Introduction
In the realm of medical devices, understanding shelf life is not merely a regulatory requirement; it is a fundamental aspect of ensuring patient safety and product efficacy. Shelf life refers to the period during which a device remains safe and effective for use, influenced by various factors such as storage conditions, manufacturing materials, and packaging methods.
As regulatory bodies like the FDA and ISO establish stringent guidelines, manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of compliance to uphold these standards. This article delves into the critical components of shelf life determination, including:
- Testing methodologies
- International standards
- Best practices for managing expired products
All while emphasizing the pivotal role of packaging in maintaining device integrity. By exploring these elements, industry professionals can better appreciate the importance of rigorous testing and adherence to regulations in safeguarding public health.
Defining Shelf Life: Key Concepts and Regulations
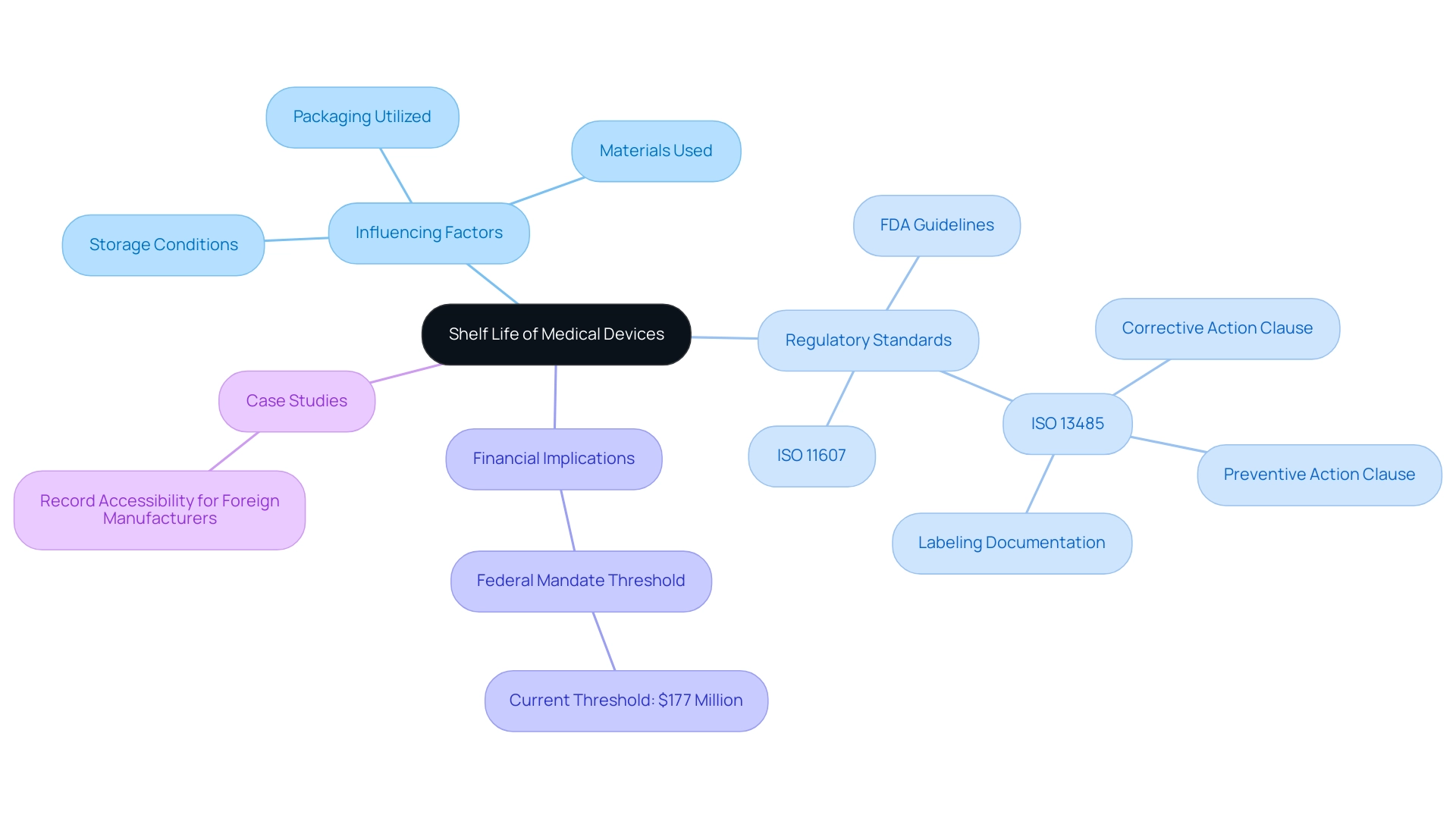
Shelf life of a medical device is defined as the duration during which it remains safe and effective for use, a determination made through rigorous testing and adherence to regulatory standards. It is essential to acknowledge that various elements can influence longevity, including:
- Storage conditions
- The materials used in production
- The packaging utilized
Regulatory organizations, such as the FDA, have set forth specific guidelines that outline how the shelf life of a medical device should be evaluated and documented.
Notably, experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and CEO of Mahu Pharma, and Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, emphasize the importance of understanding these regulations. For instance, ISO 11607 stipulates the requirements for packaging materials, ensuring that they adequately protect the integrity of the equipment over time. Furthermore, ISO 13485 offers a structure for quality management systems relevant to healthcare instruments, highlighting the necessity for extensive documentation and procedures.
As noted by the FDA, 'ISO 13485 has one Clause outlining expectations regarding corrective action and has another Clause outlining the expectations regarding preventive action.' Adhering to these regulations is essential for safeguarding patient safety and maintaining the efficacy of shelf life medical devices throughout their lifecycle, especially in light of recent updates that mandate proper labeling documentation to prevent mix-ups in packaging and labeling. The current threshold for Federal mandates, after adjustment for inflation, is $177 million, highlighting the financial implications of compliance.
Grasping these standards is essential for adherence and operational excellence in the healthcare equipment sector, as non-adherence can result in considerable financial consequences and affect patient safety.
Testing Methodologies for Shelf Life Determination
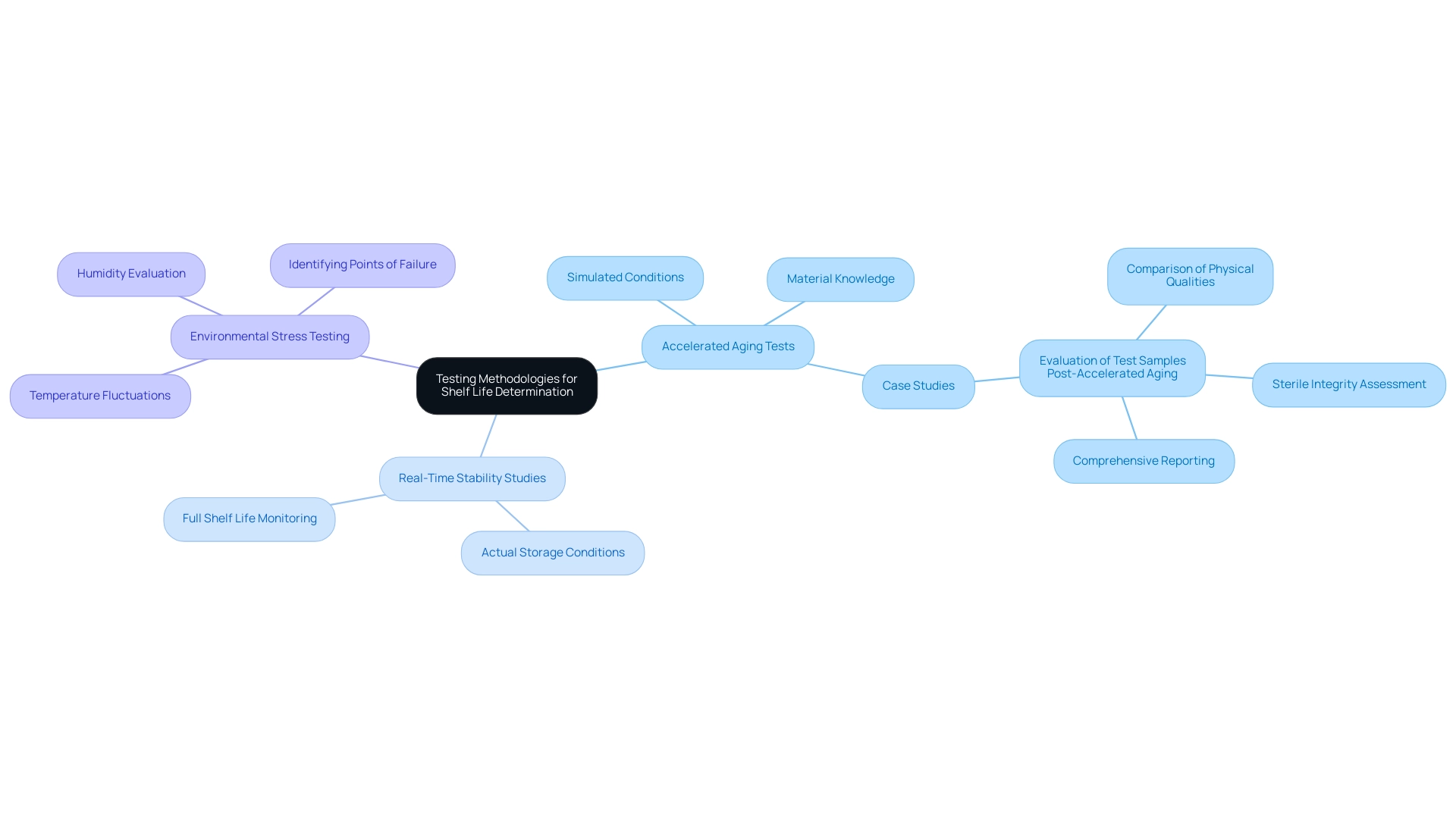
A range of testing methods are crucial for assessing the longevity of healthcare instruments, each fulfilling a distinct role. Accelerated aging tests play a crucial role by simulating the effects of time and environmental conditions on products. By subjecting medical instruments to increased temperatures and humidity conditions, these tests forecast how the item will function during its expected duration.
Eurofins Medical Device Testing boasts over 200,000 ft³ of storage space, underscoring the scale and capability of testing facilities available for these assessments. Karl J. Hemmerich, general manager and corporate technical advisor at Isomedix Corp, emphasizes this approach:
Applying accelerated-aging test techniques in conjunction with a comprehensive knowledge of the materials involved is a prudent method of doing business, with the benefits of early product introduction far outweighing the minimal risk of premature product failure.
In contrast, real-time stability studies monitor a shelf life medical device under actual storage conditions over its full shelf life, yielding a more accurate assessment of longevity.
For instance, a recent case study titled 'Evaluation of Test Samples Post-Accelerated Aging' highlighted how the physical qualities and sterile integrity of test samples were compared to those not exposed to aging conditions, producing a comprehensive report detailing the aging conditions, testing standards, and results. Environmental stress testing complements these methods by evaluating how equipment endures temperature fluctuations and humidity, thereby identifying potential points of failure. Furthermore, recent news indicates that the outcomes of accelerated aging studies will assist manufacturers and CDRH reviewers in evaluating the safety and effectiveness of surgical N95® respirators, emphasizing the importance of current testing methodologies and regulatory standards.
It is essential that all methodologies are thoroughly documented and validated to comply with regulatory standards, ensuring both safety and effectiveness in performance.
Navigating Compliance: International Standards and Guidelines
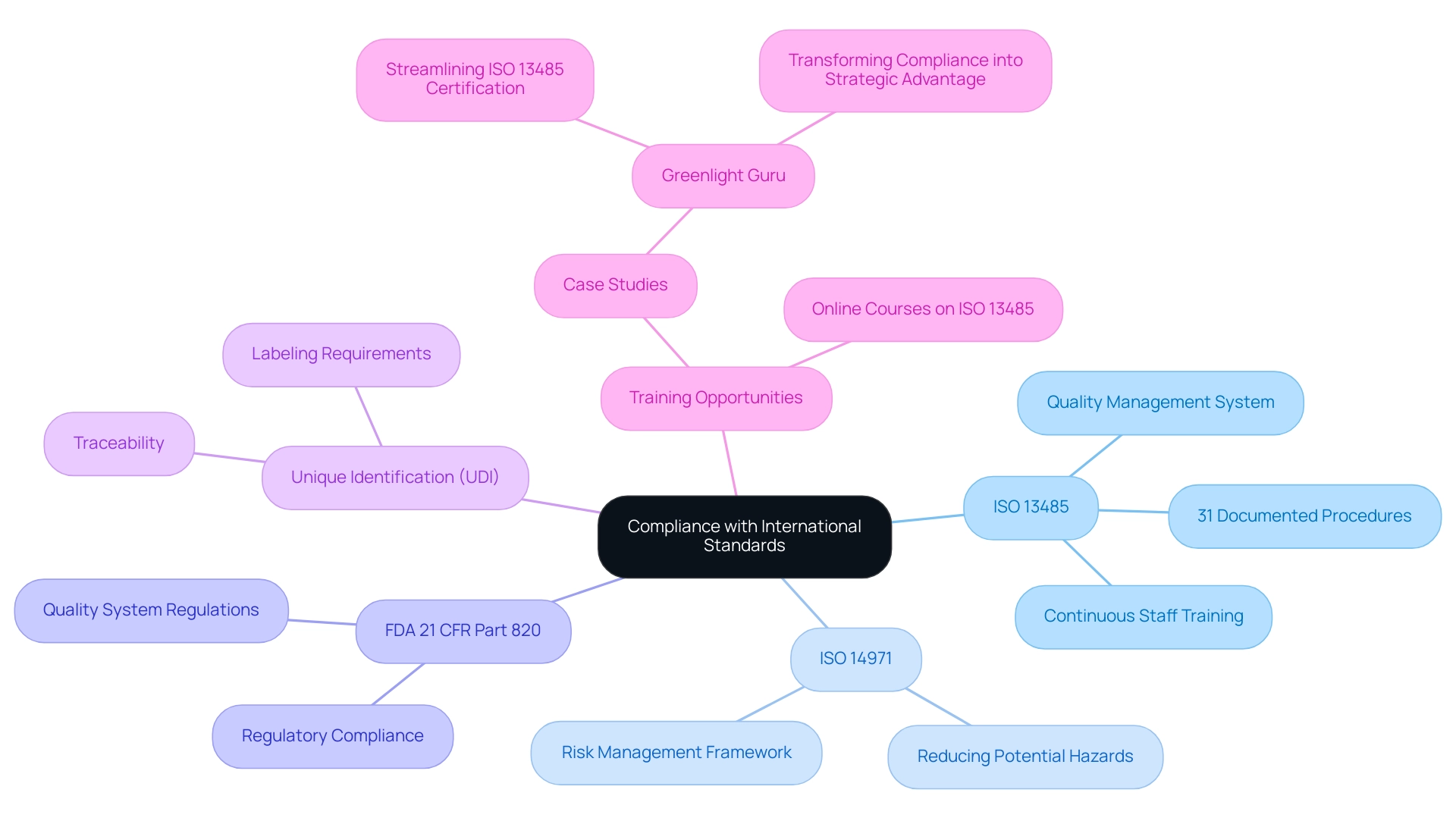
Adhering to global standards and guidelines is crucial for producers of healthcare products aiming to guarantee safety and effectiveness. Key among these standards is ISO 13485, which delineates the requirements for effective quality management systems, including the need for rigorous documentation and procedures. Compliance with ISO 13485 necessitates the establishment of 31 documented procedures, emphasizing the rigor involved in maintaining high-quality standards.
Furthermore, manufacturers must implement unique identification (UDI) as part of the product’s labeling, which is crucial for traceability and compliance. Furthermore, ISO 14971 provides a thorough structure for risk management, crucial for reducing possible dangers related to healthcare instruments. In the United States, manufacturers must also adhere to the FDA's 21 CFR Part 820, which outlines quality system regulations.
This multifaceted compliance landscape requires meticulous documentation, regular audits, and continuous staff training to uphold best practices. Comprehending these regulations and efficiently managing them is essential for attaining successful market entry and maintaining operations within the competitive healthcare equipment sector. Experts like Ana Criado, Director of Regulatory Affairs and founder of Mahu Pharma, exemplify the depth of knowledge needed in this field, bringing insights from her roles as a professor and consultant in biomedical engineering and health economics.
Her expertise is especially pertinent to accelerated aging and durability testing, as adherence to ISO 13485 directly affects the testing methodologies and validation processes for healthcare products, particularly for shelf life medical devices. A relevant example is Greenlight Guru, a quality management system software platform created specifically for the healthcare industry. Their approach demonstrates how compliance with ISO 13485 can be transformed from a checkbox exercise into a strategic advantage, enhancing product quality and operational efficiency.
Furthermore, case studies illustrating successful compliance and testing outcomes for shelf life medical devices in the context of accelerated aging can provide valuable insights for professionals in the field. Online courses focusing on ISO 13485 and quality management systems are readily available, providing vital training opportunities for professionals in the field.
Managing Expired Shelf Life: Options and Best Practices
When the storage duration of a shelf life medical device has lapsed, following certain procedures is essential to ensuring patient safety. Managing expired products effectively may involve conducting additional stability testing, which can potentially extend the shelf life of a medical device. Implementing a robust recall strategy is essential, particularly in light of recent incidents such as:
- Abbott's recall of the HeartMate 3 LVAS implant kit due to blood leakage risks
- Insulet Corporation's recall of the OmniPod 5 Android app due to software errors as of 01/08/2024
These examples emphasize the significance of proactive actions in the management of healthcare instruments.
INVIMA (Colombia National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute) plays a crucial role in this process, as it supervises the marketing and manufacturing of health products, ensuring adherence to safety and quality standards for healthcare equipment. As a Level 4 health authority acknowledged by the Pan American Health Organization and World Health Organization, INVIMA's regulatory functions are essential to preserving the effectiveness of health products available in the market. The Directorate for Healthcare Instruments and other Technologies within INVIMA specifically oversees and regulates healthcare instruments, ensuring compliance with established protocols.
Best practices for managing expired healthcare instruments include:
- Maintaining meticulous records of expiration dates
- Conducting regular inventory audits
- Providing staff training on the importance of monitoring duration
Establishing partnerships with regulatory authorities like INVIMA can further enhance compliance efforts and provide valuable guidance on best practices. Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for Medical Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, emphasizes the importance of compliance in this context.
As Matej Mikulic, a research expert in health and pharma, noted,
between 1991 and 2017, the pharmaceutical industry paid over $11.3 billion in financial penalties for unlawful promotion practices.
This underscores the critical nature of compliance within the industry. Furthermore, with 204 reported violations in the pharmaceutical sector, it is evident that adherence to these protocols is vital.
By prioritizing these protocols, organizations can mitigate risks while ensuring that patient safety remains paramount.

The Impact of Packaging on Medical Device Shelf Life
The packaging of medical equipment plays an essential role in influencing their longevity, mainly by protecting them from environmental factors like humidity, light, and temperature variations. If a manufacturer indicates that the product is a shelf life medical device with a lifespan of two years, it is expected they can empirically validate that it does not degrade within that timeframe. Adhering to standards established by regulatory bodies is essential to ensure that packaging materials do not compromise the integrity of the product.
For example, sterile barrier systems must undergo thorough validation procedures to ensure their capability to preserve sterility throughout the product's duration. Moreover, the design of packaging must account for the challenges posed by transportation and storage conditions, ensuring that the product remains protected until it reaches the end user. As highlighted by industry specialists, when the FDA comes to your location as your expiration date approaches, you will require real-time aging information to demonstrate your product's longevity.
To achieve this, manufacturers are encouraged to conduct compatibility studies that evaluate how packaging materials interact with the device over time. Such studies are essential in verifying that the packaging stays effective throughout the product's intended duration, thereby supporting the assertion of validity. The ASTM F1980 outlines standards for developing accelerated aging protocols, illustrating how packaging impacts the shelf life of medical devices by applying heat to samples to simulate long-term aging effects on packaging materials.

Conclusion
Understanding shelf life in medical devices is crucial for ensuring safety and efficacy. Influenced by storage conditions, materials, and packaging, shelf life requires strict compliance with FDA and ISO regulations. Rigorous testing methods, such as accelerated aging and real-time stability studies, are essential for accurately predicting product performance.
Manufacturers must navigate international standards like ISO 13485 and ISO 14971 to enhance product quality and manage risks effectively. Additionally, managing expired shelf life through recall strategies and further stability testing is vital for protecting patient safety and maintaining trust in medical products.
Packaging plays a key role in shelf life by safeguarding devices against environmental factors and ensuring their integrity. Conducting compatibility studies and adhering to established standards are necessary to substantiate shelf life claims.
In conclusion, prioritizing shelf life determination through thorough testing, regulatory compliance, effective management of expired products, and robust packaging practices is essential. This commitment not only meets regulatory requirements but also significantly enhances the safety and well-being of patients relying on medical devices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the shelf life of a medical device?
The shelf life of a medical device is defined as the duration during which it remains safe and effective for use, determined through rigorous testing and adherence to regulatory standards.
What factors can influence the shelf life of a medical device?
The shelf life can be influenced by several factors, including storage conditions, the materials used in production, and the packaging utilized.
Which regulatory organizations provide guidelines for evaluating the shelf life of medical devices?
Regulatory organizations, such as the FDA, provide specific guidelines that outline how the shelf life of a medical device should be evaluated and documented.
What are ISO 11607 and ISO 13485?
ISO 11607 stipulates the requirements for packaging materials to ensure they protect the integrity of medical devices over time. ISO 13485 provides a framework for quality management systems relevant to healthcare instruments, emphasizing the need for extensive documentation and procedures.
Why is adherence to regulations like ISO 13485 important?
Adhering to regulations like ISO 13485 is essential for safeguarding patient safety and maintaining the efficacy of medical devices throughout their lifecycle, especially in light of recent updates that mandate proper labeling documentation.
What are accelerated aging tests and their significance?
Accelerated aging tests simulate the effects of time and environmental conditions on medical devices by exposing them to increased temperatures and humidity, forecasting how the item will function during its expected duration.
How do real-time stability studies differ from accelerated aging tests?
Real-time stability studies monitor a medical device under actual storage conditions over its full shelf life, providing a more accurate assessment of longevity compared to accelerated aging tests.
What role does environmental stress testing play in assessing medical devices?
Environmental stress testing evaluates how medical devices endure temperature fluctuations and humidity, identifying potential points of failure.
Why is thorough documentation and validation of testing methodologies important?
Thorough documentation and validation of testing methodologies are essential to comply with regulatory standards, ensuring both safety and effectiveness in medical device performance.

