submitting their PMA application to understand the requirements, guidance documents, and processes related to PMA regulation.




