Introduction
The landscape of medical devices is rapidly evolving, shaped by advancements in technology and stringent regulatory frameworks. Defined by the FDA as instruments designed for diagnosing, treating, or preventing diseases, medical devices encompass a vast range of products—from simple bandages to complex implantable devices.
Understanding the classification and approval processes of these devices is crucial for manufacturers aiming to navigate the intricate regulatory pathways that ensure patient safety and device efficacy. As the integration of artificial intelligence and heightened cybersecurity measures become more prevalent, the industry faces both exciting opportunities and significant challenges.
This article delves into the multifaceted world of medical devices, exploring their definitions, classifications, approval processes, and the impact of emerging trends on the future of healthcare.
Defining Medical Devices: An Overview of FDA Criteria
According to the FDA, a healthcare instrument is defined as any tool, apparatus, implement, machine, contrivance, implant, in vitro reagent, or related article designed for use in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease. This definition extends to instruments that impact the structure or function of the body. Significantly, healthcare instruments accomplish their intended purposes without depending on chemical actions within or on the body, nor are they reliant on metabolic processes for their primary functions.
This broad framework encompasses an extensive array of products, ranging from straightforward bandages to sophisticated programmable pacemakers, underscoring the remarkable diversity present within the healthcare equipment category. Understanding what is a medical device fda is essential for navigating the wide-ranging classification and the complexities of regulatory pathways and the approval processes that govern these critical healthcare tools. Moreover, as emphasized by Frank Samuelson from the FDA, 'AI/ML Applications and Challenges in the Development of In-Vivo Diagnostic Tools Using AI and ML' demonstrate the changing environment of healthcare technologies and the incorporation of advanced innovations.
Additionally, insights from the case study titled 'Quality Statistical Review for Therapeutic Devices and Best Practices' emphasize the importance of standardizing statistical analysis plans and engaging early with FDA statisticians to navigate the approval processes effectively. Recent discussions among FDA speakers, including Gregory Alexander and Marina Kondratovich, further emphasize the ongoing developments in the definition and regulation of healthcare instruments. In this context, bioaccess® emerges as a trusted partner for Medtech startups, facilitating the clinical research process in Latin America by providing cost-effective, high-quality services such as approval, clinical research site activation, subject recruitment, and trial data management.
This extensive support connects the gaps in clinical research and innovation, ultimately promoting healthcare instruments through Early-Feasibility Studies (EFS), First-In-Human Studies (FIH), and beyond. Testimonials from satisfied clients highlight bioaccess®'s effectiveness in navigating complex regulatory landscapes, making them an invaluable ally for Medtech companies looking to thrive in Latin America.
Understanding FDA Classifications: Categories of Medical Devices
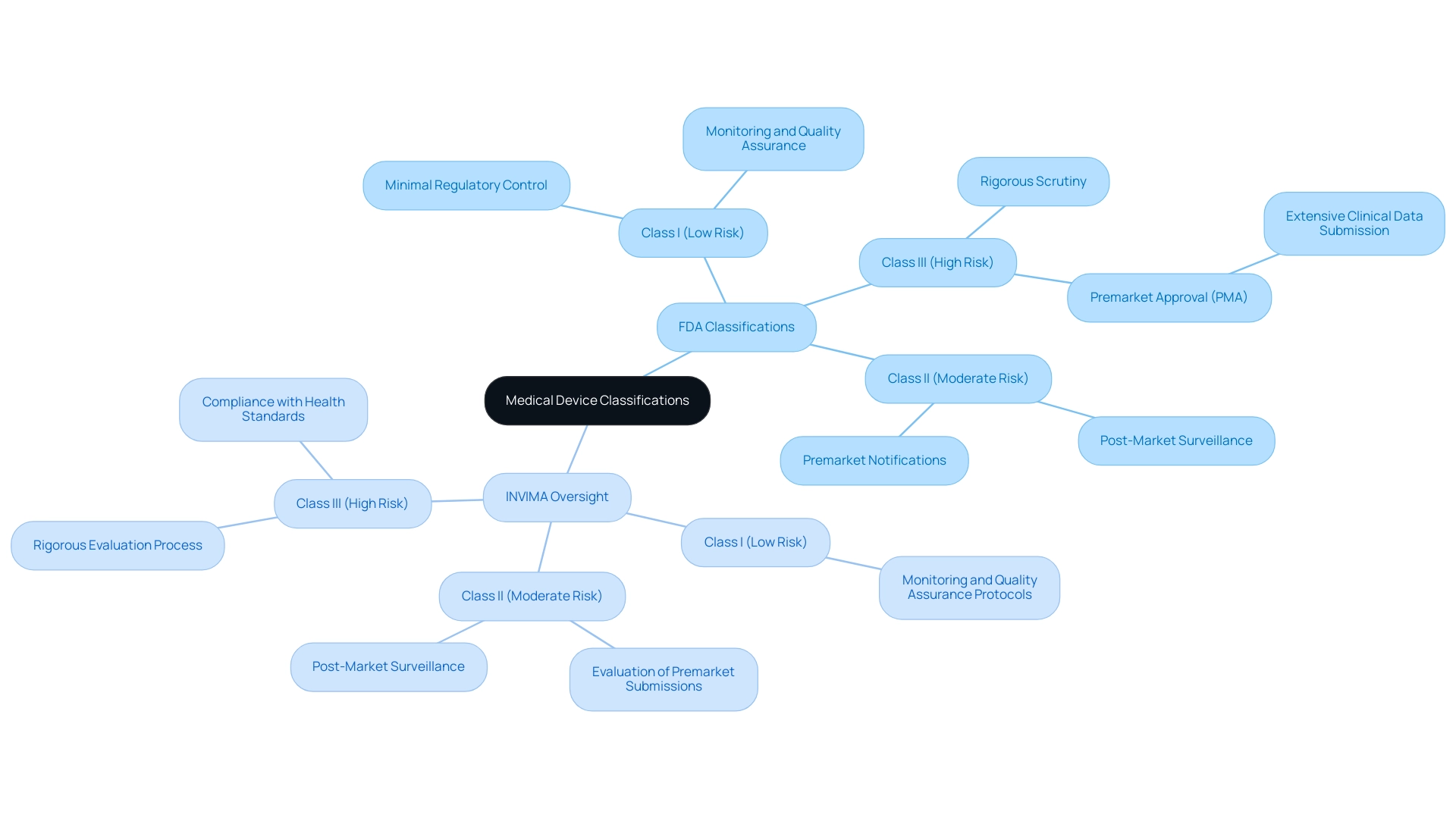
While the FDA categorizes health equipment into three distinct groups based on associated risk levels—Class I, Class II, and Class III—Colombia’s INVIMA (National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute) plays a similarly critical role in regulating health products within the country. Founded in 1992, INVIMA supervises the marketing and production of medical products, ensuring adherence to health standards and best practices. INVIMA employs a systematic approach to monitor and evaluate health products, which includes regular inspections and audits to assess compliance with established regulations.
Just as Class I products are considered low-risk with minimal regulatory control, INVIMA implements monitoring and quality assurance protocols for low-risk items, ensuring they meet safety and efficacy standards. Class II products in the U.S., which require premarket notifications, are similarly overseen by INVIMA, particularly through its Directorate for Medical Equipment and other Technologies, which evaluates premarket submissions and conducts post-market surveillance. Class III products, representing the highest risk, necessitate rigorous scrutiny, akin to the premarket approval (PMA) process in the U.S., where extensive clinical data must be submitted for evaluation.
As acknowledged by the Pan American Health Organization/World Health Organization, INVIMA is designated as a Level 4 health authority, demonstrating its capability in ensuring the security, efficacy, and quality of healthcare devices in Colombia. Katherine Ruiz, an expert in Regulatory Affairs for Devices and In Vitro Diagnostics in Colombia, emphasizes the importance of INVIMA’s role in facilitating access to innovative technologies while safeguarding public health. Understanding what is a medical device fda is essential for this classification system, whether by the FDA or INVIMA, to maintain regulatory oversight and protect patient safety.
Navigating the Approval Process: Pathways for Medical Device Submission
Navigating the approval process for medical products raises important questions, such as what is a medical device fda, and is a multifaceted endeavor primarily characterized by two key pathways: the 510(k) premarket notification and the premarket approval (PMA). The 510(k) process is designed for products demonstrating substantial equivalence to existing legally marketed items, requiring manufacturers to present sufficient evidence supporting this equivalence. In contrast, the PMA pathway necessitates a more stringent approach, especially for Class III products, as it demands extensive clinical data to establish safety and efficacy.
This difference in rigor reflects the varying levels of risk associated with different categories of equipment. Additionally, the De Novo classification route acts as an option for new instruments that do not belong to a current category, enabling a customized oversight approach.
Recent statistics show that in 2024, around 60% of health-related products obtained 510(k) clearance, whereas merely 10% went through the PMA process, emphasizing the inclination for the 510(k) route among producers. Comprehending what is a medical device fda is essential for manufacturers seeking to adhere to standards and accelerate their time to market, especially in light of changing regulations. As Mihajlo Jakovljevic states,
The landscape of healthcare product approval is continuously changing, making it imperative for manufacturers to stay informed on the latest requirements and trends.
Moreover, the recent EU Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR) has introduced stricter requirements for clinical evidence and post-market surveillance, leading to longer approval timelines and potential manufacturing delays. This policy change is significant, as it may impact the global market strategies of manufacturers.
In this complex landscape, engaging comprehensive clinical trial management services can greatly assist in overcoming challenges.
Services such as feasibility studies, site selection, compliance reviews, trial setup—including obtaining ethics committee and health ministry approvals—project management, and reporting of study status and adverse events are crucial for ensuring adherence to both FDA and Anvisa regulations. Katherine Ruiz, a specialist in compliance matters for healthcare products and in vitro diagnostics in Colombia, can offer essential advice throughout this process. Furthermore, disability advocates have expressed worries regarding the accessibility of healthcare tools and the necessity for inclusive design, highlighting the significance of taking these viewpoints into account during the approval process.
This evolving regulatory environment highlights the necessity for manufacturers to not only be aware of the distinct pathways but also to adapt to the shifting expectations within the industry, including the need for import permits and nationalization of investigational products.
The Impact of FDA Regulations on Patient Safety and Device Efficacy
FDA regulations are essential in guaranteeing both the well-being of patients and the effectiveness of what is a medical device FDA. Through meticulous premarket evaluations and robust post-market surveillance, the FDA effectively monitors what is a medical device FDA performance and security throughout their lifecycle. Understanding what is a medical device FDA is essential for detecting potential risks and ensuring compliance with strict standards.
For example, manufacturers are mandated to report adverse events and product defects, which can trigger recalls and safety alerts, thus safeguarding patient health. Recent evidence highlights that despite a 3% increase in patient acuity—indicating that hospitals are now treating a more severely ill patient population—key patient outcomes have improved, showcasing the importance of vigilant regulation. In Colombia, the National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute (INVIMA) plays a crucial role as a Level 4 health authority acknowledged by PAHO/WHO, supervised classification of health products and ensuring adherence to national regulations.
INVIMA's responsibilities include:
- Feasibility studies
- Site selection
- Compliance reviews
- Trial setup
- Import permits
- Project management
- Reporting
These are essential for effective clinical trial management. Additionally, Ana Criado, our Director of Regulatory Affairs and a professor in biomedical engineering, brings extensive expertise in regulatory processes, health economics, and cannabis regulations, further enriching our understanding of medical equipment oversight. A study of the quadrivalent human papillomavirus vaccine evaluated long-term effectiveness, immunogenicity, and protection for up to 14 years, highlighting the FDA's role in ensuring product reliability.
As noted by health and life sciences expert Jenna Phillips, 'Leveraging real-world clinical data in novel ways can result in important changes to pharmaceutical companies’ ways of working to deliver a competitive advantage to products that are coming to market more quickly, and safely, than ever before.' Furthermore, the CDC will host webinars this week on hospital respiratory data reporting, reflecting ongoing efforts to enhance patient safety. This synergy between regulation and innovation not only protects patients but also enhances the credibility of the healthcare industry, fostering trust among providers and patients alike.
Emerging Trends in Medical Devices: AI, Cybersecurity, and Future Challenges
The healthcare equipment sector is experiencing transformative advancements, mainly marked by the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and a heightened focus on cybersecurity. Recently, the FDA approved 2 renal denervation instruments intended to treat high blood pressure, highlighting regulatory advancements that support these innovations. AI technologies are being leveraged to enhance diagnostic accuracy, streamline patient monitoring, and tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs.
The market is poised to gain considerably from these innovations, with AI integration figures for healthcare equipment showing a strong growth path as we near 2024. Johnson & Johnson's insight that procedure volumes are expected to grow above pre-pandemic levels for all of 2024 signals a positive trend for the sector overall. However, alongside these advancements arise critical concerns regarding data privacy and security.
The interconnected nature of contemporary healthcare instruments presents substantial cybersecurity challenges that the industry must proactively address to safeguard patient information and maintain system integrity. Experts emphasize that with the growth of interconnected technology, the risk of cyber threats increases, requiring stringent security measures. For instance, major healthcare companies are now prioritizing cybersecurity protocols to mitigate these risks.
Furthermore, technological innovations such as 3D printing are fueling expansion in customized healthcare products, greatly lowering expenses and energy usage in production, as anticipated in the case study of 3D printing in healthcare tools. As stakeholders navigate this evolving landscape, understanding what is a medical device FDA is essential for staying informed about emerging trends and challenges in medical devices, particularly those related to AI and cybersecurity, to ensure the continued safety and efficacy of medical technologies.
Conclusion
The medical device landscape is shaped by complex regulations and classifications crucial for ensuring patient safety and device efficacy. The FDA's criteria and INVIMA's oversight in Colombia emphasize the importance of a systematic regulatory framework that differentiates between Class I, II, and III devices. Each class has specific requirements, with the 510(k) premarket notification pathway being preferred for its efficiency, while the more rigorous premarket approval (PMA) process is reserved for higher-risk devices.
As the industry progresses, the integration of technologies like artificial intelligence offers exciting opportunities for enhanced diagnostics and personalized treatments. However, these advancements also introduce challenges, particularly concerning data privacy and cybersecurity. The interconnected nature of modern medical devices necessitates strong security measures to protect patient information and ensure device integrity.
In conclusion, maintaining regulatory compliance while embracing technological advancements will be pivotal for the future of medical devices. Stakeholders must stay informed about the evolving regulatory landscape and emerging trends to drive innovation and safeguard patient well-being. This balance between regulation and innovation is essential for building trust within the healthcare ecosystem and advancing the medical device field.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is defined as a healthcare instrument by the FDA?
According to the FDA, a healthcare instrument is any tool, apparatus, machine, implant, in vitro reagent, or related article designed for use in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease, impacting the structure or function of the body without relying on chemical actions or metabolic processes.
What types of products fall under the category of healthcare instruments?
Healthcare instruments encompass a wide range of products, from simple bandages to complex programmable pacemakers, showcasing the diversity within the healthcare equipment category.
Why is understanding the definition of a medical device important?
Understanding the definition of a medical device is essential for navigating the various classifications and the complexities of regulatory pathways and approval processes that govern these healthcare tools.
What role does bioaccess® play in the Medtech industry?
Bioaccess® acts as a partner for Medtech startups by facilitating the clinical research process in Latin America, offering services such as approval, clinical research site activation, subject recruitment, and trial data management.
How does the FDA categorize healthcare instruments?
The FDA categorizes healthcare instruments into three classes based on risk levels: Class I (low risk), Class II (moderate risk), and Class III (high risk), each with different regulatory controls and requirements.
What is INVIMA and what role does it play in Colombia?
INVIMA, the National Food and Drug Surveillance Institute in Colombia, regulates health products, ensuring compliance with health standards through systematic monitoring, evaluations, inspections, and audits.
How does INVIMA's classification system compare to the FDA's?
INVIMA's classification system is similar to the FDA's, with Class I products being low-risk with minimal regulatory control, Class II products requiring premarket notifications, and Class III products needing rigorous scrutiny akin to the FDA's premarket approval process.
What recognition has INVIMA received regarding its regulatory capabilities?
INVIMA is recognized as a Level 4 health authority by the Pan American Health Organization/World Health Organization, indicating its capability to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of healthcare devices in Colombia.




